
| Species | Cell type | Size in micrometres |
| Paramecium caudatum | free-living ciliate [43] | 120–330 |
| Amoeba proteus | free-living amoebozoan [44] | 220–760 |
| Noctiluca scintillans | free-living dinoflagellate [45] | 700–2000 |
| Syringammina fragilissima | foraminifera amoeba [35] | up to 200 000 |
Full Answer
What are the four major groups of protozoa?
- (1) Amoeboid protozoa or sarcodines They are unicellular, jelly-like protozoa found in fresh or sea water and in moist soil. ...
- (2) Flagellated protozoa or zooflagellates They are free living, non-photosynthetic flagellates without a cell wall. ...
- (3) Ciliated protozoa or ciliates They are aquatic individuals that form a large group of protozoa. ...
What are common diseases caused by protozoa?
- undercooked fish, crabs, and mollusks;
- undercooked meat;
- raw aquatic plants, such as watercress; and
- raw vegetables that have been contaminated by human or animal feces.
What are the 4 major groups of protists?
major groups of protists. animallike,planetlike,funguslike. Characteristics of animallike protists. no cell wall,heterotrophs,move around,nucleus. 4 main groups of animallike protists. sarcodines,ciliates,zooflagellates,sporozoans. characteristics of sarcodines. pseudopods,some have shells. most familiar sarcodine.
What are 2 diseases caused by protozoans?
- Rhizopods
- Ciliates
- Flagellated
- Sporozoans
See more
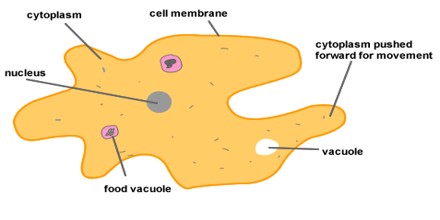
What are the 4 main types of protozoa?
Protozoa are unicellular, heterotrophic, eukaryotic organisms comprising four organization types: amebae, flagellates, ciliates, and parasitic sporozoans.
How many species of protozoa are there?
More than 50,000 species have been described, most of which are free-living organisms; protozoa are found in almost every possible habitat.
What are 3 examples of protozoa?
Examples of protozoa are Amoeba, Paramoecium, Trypanosoma, Plasmodium, etc.
What are the 5 examples of protozoa?
The following is a list of some of the common protozoan and algal microbes we share the world with.paramecia. Paramecium caudatum (highly magnified). ... amoeba. Amoeba (Amoeba proteus). ... Euglena. Euglena gracilis (highly magnified) in fresh water. ... diatoms. ... Volvox.
How many major groups protozoan have?
four major groupsHint: Protozoans are unicellular eukaryotic organisms with heterotrophic nutrition classified under the kingdom Protista. They are classified based on their mode of locomotion into four major groups.
What are the different classes of protozoa?
Protozoans consist primarily of eukaryotic and single-celled organisms. They are represented by four major groups namely Flagellates, Ciliates, Sarcodina, and Sporozoans.
What are the 10 example of protozoa?
Table of ContentsProtozoa: Example # 1. Giardia:Protozoa: Example # 2. Trypanosoma:Protozoa: Example # 3. Trichonympha:Protozoa: Example # 4. Leishmania:Protozoa: Example # 5. Entamoeba:Protozoa: Example # 6. Plasmodium:Protozoa: Example # 7. Toxoplasma:Protozoa: Example # 8. Paramecium:More items...
How many classes are in phylum protozoa?
four classesHence, we can say that on the basis of their locomotory structure, the Phylum Protozoa is divided into four classes or groups.
Which is the largest protozoa?
Balantidium coliBalantidium coli is the largest protozoan—and the only ciliate—that infects humans.
Why are the different phyla of the kingdom Protista not closely related?
Although the different phyla of the kingdom Protista are not closely related, they are nonetheless classified together because of their large differences from the other kingdoms of plants, animals and fungi. The name “protozoa” has a dynamic history, at one time including only the “animal-like” unicellular forms of life.
