| Total fibre (g/100 g) | Soluble fibre (g/100 g) | |
|---|---|---|
| Wheat grain | 11.6–17.0 | 1.4–2.3 |
| Wheat bran | 36.5–52.4 | 1.5–4.0 |
How healthy is wheat bran?
Whether you’re eating wheat bran or oat bran, you will get the following minerals:
- Calcium
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Zinc
- Copper
- Manganese
- Selenium
What is wheat bran and what is it used for?
Wheat is a plant. The outer shell of the grain (the bran) is used to make medicine. Wheat bran is a source of fiber. It is used most often for constipationand other bowel disorders.
What is the nutritional value of wheat bran?
Wheat bran, crude contains 125 calories per 58 g serving. This serving contains 2.5 g of fat, 9 g of protein and 37 g of carbohydrate. The latter is 0.2 g sugar and 25 g of dietary fiber, the rest is complex carbohydrate.
Does wheat bran have calories?
Wheat bran also has a decent amount of zinc and copper. Additionally, it provides over half of the daily value (DV) of selenium and more than the DV of manganese. Not only is wheat bran nutrient dense, it’s also relatively low calorie. Half a cup (29 grams) has only 63 calories, which is minuscule considering all the nutrients it packs.

Does wheat bran have soluble fiber?
Soluble fiber is found in oat bran, barley, nuts, seeds, beans, lentils, peas, and some fruits and vegetables. It is also found in psyllium, a common fiber supplement. Some types of soluble fiber may help lower risk of heart disease. Insoluble fiber is found in foods such as wheat bran, vegetables, and whole grains.
How much insoluble fiber is in wheat bran?
When it comes to insoluble fiber, wheat bran is one of the richest sources. Just 1/2 cup contains 12.5 grams of total fiber. That's 50 percent of the daily recommended total fiber intake. To get more of this fiber-rich source in your diet, choose whole wheat pasta and whole wheat bread.
How much soluble fiber is in bran?
Total Soluble Fiber A 3/4-cup serving of cooked oat bran contains 2.2 grams of soluble fiber.
What cereal has the most soluble fiber?
Oat cereals: Oats are high in soluble fiber, making oat cereals a better choice than bran for this particular dietary component. A bowl of oatmeal made from 3/4 cup of dry oats contains 3 g of soluble fiber. A serving of cooked oat bran cereal (3/4 cup) has 2.2 g, and 1 cup of oat flakes has around 1.5 g.
How much wheat bran should I eat daily?
For males 19 to 50 years, it is 38 grams; for males 51 years and older, it is 30 grams. For females 19 to 50 years, it is 25 grams; for females 51 years and older, it is 21 grams. During pregnancy, 28 grams; during breastfeeding, 29 grams. For constipation: 20-25 grams of wheat bran per day has been used.
Which is healthier oat bran or wheat bran?
A cup of wheat bran has 125 calories and 2.5 grams of fat, while a cup of oat bran has 231 calories and 6.5 grams of fat. Wheat bran is higher in fiber, with 25 grams per cup compared to oat bran's 14.5 grams. Oat bran has more protein, but overall, wheat bran is more conducive to weight loss.
How can I get 10 grams of soluble fiber a day?
For example, to eat at least 10 grams of soluble fiber in a day, try: Breakfast with 1 cup cooked oatmeal with berries and 2 tbsp ground flax (3 grams) Lunch with 1 cup chili made with beans and a pear for dessert (4 grams) Snack with ½ cup raw carrots and ¼ cup hummus (2 grams) Dinner that has 1 cup of steamed cabbage ...
What food has the highest amount of soluble fiber?
What are the best foods high in soluble fiber?Oats. Fiber: 4 grams per cup (cooked) ... Black Beans. Fiber: 17 grams per cup. ... Lentils. Fiber: 16 grams per cup (cooked) ... Chia. Fiber: 10 grams per 1-oz serving. ... Flaxseed. Fiber: 3 grams per tablespoon. ... Barley. Fiber: 6 grams per cup (cooked) ... Brussels sprouts. ... Avocados.More items...•
What grains have the most soluble fiber?
Whole Grains: Most grains have some soluble fiber content, but the champions are oats and barley. Both are rich in a type of soluble fiber called beta-glucan.
What has a lot of soluble fiber?
Top 20 Foods High in Soluble FiberBlack beans. Black beans are not only a great way to give your dishes a meaty texture but also an amazing source of fiber. ... Lima beans. Lima beans, also known as butter beans, are large, flat, greenish-white beans. ... Brussels sprouts. ... Avocados. ... Sweet potatoes. ... Broccoli. ... Turnips. ... Pears.More items...•
How much soluble fiber should you have a day?
