How much waste does each person produce annually?
These Facts and Figures are current through calendar year 2018. The total generation of municipal solid waste (MSW) in 2018 was 292.4 million tons (U.S. short tons, unless specified) or 4.9 pounds per person per day. Of the MSW generated, approximately 69 million tons were recycled and 25 million tons were composted.
How much waste does the average American produce?
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, the average American produces about 4.4 pounds (2 kg) of garbage a day, or a total of 29 pounds (13 kg) per week and 1,600 pounds (726 kg) a year. This only takes into consideration the average household member and does not count industrial waste or commercial trash.
How much waste is produced around the world each day?
The world generates at least 3.5 million tons of plastic and other solid waste a day, 10 times the amount a century ago, according to World Bank researchers. The U.S. is the king of trash, producing a world-leading 250 million tons a year —roughly 4.4 pounds of trash per person per day.
How much waste does the average human produce?
According to the EPA, the average American person will produce about 5.91 pounds of trash, with about 1.51 pounds being recycled; 4.40 pounds is the rough average daily waste per person. That’s a lot! How much waste does a person produce in a year? on average Americans generate 4.3 pounds of trash per day.

How much waste does the world produce per day?
The world generates at least 3.5 million tons of plastic and other solid waste a day, 10 times the amount a century ago, according to World Bank researchers. The U.S. is the king of trash, producing a world-leading 250 million tons a year—roughly 4.4 pounds of trash per person per day.
How much waste do we generate every year?
According to the United Nations we dump 2.12 billion tons of waste every year.
How much waste is in the World 2021?
Globally to date, there is about 8.3 billion tons of plastic in the world – some 6.3 billion tons of that is trash. Imagine 55 million jumbo jets and that's how much plastic exists here.
How much waste is generated in the World 2020?
The world generates 2.01 billion tonnes of municipal solid waste annually, with at least 33 percent of that—extremely conservatively—not managed in an environmentally safe manner. Worldwide, waste generated per person per day averages 0.74 kilogram but ranges widely, from 0.11 to 4.54 kilograms.
Is zero waste possible?
Living 100% zero waste is hardly possible. However, getting closer to zero waste is doable, by focusing on our efforts on refusing, reducing, and reusing things, and maximizing recycling efforts.
What country wastes the most?
Canada1. Canada. Canada's estimated total waste generation is the largest in the entire world. It has an estimated annual waste total is 1,325,480,289 metric tons.
What country generates the most waste?
AmericansAs a nation, Americans generate more waste than any other nation in the world with 4.5 pounds (2.0 kg) of municipal solid waste (MSW) per person per day, fifty five percent of which is contributed as residential garbage.
How much litter is in the world?
Altogether, it adds up to around 52 billion pieces of litter cluttering up the landscape. That breaks down to more than 6,700 items per mile.
How much waste is thrown away every year?
Every year we dump a massive 2.12 billion tons of waste. If all this waste was put on trucks they would go around the world 24 times. This stunning amount of waste is partly because 99 percent of the stuff we buy is trashed within 6 months.
How much toxic waste was dumped in Nigeria?
In one example, 4,000 tons of toxic waste was shipped to Nigeria and simply dumped. The waste included 150 tons of highly toxic polychlorinated biphenyls, or PCBs, that are known to cause hormone deficiencies and reduced cognitive development in children.
What is the practice of using underdeveloped states as a cheap way for richer countries to get rid of toxic waste?
The practice of using underdeveloped states as a cheap way for richer countries to get rid of toxic waste is sometimes referred to as toxic colonialism .
What is global waste trade?
Global waste trade. Toxic and hazardous wastes are often sold by developed countries to poorer developing countries. This practice is known as the global waste trade. Wealthy nations are basically exporting their problem to poor countries mainly in Africa and Asia.
How many people are affected by dumpsites?
Affecting 64 million people. The dumpsites created by the global waste trade have at least one thing in common: They pose a serious threat to human health and the environment in the communities they are located in. About 64 million people are directly affected by dumpsites created by the global waste trade.
How much e-waste does Indonesia receive annually?
Receives around 192,000 tonnes of e-waste annually. Pollutes soil, air and water and causes serious health threats for the 10,000 people making a living from sorting and recycling. The Bantar Gebang dump in Bekasi, Indonesia. Total amount of waste up to 40 million tonnes.
What is persistent organic pollutants?
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are organic chemical substances that pose a serious, global threat to human health and to ecosystems. Because of their persistence, POPs bioaccumulate in people and nature. Even so, many POPs are still used as for example pesticides.
