
Was the USSR stronger than the USA?
The USSR was never stronger than the United States. America has a stronger economy, army and navy. And now Russia is weaker than the United States. in Russia do not know how to make cars, cell phones, computers, TVs. Russia does not build aircraft carriers. Salary and pension are small.
Were there many black people in the USSR?
Today, fewer than 50 descendants of these African Americans are believed to still live in Russia. In all, their numbers in the former Soviet republics could be between 100 and 200, according to researchers.
Were the USSR and the Soviet Union the same thing?
USSR stands for United States Socialist Republic (also Union of Soviet Socialist Republics and 45 more) Were the USSR and the Soviet Union the same thing? Soviet Union and USSR is the same thing. (USSR = Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ) That’s history. It was a union of 15 Socialist (note Not Communist) republics:
What is the difference between USSR, Soviet Union and Russia?
What is the difference between Russia and Soviet Union? The major difference between the Soviet Union and Russia is the eras in which they existed. The USSR lasted from 1917 to about 1991 while Russia continued from that point in time.
See more
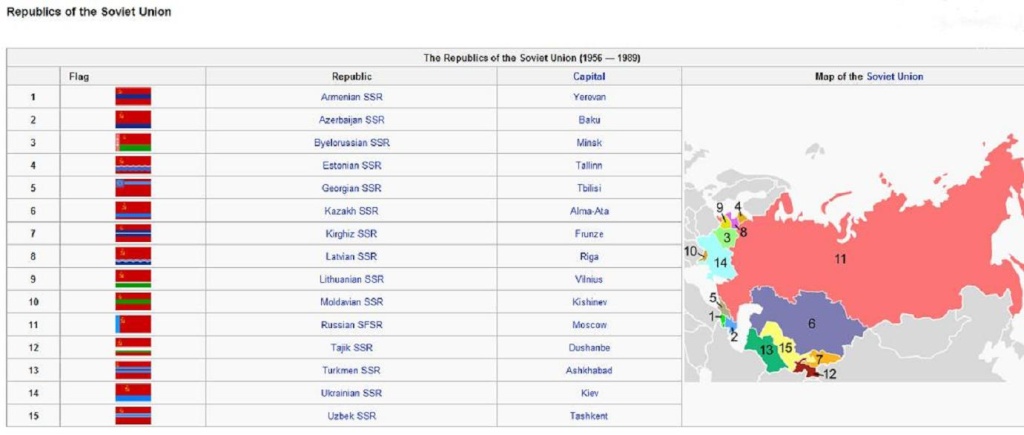
How many republics were there in the Soviet Union?
Over time new republics joined, and by 1956 the final total of 15 was established. In 1991 the Soviet Union collapsed and its 15 republics became independent countries. Here’s the list of the Soviet Socialist Republics in the order they are named in the Soviet constitution of 1977. The order actually reflects the population at the time of the creation of the republics.
How many independent republics were there in the USSR?
In the beginning there were four independent republics that signed the declaration of the creation of the USSR, or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, in 1922. Among them was the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR), the Ukrainian and the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republics (SSR), as well as the Transcaucasian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. Read more on how the USSR was formed here.
What was the Russian republic after the 1917 Revolution?
The Russian republic that appeared after the 1917 Revolution and the fall of the Russian Empire, was actually the cradle of the future Soviet Union. The Bolsheviks even moved the capital to Moscow to underline that a new state had been formed. RSFSR had a complicated inner structure with several autonomous republics within it. And after the collapse of the Soviet Union, the Russian Federation was formed with almost the same federal structure as it had before. And it was Russia that was to become the legal successor of the USSR.
What was the first Russian capital?
Ukraine’s capital Kiev was the first Russian capital and is considered to be the ‘mother of Russian cities’. Ukraine was also a long term part of the Russian Empire, but after the Revolution acted like an independent state. In 1940 and after World War II Ukraine’s territory was expanded.
What was the name of the capital of Kyrgyzstan?
The capital, Pishpek, in the Soviet times was named Frunze after a famous Bolshevik revolutionary born there; after the collapse of the Soviet Union, the city got its modern title, Bishkek.
What was the capital of the Soviet Union in 1930?
Within a year Soviet authorities committed to a new national delimitation, and fresh territorial units were formed based along ethnic lines, including the Uzbek republic which firstly had a capital in Bukhara, then in Samarkand and from 1930 finally in its current capital, the city of Tashkent.
When was Turkmenistan founded?
The Turkmen Soviet Socialist republic with the capital in Ashgabat was formed in 1924 after the Soviet national delimitation of the former Bukharan People's Soviet Republic and the Khorezm People's Soviet Republic. (See point 4 above, about the Uzbek republic above, which appeared at the same time). Now Turkmenistan is one of the most closed countries in the world.
What countries were part of the Soviet Union?
The Soviet Union (full name: Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, or USSR) was a socialist state that was created by Vladimir Lenin in 1922. During its existence, the USSR was the largest country in the world. The USSR collapsed in 1991 and left in its place 15 independent states that we know today: 1 Armenia 2 Moldova 3 Estonia 4 Latvia 5 Lithuania 6 Georgia 7 Azerbaijan 8 Tajikistan 9 Kyrgyzstan 10 Belarus 11 Uzbekistan 12 Turkmenistan 13 Ukraine 14 Kazakhstan 15 Russia
What country was known as the Soviet Armenia?