Although there is no dietary reference intake for insoluble or soluble fiber, many experts recommend a total dietary fiber intake of 25 to 30 grams per day with about one-fourth — 6 to 8 grams per day — coming from soluble fiber.
Which nuts have the most soluble fiber?
Most nuts are fiber-rich, but hazelnuts are an especially great source of soluble fiber. About a third of the fiber in hazelnuts is soluble. They also contain unsaturated fats, vitamin E, iron and other nutrients.
How much insoluble fiber is in oat bran?
Comparable amounts of fiber provided by wheat and oat brans have the same effect on daily stool output, even though > 90% of wheat bran fiber but only 50-60% of oat bran fiber is insoluble.
What are the best insoluble fiber foods?
Whole-wheat flour, wheat bran, nuts, beans and vegetables, such as cauliflower, green beans and potatoes, are good sources of insoluble fiber.
Is oat bran soluble or insoluble fiber?
Soluble fiberSoluble fiber is found in oat bran, barley, nuts, seeds, beans, lentils, peas, and some fruits and vegetables. It is also found in psyllium, a common fiber supplement. Some types of soluble fiber may help lower risk of heart disease.
What is better wheat germ or wheat bran?
Wheat bran is healthier than wheat germ because it has less calories and contains more fiber, calcium, iron, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus and niacin per serving than what germ. Although wheat germ provides a good number of these nutrients as well. Wheat germ contains more zinc, folate and protein.
How many calories are in wheat bran?
It’s also low in calories and fat, while supplying a good amount of protein per serving. One ounce (approximately 28 grams) of wheat bran contains about: 60.5 calories.
How to eat wheat bran?
How do you eat wheat bran? You can find it as small flakes or in powdered form. The best way to eat bran is adding it to your everyday recipes, like yogurt parfait, hot or cold cereal, salads, soups, casseroles, and smoothies.
What is the difference between wheat bran and wheat germ?
Wheat Bran vs. Wheat Germ. Wheat germ is the embryo of the wheat kernel, while wheat bran is the outer shell that’s stripped away during processing in the production of w heat flour . Wheat germ provides a concentrated dose of vitamins and minerals, including manganese, thiamine, selenium, phosphorus and zinc.
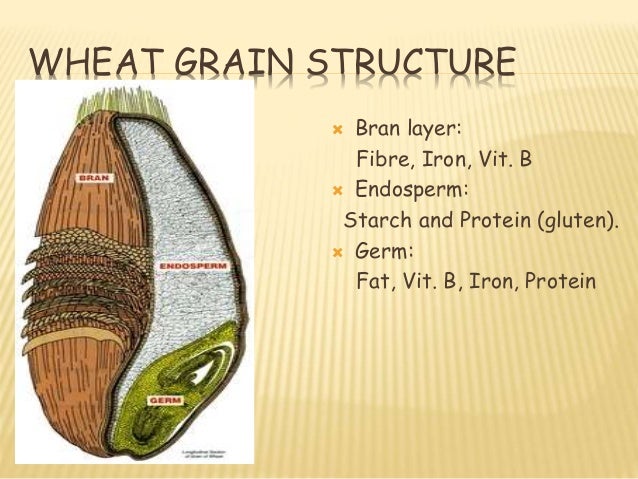
What is the outer layer of the wheat kernel?
Wheat bran, also known as miller’s bran, is the outer layer of the wheat kernel. A wheat kernel actually has three parts: the germ, the bran and the endosperm. Wheat bran, which is the hard exterior of the kernel, is separated from the endosperm and germ during the milling process. The nutty and sweet flavor of wheat bran only adds to its appeal. ...
How much fiber is in wheat brain?
Well, just a quarter-cup of wheat brain contains six grams of dietary fiber. It’s so important to eat a high-fiber diet because as foods rich in fiber pass through your digestive system, unabsorbed by digestive enzymes, they take fat and cholesterol particles, waste and toxins with them.
What is the best bran for digestion?
If you’re looking to improve your digestion and “keep things moving,” then opt for wheat bran. If you are more focused on detoxification and potentially reducing cholesterol, go for oat bran. Other than that, choose the type that’s more satisfying to you.
Which bran is better for you?
So if you’re wondering which bran is best, there’s no clear answer here. Both types of bran are nutritious and provide a number of health benefits. If you’re looking to improve your digestion and “keep things moving,” then opt for wheat bran. If you are more focused on detoxification and potentially reducing cholesterol, go for oat bran. Other than that, choose the type that’s more satisfying to you.