Which phylum contains amoebas?
The phylum Rhizopoda contains the amoebas. The small, unicellular protozoa are some of the only protozoa that do not have any sort of hard covering. The amoebas move by extending their cytoplasm into the environment. These extensions are called pseudopodia.
What are the structures of the cilia?
Instead of flagella for locomotion, organisms in the phylum Ciliophora use much smaller structures called cilia. The cilia of these organisms cover their entire cell, and work together to propel the cell forward. Much like the individual paddles of a row boat, each cilia gives a forward moving power stoke, then whips back to the starting position in the recovery stroke. Organisms in the Ciliophora include a wide variety of body plans, including free-swimming organisms and sessile organisms that use their cilia to filter food from the water. Most ciliates exist on the bottom of marine environments, known as the benthic zone. However, these protozoa have also specialized as parasites in the digestive tracts of larger organisms.
What is the phylum of the Euglenida?
The Euglenida are a phylum of protozoa recognized by the pellicle that gives them shape and the flagella which they use for locomotion. The pellicle is a shell of sorts that exists beneath the cell membrane. It is composed of strips of proteins, which interlock for support. Some organisms in the Euglenida are photosynthetic, and contain chloroplasts. Others obtain food from dissolved nutrients in the environment, while still others are parasitic.
What are the kinetoplastida made of?
Closely related to the Euglenida, the Kinetoplastida are also protected by a pellicle, although it is made exclusively of microtubules. Organisms in the Kinetoplastida share the unique characteristic of having a single, much enlarged and elongated, mitochondrion. Typically, cells have many small mitochondria, as opposed to one large one. The Kinetoplastida includes many parasitic organisms that cause disease in humans. Of these, leishmaniosis is the most notable, affecting over a million people a year. However, advances in medical treatments saves most of those infected, and only around 1000 people die annually from these protozoa.
How many people die from kinetoplastida?
However, advances in medical treatments saves most of those infected, and only around 1000 people die annually from these protozoa.
Is everything except fish a protozoa?
C. Everything except the fish! B is correct. Even on a microscopic level, there are many species that may look like protozoa, but are actually complex organisms with multiple cell layers. On the other side, many bacteria exist in a scoop of pond water, and are part of the domain Bacteria, not Protista.
How many phases are there in protozoa?
Life cycle. Some protozoa have two-phase life cycles, alternating between proliferative stages (e.g., trophozoites) and dormant cysts. As cysts, protozoa can survive harsh conditions, such as exposure to extreme temperatures or harmful chemicals, or long periods without access to nutrients, water, or oxygen.
What is a protozoan?
Protozoa (also protozoan, plural protozoans) is an informal term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal -like behaviours, ...
What was Goldfuss's first class of organisms?
Goldfuss created Protozoa as a class containing what he believed to be the simplest animals. Originally, the group included not only single-celled microorganisms but also some "lower" multicellular animals, such as rotifers, corals, sponges, jellyfish, bryozoa and polychaete worms.
Which group of protozoa does not move at all?
The group includes flagellates (which move with the help of whip-like structures called flagella ), ciliates (which move by using hair-like structures called cilia) and amoebae (which move by the use of foot-like structures called pseudopodia ). Some protozoa are sessile, and do not move at all.
What is the term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes that feed on organic matter
Protozoa. This article is about the organism. For the infection, see Protozoan infection. Protozoa (also protozoan, plural protozoans) is an informal term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris.
What are the pellicles of protozoa?
Pellicles of protozoan organisms vary from flexible and elastic to fairly rigid. In ciliates and Apicomplexa, the pellicle is supported by closely packed vesicles called alveoli. In euglenids, it is formed from protein strips arranged spirally along the length of the body.
When was the protozoa first introduced?
In some systems of biological classification, Protozoa remains a high-level taxonomic group. When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss in 1818, Protozoa was erected as a class within the animals, and its etymology is literally "first animals".
What is a protozoan?