15. Armenia. With 11,500 square miles, the Republic of Armenia was commonly known as Soviet Armenia during the time of the USSR. The country was among the Soviet Union's constituent republics in December 1922. Soviet Armenia was created in 1920 during a time when the Soviets seized control of the First Republic of Armenia.
What is the Republic of Tajikistan?
The Republic of Tajikistan is a landlocked, mountainous country located in Central Asia. Tajikistan was known as Soviet Tajikistan or Tajik SSR. Soviet Tajikistan existed between 1929 and 1991. From 1927 to 1934, collective farming and the accelerated expansion of cotton production took place particularly in the southern region of the territory. Other small scale developments took place over time which resulted in improved irrigation infrastructure. The territory was renamed the Republic of Tajikistan on August 31, 1991 and it declared its independence on September 9, 1991. Tajikistan was recognized as an independent state by the Soviet Union on December 26, 1991. Following its independence, the country fell into the Civil War involving different factions. As a result, more than half a million residents fled the country due to increased poverty and persecution.
Which country is the largest in the world?
With 6.6 million square miles, the Russian Federation is the world's largest country and is located in Eurasia. Soviet Russia together with other Soviet Republics formed the USSR. Russia was the largest member of the Soviet Union with more than half of the USSR's total population.
When was Moldova declared a state?
Moldova was declared a sovereign state on June 23, 1990 but was officially known as the Soviet Socialist Republic of Moldova until May 23, 1991. Despite the country remaining a USSR constituent republic, it was renamed the Republic of Moldova. Following its independence, Moldova was affected by civil war.
When did Latvia become a country?
Following the demise of the Soviet Union, the country restored its official name as the Republic of Latvia attaining its full independence on August 21, 1991.
When did Lithuania become independent?
It was named the Republic of Lithuania and the USSR acknowledged Lithuania as an independent state on September 6, 1991. Following the country's independence, Lithuania joined both NATO and the European Union in 2004 and the United Nations on September 17, 1991. 10. Georgia.
Etymology
The word soviet is derived from the Russian word sovet (Russian: совет ), meaning "council", "assembly", "advice", ultimately deriving from the proto-Slavic verbal stem of vět-iti ("to inform"), related to Slavic věst ("news"), English "wise", the root in "ad-vis-or" (which came to English through French), or the Dutch weten ("to know"; cf.
Geography
The Soviet Union covered an area of over 22,402,200 square kilometres (8,649,500 sq mi), and was the world's largest country, a status that is retained by its successor state, Russia. It covered a sixth of Earth's land surface, and its size was comparable to the continent of North America.
History
Modern revolutionary activity in the Russian Empire began with the 1825 Decembrist revolt. Although serfdom was abolished in 1861, it was done on terms unfavorable to the peasants and served to encourage revolutionaries.
Foreign relations
During his rule, Stalin always made the final policy decisions. Otherwise, Soviet foreign policy was set by the commission on the Foreign Policy of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, or by the party's highest body the Politburo. Operations were handled by the separate Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Politics
There were three power hierarchies in the Soviet Union: the legislature represented by the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union, the government represented by the Council of Ministers, and the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU), the only legal party and the final policymaker in the country.
Administrative divisions
Constitutionally, the USSR was a federation of constituent Union Republics, which were either unitary states, such as Ukraine or Byelorussia (SSRs), or federations, such as Russia or Transcaucasia (SFSRs), all four being the founding republics who signed the Treaty on the Creation of the USSR in December 1922.
Military
Under the Military Law of September 1925, the Soviet Armed Forces consisted of the Land Forces, the Air Force, the Navy, Joint State Political Directorate (OGPU), and the Internal Troops.
What were the Soviet authorities known for?
Soviet authorities were known for their fierce fight against religiosity - Lenin and Stalin were building an absolutely secular state. Monasteries and convents were closed and converted into prisons; churches were blown up or adapted for economic needs. (Click here to find out how the Soviets used captured churches.)
When did Stalin meet with religious leaders?
In 1943, Stalin even had a meeting with religious leaders. At that meeting a Patriarch was elected, and an agreement was reached on cooperation between the Church and the Soviet government. (Click here to read more about Stalin's relations with the Church.)
Why was Yermogen removed from the Soviet Union?
However, soon he was removed from his post on suspicion of anti-Soviet sentiment (in the 1930s he had served almost 10 years in the camps).

Armenia
Moldova
- Officially known as Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic or MSSR, Moldova was among the Soviet Union's 15 republics from 1940 to 1991. Soviet Moldova was created on August 2, 1940 from a region that was annexed from Romania known as Bessarabia and parts of an autonomous state within the Ukrainian SSR. Moldova was declared a sovereign state on June 2...