What is the fibre content of whole wheat?
The fibre content of the wholewheat grain ranges from 11.6% to 12.7% dry weight ( Carson and Edwards 2009 ). Most of the fibre that is in the outer layers of the grain (pericarp and seed coat) is typically called wheat bran. It is one of the richest sources of fibre, 46% is non-starch polysaccharide (NSP). The main NSPs present are arabinoxylan, cellulose and beta-glucan that are respectively 70%, 24% and 6% of the NSP of the bran ( Maes and Delcour 2002 ). The concentration of soluble fibre in wheat is significantly less than in other cereals, e.g. barley and oats, 3–11% and 3–7% respectively, compared with less than 1% in wheat (dry weight) ( Wood 1997 ). The amount and type of fibre in wheat, and specifically in wheat bran, is shown in Table II.
How much phytic acid is in wheat bran?
2002 ). In wheat bran, it ranges from 3116 to 5839 mg/100 g dry weight ( Bilgicli and Ibanoglu 2007 ). An average 2–3 tablespoon serving of commercial wheat bran is estimated to contain 200–300 mg of phytic acid. There is a lack of data on average daily intakes of phytic acid. In Spain, where daily bread consumption is calculated at 151 g/day, phytic acid intake from bread is estimated at 159 mg/day (if white bread was consumed) to 350 mg/day (wholewheat bread) ( Garcia-Estepa et al. 1999 ). On the basis of a similar calculation, phytic acid intake is estimated at 96 g/day (if white bread is consumed) to 211 mg/day (wholemeal bread).
What is wheat milling?
Conventional milling of wheat grains is based on separating the endosperm (which produces white flour when milled) from the bran layers and embryo. The aleurone cells, along with the other bran layers and the embryo, are removed to form the bran fraction. Although some processing is necessary for palatability, safety and even nutrient bioavailability ( Topping 2007 ), there has been interest in the potential health benefits of high fibre food products for several years.
Where is phytic acid found in grains?
It is concentrated in the external covers in the pericarp and aleurone layer of the grain as well as, at lower levels, in the germ ( Cheryan 1980 ); 90% of the phytic acid in grain is in the aleurone layer with 10% in the embryo ( Dost and Tokul 2005 ). Consequently, the amount of phytic acid is greatly determined by the fractions removed during milling: white flour has almost no phytate. Wheat contains around 1.13% phytate (dry weight) ( Cheryan 1980) or 3% expressed as gross product ( Pointillart and Gueguen 1992 ).
What is the most commonly consumed grain in the world?
Wheat is the most heavily consumed grain in the world. For example, in the UK wheat consumption is more than 10 times as much as rice (which is mostly consumed as white rice), and oats (419,000 tonnes in 2008/2009), or maize (305,000 tonnes). Usage of wheat for flour and starch milling in 2008/2009 was 6.1 million tonnes. Total human and industrial consumption of wheat for the same year was estimated at 6.836 million tonnes ( FAO 2010 ), implying wheat consumption of nearly 110 kg per capita. Data for consumption of wheat bran per se are not currently available; however, bran for human consumption is produced by flour millers rather than other wheat users. It is estimated that it accounts for approximately 10% of their total output of co-products (i.e. products other than flour); this would amount to 112,000 tonnes in 2008/2009 (Alex Waugh, NABIM, personal communication). Wheat is consumed in Europe typically as bread, pasta, breakfast cereals and biscuits, cakes and pastries. With information taken from manufacturer's webites, Table IV shows sources of wheat bran in the diet.
What percentage of the diet is cereal?
Cereals are staple foods in western countries, and typically contribute about 50% of dietary fibre intake ( Lambo et al. 2005 ). The recommendation that cereals form the basis of the diet is well recognized in the majority of countries with dietary guidelines including most EU member states, the USA and Canada.
How to determine fiber intake?
Fibre intakes are ascertained through dietary survey either a full dietary recall including portion sizes, diet diaries or food frequency questionnaires. These methods are often time-consuming and when dealing with a large dataset take a great deal of time, effort, attention to detail and consistency of methodology. The DINE questionnaire ( Roe et al. 1994) was developed to be administered and scored in under 10 minutes by primary care staff without specialized nutritional knowledge. The questionnaire gives an output of low, medium or high for fat and fibre intakes. This validated questionnaire is in wide use and is currently being modified to provide a more numeric value for fibre intake based on more modern AOAC fibre values.
What Is Soluble Fiber?
Insoluble fiber stays in its bulky form as it travels through your body, helping food pass through the stomach and intestines more easily. Whole grains, wheat bran, and certain vegetables all contain lots of insoluble fiber.