In some systems of biological classification, protozoan is a high-level taxonomic group. When first introduced in 1818, protozoa was erected as a taxonomic class, but in later classification schemes, it was elevated to a variety of higher ranks. These higher ranks pertain to phylum, subkingdom, and kingdom.
What is a flagellated protozoa?
Flagellated Protozoa Radiolaria. Wikimedia Commons. A flagellate is a type of protozoa. Wenrich (1924) reports one flagellate and seven ciliates from the skin of tadpoles, and Sassuchin (1928) has added a list of species which he has found in the slime of the tadpole skin.
What are flagellates in termites?
Termites .The interesting group of flagellates is those that live in the intestines of termites. One of them is Trichonympha campanula. Termites, by themselves, cannot make use of hardwood they ear, because they cannot digest the substance cellulose of wood. The flagellates in a termite's intestine change the cellulose into a form that can be digested by the termite. The relationship between the termite and its intestinal flagellate is advantageous to the flagellates since they also get their food from the intestine of their host.
How many species of flagellates are there?
Flagellates are a unicellular type of protozoans and are about 2,000 species. Some flagellates are free-living, such as Chlamydomonas. Some are parasitic, such as Trichomonas. Some live singly such as Euglena. Some live in colonies, such as Synura. Euglena belongs to a group of protists that move about with the help of one or more thread-like flagella, commonly referred to as flagellates.
How many species of Sarcodina are there?
There are about 8000 species in this group. Like the ciliates, most Sarcodina is free-living in freshwater and the sea. But there are also species which are parasites of animals. Six species of amoeba have long been known to infect people, one in the mouth and five in the large intestine.
How many protists are there in a pond?
It is estimated that a pond of ordinary size contains billions of free-living protists and a human body hosts a large number of parasitic protists.
What are parasitic protists called?
Parasitic protists also have specific habitats. Some live only on the surface of the host's body and are called ectoparasites. On the other hand, those that live inside the hosts' body are called endoparasites.
How many species are there in the protozoa?
There is great diversity among protozoa, with over 50,000 species belonging to this phylum. The four major types of protozoa, previously introduced and discussed in this lesson, each have certain unique characteristics. This includes their motility, preferred habitat, cellular structure, and method of reproduction.
What is a protozoa?
What is protozoa? Protozoa is a phylum of eukaryotic organisms, classified as part of the kingdom Protista. As members of the kingdom Protista, protozoa are neither plants, nor animals, nor fungi. All protozoa are heterotrophic, which means they do not produce their own food via photosynthesis. Instead, they rely on consuming organic matter from other organisms.
What are the characteristics of protozoans?
A defining characteristic observed in most protozoans is motility, i.e., the ability to move around. It was this ability that led to the initial classification of protozoans as "animals" when first observed by biologists.
How big are protozoa?
The size of protozoa can vary greatly between different species, with the smallest ones spanning a single micrometer, while the largest can be several millimeters in diameter. Similarly, there is also great diversity in the structure of protozoans.
Where do protozoa live?
Free-living protozoa do not require a host organism to live and are generally found in aquatic environments, both freshwater (such as lakes, rivers, and ponds) and salt water (such as oceans and seas). They may also be found living in moist soils and sand.

Evolution
Others
Description
Clinical significance
Biology
Examples
Morphology
Characteristics
- The Diplomonodida are a phylum of organisms that have many flagella for locomotion. The average number is around 8. While there are many species that vary in their place in the ecosystem, the most well-known of these protozoa is the genus Giardia, which can be consumed in unclean water and cause flu-like symptoms and diarrhea in humans.
Ecology
Causes
Overview
Characteristics
Reproduction in Protozoa can be sexual or asexual. Most Protozoa reproduce asexually through binary fission.
Many parasitic Protozoa reproduce both asexually and sexually. However, sexual reproduction is rare among free-living protozoa and it usually occurs when food is scarce or the environment changes drastically. Both isogamy and anisogamy occur in Protozoa with anisogamy being the m…
History
Classification
Ecology
Bibliography
External links