Estonia
- Estonia is one of the three Baltic Statesin northeastern Europe. Formerly known as the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic or ESSR, the region was a constituent republic of the Soviet Union. Initially, the ESSR was formed on the Republic of Estonia's territory on July 21,1940 as a result of the Soviet troop’s invasion on June 17, 1940. The country was also established following the aut…
Latvia
- The Republic of Latvia is another Baltic State located in Northern Europe. The country is one of former Soviet Union's constituent republics also known as Soviet Latvia or Latvia SSR. Soviet Latvia was established during World War II on July 21, 1940 as a puppet state of the Soviet Union. Both the European community and the US refused to acknowledge the annexation of Latvia into …
Lithuania
- The Republic of Lithuania is one of the three Baltic States located in Northern Europe covering about 25,000 square miles. The country existed as a Soviet Union republic from 1940 to 1990 and was known as Soviet Lithuania or the Lithuanian SSR. Soviet Lithuania was established on July 21, 1940. The German Nazis occupied the territory between 1941 and 1944 and the territory was lat…
Georgia
- The Republic of Georgia is at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Formerly known as Soviet Georgia or Georgian SSR, the region covers an area of 27,000 square miles. Soviet Georgia was one of the Soviet Union's constituent republics admitted to the USSR on December 30, 1922. On November 18, 1989, the territory declared its independence from the So…
Azerbaijan
- The Republic of Azerbaijan is a country located at the crossroads of Southeastern Europe and Southwest Asia. The country was formerly known as Soviet Azerbaijan or Azerbaijan SSR. Azerbaijan SSR was renamed on November 19, 1990, as the Republic of Azerbaijan and remained in the Soviet Union until its full independence in 1991. Following the adoption of the country's ne…
Tajikistan
- The Republic of Tajikistan is a landlocked, mountainous country located in Central Asia. Tajikistan was known as Soviet Tajikistan or Tajik SSR. Soviet Tajikistan existed between 1929 and 1991. From 1927 to 1934, collective farming and the accelerated expansion of cotton production took place particularly in the southern region of the territory. Other small scale developments took pla…
Kyrgyzstan
- With 77,000 square miles, Kyrgyzstan is a mountainous and landlocked country. Initially, the Soviet Union had established its power in the region in 1919. However, Soviet Kyrgyzstan was established on December 5, 1936. The territory's name was changed to the Republic of Kyrgyzstan through a vote by the Supreme Soviet in December 1990. On December 25, 1991, Kyrgyzstan att…
Belarus
- In 1919, the region of Belarus that was under the Russian rule was established and it was known as Soviet Belarus, Soviet Byelorussia, or BSSR. However, Lithuanian Byelorussia SSR soon emerged which caused competition between the Soviet Union and Poland. The western region of modern day Belarus remained as part of Poland but was later annexed by the BSSR while the Bel…
Overview
The Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party o…
Etymology
The word soviet is derived from the Russian word sovet (Russian: совет), meaning 'council', 'assembly', 'advice', ultimately deriving from the proto-Slavic verbal stem of *vět-iti ('to inform'), related to Slavic věst ('news'), English wise, the root in ad-vis-or (which came to English through French), or the Dutch weten ('to know'; compare wetenschap meaning 'science'). The word sovietnik means 'councillor'.
Geography
The Soviet Union covered an area of over 22,402,200 square kilometres (8,649,500 sq mi), and was the world's largest country, a status that is retained by its successor state, Russia. It covered a sixth of Earth's land surface, and its size was comparable to the continent of North America. Its western part in Europe accounted for a quarter of the country's area and was the cultural and economic center. The eastern part in Asia extended to the Pacific Ocean to the east and Afghani…
History
Modern revolutionary activity in the Russian Empire began with the 1825 Decembrist revolt. Although serfdom was abolished in 1861, it was done on terms unfavorable to the peasants and served to encourage revolutionaries. A parliament—the State Duma—was established in 1906 after the Russian Revolution of 1905, but Tsar Nicholas II resisted attempts to move from absolute
Foreign relations
During his rule, Stalin always made the final policy decisions. Otherwise, Soviet foreign policy was set by the commission on the Foreign Policy of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, or by the party's highest body the Politburo. Operations were handled by the separate Ministry of Foreign Affairs. It was known as the People's Commissariat for Foreign Affairs (or Nar…
Politics
There were three power hierarchies in the Soviet Union: the legislature represented by the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union, the government represented by the Council of Ministers, and the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU), the only legal party and the final policymaker in the country.
At the top of the Communist Party was the Central Committee, elected at Party …
Administrative divisions
Constitutionally, the USSR was a federation of constituent Union Republics, which were either unitary states, such as Ukraine or Byelorussia (SSRs), or federations, such as Russia or Transcaucasia (SFSRs), all four being the founding republics who signed the Treaty on the Creation of the USSR in December 1922. In 1924, during the national delimitation in Central Asia, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan were formed from parts of Russia's Turkestan ASSR and two Soviet dependenci…
Military
Under the Military Law of September 1925, the Soviet Armed Forces consisted of the Land Forces, the Air Force, the Navy, Joint State Political Directorate (OGPU), and the Internal Troops. The OGPU later became independent and in 1934 joined the NKVD, and so its internal troops were under the joint leadership of the defense and internal commissariats. After World War II, Strategic Missile Forces