How Much Soluble Fiber Do You Need?
The USDA recommendation for dietary fiber is 14 grams per 1,000 calories, which works out to 28 grams for a 2,000-calorie diet and 42 grams for a 3,000-calorie diet.
Why is soluble fiber important?
Soluble fiber is important to your health, digestive and otherwise. The short-chain fatty acids produced by soluble fiber fermentation feed the good bacteria in your gut, improving gastrointestinal health. The kinetics of soluble fiber digestion also have far-reaching effects beyond your gut.
What are the two types of fiber?
By. anchour-michael. You’ve likely heard that you need to get more fiber in your diet, but you might not realize that dietary fiber comes in two varieties: soluble and insoluble. When you think fiber, you’re probably thinking about non-soluble fiber, also known as roughage. Foods like wheat bran and whole grains bulk up ...
How long does it take to add fiber to your diet?
As you can see, adding soluble fiber to your diet is easy (and delicious), but be aware that increasing your fiber intake too quickly can cause GI distress, so add it to your diet gradually over several weeks.
Which type of fiber is found in plants?
Plant foods contain both soluble and insoluble fiber, although the proportion of each type varies by food.
Do plant based foods have soluble fiber?
Because plant-based foods contain both types of fiber, and because you don’t need as much soluble fiber as insoluble, you’ll likely get enough soluble fiber by increasing your overall fiber intake to hit the USDA recommendation. But if you’re curious to know which foods contain the most soluble fiber, check out this list, ...
How long is wheat bran good for?
When taken by mouth: Wheat bran 30 grams daily for up to 3 months is LIKELY SAFE for most people. It may cause gas ( flatulence) and stomach discomfort, especially when first used.
What is wheat bran used for?
Overview. Wheat is a plant. The outer shell of the grain (the bran) is used to make medicine. Wheat bran is a source of fiber. It is used most often for constipation and other bowel disorders. It is also used to prevent various cancers, for high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and other conditions, there is no good scientific evidence ...
How much fiber should a child consume daily?
General: There is a recommended daily intake of fiber for all children over 1 year of age. For children 1 to 3 years, it is 19 grams; for children 4 to 8 years, it is 25 grams. For boys 9 to 13 years, it is 31 grams; for boys 14 to 18 years, it is 38 grams. For girls 9 to 18 years, it is 26 grams.
Does wheat bran soften stools?
But it doesn't seem to soften stools. Hemor rhoids. Taking wheat bran may help to decrease the chance of getting hemorrhoids. High blood pressure. Taking wheat bran seems to slightly reduce blood pressure. A long-term disorder of the large intestine that causes stomach pain ( irritable bowel syndrome or IBS ).
Does wheat bran interact with digoxin?
Digoxin (Lanoxin) interacts with WHEAT BRAN. Wheat bran is high in fiber. Fiber can decrease the absorption and decrease the effectiveness of digoxin (Lanoxin). As a general rule, any medications taken by mouth should be taken one hour before or four hours after wheat bran to prevent this interaction. Dosing.
Does wheat bran help with colon cancer?
The most reliable research shows that taking fiber, including wheat bran, doesn't prevent colon cancer or rectal cancer from reappearing in people who have already had them. Diabetes. Taking wheat bran doesn't seem to consistently improve blood sugar control.
Is wheat bran safe for a hernia?
Other conditions. More evidence is needed to rate the effectiveness of wheat bran for these uses. Side Effects. When taken by mouth: Wheat bran 30 grams daily for up to 3 months is LIKELY SAFE for most people.
How much fiber is in one ounce of wheat bran?
One ounce of wheat bran contains 12 grams of fiber. Oat bran has soluble fiber, which attracts water, turning into a gel during digestion, which effectively slows digestion, making you feel satiated longer. One ounce of oat bran contains 4 grams of fiber. A significant difference between oat bran and wheat bran is that oat bran has a beta-glucan, ...
What are the minerals in wheat bran?
In particular, wheat bran has more iron, magnesium, potassium, zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium.
Who Can Eat Wheat Bran or Oat Bran?
One of the most significant differences between oat bran and wheat bran is that oat bran is gluten-free, while wheat bran is not.
How many calories are in oat bran?
Cooked oat bran can have 88 to 150 calories depending on the brand and serving size, typically 1/3 cup or 31 grams. On the other hand, one serving of wheat bran has 50 calories, generally ¼ cup or 15 grams.
What is the difference between wheat bran and oat bran?
