How do you determine the bond angle?
Chem help: how do I determine the bond angle of a molecule?
- Get the group number of the primary element
- If its a negative charge, add that to the group number from 1) or subtract the positive charge
- Add the bonded pairs
- Divide by 2 to get the bonded pairs
- Now subtract the bonded pairs by the number of bonds to find the loan pairs.
How to predict bond angles?
- Write the Lewis structure of the molecule or polyatomic ion.
- Count the number of regions of electron density (lone pairs and bonds) around the central atom. ...
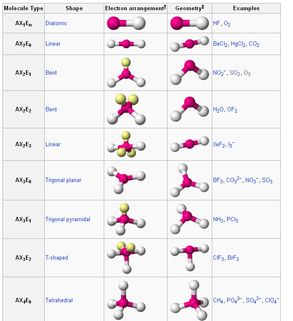
- Identify the electron-pair geometry based on the number of regions of electron density: linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, or octahedral ( Figure 8 ).
Do lone pairs affect bond length?
Lone pairs are essentially nonbonding electrons, which arise from more filled antibonding orbitals. Filling antibonding orbitals decreases bond order, which in turn decreases bond strength and increases bond length. As a rule of thumb the more lone pairs around the longer your bonds.
How many bonds and lone pairs are in BR?
We have three Fluorine atoms surrounding the central Br atom, therefore three bond pairs. We have two lone pairs on the Bromine atom, an exception to the octet rule. The steric number is an important term here, which we need to find out for any VSEPR calculation.
Does bond angle increase with a lone pair?
i) The bond angle decreases due to the presence of lone pairs, which cause more repulsion on the bond pairs and as a result the bond pairs tend to come closer.
Do lone pairs cause smaller bond angles?
Lone Pairs Occupy More Space than Bonding Pairs Because a lone pair of electrons requires more space than a bonding pair, the molecular geometry distorts to afford the lone pair greater space, with the result that bond angles are smaller than those of the ideal geometry.
What effect does a lone pair have on bond angle and molecular shape?
The lone pair decreases the bond angle of the compound because there is repulsion between the bond pairs and the lone pairs. The molecular shape is distorted due to the presence of the lone pair of electrons.
What causes bond angle to decrease?
A bond angle decrease when a lone pair of electrons at the central atom starts to repel the bonded pair of electrons so, the bonds are displaced slightly inside. A bond angle increase when there is an increase in the back bonding bond angle increases.
What causes an increase in bond angles?
As more electron density remains on the central atom, electron repulsion between the bonded pairs increases and bond angles increase.
Why bond angle is inversely proportional to lone pair?
Lone pair repulsion: The presence of a lone pair of electrons at the central atom has an effect on the bond angle of the molecule. Bond angle decreases when the lone pair attempts to reject the bond pair it is trying to repel.
What affects bond angle?
Many factors lead to variations from the ideal bond angles of a molecular shape. Size of the atoms involved, presence of lone pairs, multiple bonds, large groups attached to the central atom, and the environment that the molecule is found in are all common factors to take into consideration.
How do lone pairs affect shape?
The premise of the VSEPR theory is that electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible.
What factors affect bond angles?
Many factors lead to variations from the ideal bond angles of a molecular shape. Size of the atoms involved, presence of lone pairs, multiple bonds, large groups attached to the central atom, and the environment that the molecule is found in are all common factors to take into consideration.
How do lone pairs affect molecular geometry?
If there is one lone pair of electrons and three bond pairs the resulting molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal (e.g. NH3). If there are two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons the molecular geometry is angular or bent (e.g. H2O).
What do bond angles depend?
Bond angle depends on the state of hybridisation of the central atom. H2O has 2 lone pairs. The bond angle observed is 104.80. Electronegativity of central atom: More electronegative the central atom is more will be the bond angle.
What determines the bond angle?
Complete answer: The bond angle generally depends on the number of lone pairs present in an atom. An atom which has no lone pairs shows a shape of trigonal planar shape and in this case bond angle is of 120∘. The molecule which contains one lone pair which forms a bent shape and bond angle is of 118∘.
How Lone Pairs Affect Bond Angles?
I don't think I understand how lone pairs change bond angles. Let's say there was a tetrahedral molecule. I know that those bond angles are 109.5, but when lone pairs start getting introduced, do the bond angles increase or decrease and why? Does this apply to all molecules that get lone pairs introduced to it? What if there is more than one lone pair?
Why do bond angles decrease when adding lone pairs?
If you start removing elements and adding lone pairs (AX3E1, for example), such as CH3-, bond angles DECREASE because the lone pairs create more repulsion that just a normal element would (here, I am comparing CH4 to CH3-). Remember that bond angles only refer to angles between elements—so bond angles would not refer to the angle between ...
What is the bond angle of CH4?
So let's say you start off with a tetrahedral molecule (AX4) such as CH4. The bond angles H-C-H would be 109.5 degrees.
What is the angle between the bonds of H-C-H in CH3-?
Because lone pairs create more repulsion, the angles between the bonds of H-C-H in CH3- are less than 109.5 degrees.
Lone Pair Effect on Bond Angles
How do lone pairs affect the standard bond angles for each shape? If a lone pair does exist, to what extent does it affect the bond angle and is there any way to calculate this?
Re: Lone Pair Effect on Bond Angles
Hey! Not sure about calculating the exact measure of bond angles being influenced by a lone pair, I believe that's a little above this course's pay grade, but I do know that bond angles in a molecule adjacent to the bond angle containing the lone pair will be slightly smaller than they would have been if the lone pair was another atom bonded to the central atom.
Re: Lone Pair Effect on Bond Angles
Tim Foster 3C wrote: Hey! Not sure about calculating the exact measure of bond angles being influenced by a lone pair, I believe that's a little above this course's pay grade, but I do know that bond angles in a molecule adjacent to the bond angle containing the lone pair will be slightly smaller than they would have been if the lone pair was another atom bonded to the central atom.
What happens when the number of lone pairs of electrons increases?
It can be seen that the increase in the number of lone pairs of electrons results in the decrease in the bond angle.
How does electronegativity affect bond angle?
As electronegativity decreases from F to I,the bond pairs are closer to the central atom and the repulsion between the bond pairs increase and so the bond angle al
What is a dative bond?
Dative bonding (also called coordinate covalent bonding) was first used to explain the bonding in transition metal complexes where the metal was electron poor but still was able to form multiple bonds to ligands. Clearly, the electrons for those bonds didn’t come from the metal so they came from the ligands. Hence, the name coordinate covalent bonds. Is this kind of scenario, it is possible to identify a bond as a coordinate covalent bond (dative bond).
What is a bond pair?
BOND PAIR : a pair of electrons (two electrons) responsible for bond formation between two atoms.
How many pairs of electrons does CH4 have?
CH4 has 4 bond pairs and 0 lone pairs of electrons and has a bond angle of 109.5°.
What is the name of the bonding process that occurs in the orbital of a Lewis acid?
There is another name for exactly this kind of bonding process. In main-group chemistry, the term is Lewis acid/base reaction. Lewis bases have a lone pair they donate into the empty orbital of a Lewis acid to make a new covalent bond. So Lewis acid/ba
Where are lone pairs of electrons held in their position?
Lone pairs of electrons are held in their position by the protons in the nucleus of the atom on which are found. Contrast this with bond pairs of electrons which are held in their position by the protons in atoms in which they are shared.