A significant difference between oat bran and wheat bran is that oat bran has a beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber that may help prevent heart disease, lower cholesterol, and manage diabetes. The beta-glucan binds cholesterol-rich bile acids in the intestine , transporting them through the digestive tract and out the body .
What are the two types of fiber?
There are two different types of fiber: insoluble and soluble. Both are important for health, as soluble fiber promotes a healthy heart, and insoluble aids in bowel function.
Which has more vitamins: wheat bran or oat bran?
Wheat bran has more vitamins than oat bran per serving, by about double the amount. Oat bran, however, does have three times more thiamin than wheat bran. Thiamin helps cells in the body change carbs into energy. On the other hand, wheat bran has three times more niacin and vitamin B6 and double the riboflavin amount.
Why is fiber a gel?
Because it is undigested, it provides 0 calories. Instead of being used for energy, fiber is excreted from our bodies. Soluble fiber forms a gel when mixed with liquid, while insoluble fiber passes through our intestines largely intact.
What are the benefits of fiber?
We all know the benefits of fiber! Fiber not only promotes gut health, but also helps reduce the risk of developing many chronic diseases. For instance, fiber prevents constipation, hemorrhoids and diverticulosis.
How much fiber is in Bulgur?
Most Whole grains. Bulgur, for instance, contains 4.2 grams of insoluble fiber in 1/2 cup
What are the two types of fiber?
Types of Fiber: Soluble Fiber and Insoluble Fiber. Both soluble and insoluble fiber are undigested. They are therefore not absorbed into the bloodstream. Fiber content is often listed under “Total Carbohydrates” on a Nutrition Facts label. Because it is undigested, it provides 0 calories.
Is fiber good for cancer?
A high-fiber diet is also linked to lower risk of developing some cancers, especially colon and breast cancer. In addition, it helps lower LDL cholesterol and total cholesterol. Furthermore, high-fiber foods generally have a lower glycemic index value, an important element in managing Type 2 diabetes.
Are Weetabix insoluble fibre?
Cereals have gained a bit of a bad rep of late due to the high sugar content in many brands, but low sugar breakfast cereals can be a great source of fibre. Try Weetabix (which provides 3.8g of fibre per two-biscuit serving) or Shredded Wheat (6g of fibre per serving when consumer with semi-skimmed milk).
What cereals have soluble fibre?
Soluble Fibre – Soluble fibre attracts water to form a gel-like substance, which slows down digestion and delays the emptying of your stomach.
Is Weetabix a healthy breakfast?
Ultimately Weetabix is a great cereal to have for breakfast. It is low in salt and sugar — one biscuit contains one hundredth of a teaspoon of salt, which is 0.8% of the FSA’s suggested daily salt intake, and less than a fifth of a teaspoon of sugar (0.9g). It can absolutely be eaten in a balanced and healthy diet.
Which grains have soluble fiber?from healthyeating.sfgate.com
Whole Grains: Most grains have some soluble fiber content, but the champions are oats and barley. Both are rich in a type of soluble fiber called beta-glucan. This soluble fiber is what gives oatmeal its characteristically creamy texture, and barley its ability to gently thicken soups. Among the "ancient grains" and pseudograins, amaranth is also very high in soluble fiber.
What Is Soluble Fiber?from draxe.com
The definition of soluble fiber is fiber that dissolves in water and is viscous and fermentable. Insoluble fiber is different than soluble fiber because it does not dissolve in water and remains intact while it travels through the digestive system.
How much oats are good for cholesterol?from healthline.com
It’s estimated that 3 grams of oat beta glucan per day can reduce your risk of heart disease ( 37, 38 ).
What are soluble fiber supplements made of?from draxe.com
Other soluble fiber supplements are made with ingredients including powdered cellulose, guar gum, pectin, acacia fiber and wheat dextrin. It’s best to start with a low dose of a fiber supplement and increase gradually as needed based on your reaction.
How to prevent constipation and bloating?from draxe.com
To help prevent digestive issues, including bloating or constipation, it’s best to add soluble fiber foods to your gradually and also to drink plenty of water.
How does fiber affect the gut?from livestrong.com
Improves Gut Health. Soluble fiber is fermented in the colon by bacteria, according to Jackson Seigelbaum Gastroenterology. This fermentation fuels the growth of these healthy bacteria, which have wide-ranging effects on health, including: Improving immunity.
How much fiber is in a pears?from healthline.com
What’s more, they’re an excellent source of fiber, with 5.5 grams in one medium-sized fruit. Soluble fiber contributes 29% of the total dietary fiber content of pears, the main form being pectin ( 17. Trusted Source. , 18 ). Due to their high fructose and sorbitol contents, pears can sometimes have a laxative effect.