How much of the waste is recycled in developing countries?
Social inclusion: Resource recovery in most developing countries relies heavily on informal workers, who collect, sort, and recycle 15%–20% of generated waste. Projects address waste picker livelihoods through strategies such as integration into the formal system, as well as the provision of safe working conditions, social safety nets, child labor restrictions, and education.
How much waste will be generated in 2050?
With rapid population growth and urbanization, annual waste generation is expected to increase by 70% from 2016 levels to 3.40 billion tonnes in 2050. Compared to those in developed nations, residents in developing countries, especially the urban poor, are more severely impacted by unsustainably managed waste.
How do waste projects help the environment?
Climate change and the environment: Projects promote environmentally sound waste disposal. They support greenhouse gas mitigation through food loss and waste reduction, organic waste diversion, and the adoption of treatment and disposal technologies that capture biogas and landfill gas. Waste projects also support resilience by reducing waste disposal in waterways, addressing debris management, and safeguarding infrastructure against flooding.
What is the World Bank's infrastructure?
Infrastructure: The World Bank provides capital investments to build or upgrade waste sorting and treatment facilities, close dumps, construct or refurbish landfills, and provide bins, dumpsters, trucks, and transfer stations.
How does waste management help in Vietnam?
In Vietnam, investments in solid waste management are helping the city of Can Tho prevent clogging of drains, which could result in flooding. Similarly, in the Philippines, investments are helping Metro Manila reduce flood risk by minimizing solid waste ending up in waterways. By focusing on improved collection systems, community-based approaches, and providing incentives, the waste management investments are contributing to reducing marine litter, particularly in Manila Bay.
How does the World Bank work in municipal waste management?
Health and safety: The World Bank’s work in municipal waste management improves public health and livelihoods by reducing open burning, mitigating pest and disease vector spreading, and preventing crime and violence.
What is the World Bank's commitment to solid waste?
World Bank engagement in solid waste management is supported through valuable partnerships, including funding from the Tokyo Development Learning Center, Climate and Clean Air Coalition , Korean Green Growth Trust Fund, and the Global Partnership on Results-Based Approaches (GPRBA), as well as collaboration on capacity building and knowledge sharing through a memorandum of understanding with the International Solid Waste Association ( ISWA).
How much has the per capita waste generation increased since 1990?
As countries continue developing, there is a reduction in biological solid waste and ash. Per capita waste generation in OECD countries has increased by 14% since 1990, and 35% since 1980. Waste generation generally grows at a rate slightly lower than GDP in these countries.
Why does municipal solid waste grow faster in developing countries?
Labour costs are relatively low but waste management is generally a higher proportion of municipal expenditure. As urbanization continues, municipal solid waste grows faster than urban populations because of increasing consumption and shortening product life spans.
Why do developed countries produce more waste per capita?
Developed countries produce more waste per capita because they have higher levels of consumption. There are higher proportions of plastics, metals, and paper in the municipal solid waste stream and there are higher labour costs. As countries continue developing, there is a reduction in biological solid waste and ash. Per capita waste generation in OECD countries has increased by 14% since 1990, and 35% since 1980. Waste generation generally grows at a rate slightly lower than GDP in these countries. Developed countries consume more than 60% of the world industrial raw materials and only comprise 22% of the world's population. As a nation, Americans generate more waste than any other nation in the world with 4.5 pounds (2.0 kg) of municipal solid waste (MSW) per person per day, fifty five percent of which is contributed as residential garbage.
Where is electronic waste shipped?
Waste is shipped between countries for disposal and this can create problems in the target country. Electronic waste is commonly shipped to developing countries for recycling, reuse or disposal.
How much waste does the US produce?
The US produces an average of more than 1,700 pounds of food, plastic, and hazardous waste per person. At that rate, 5% of the world’s population generates 40% of the world’s waste. New Jersey is home to the largest number of hazardous waste sites (114).
What is the majority of waste created in middle- or high-income countries?
The majority of waste created in middle- or high-income countries is made up of inorganic material such as paper or plastic. Developing countries are responsible for producing over half of the earth’s total solid waste. Over 90% of waste is mismanaged in low-income countries.
How much waste will be thrown away in 2021?
As of February 2021, more than 50 million tons of hazardous waste had been thrown away globally. The US saw $8.7 million in revenue of hazardous waste treatment and disposal in 2019, up 176% from 2000. The US produces an average of more than 1,700 pounds of food, plastic, and hazardous waste per person.
How much will the hazardous waste industry decrease in 2020?
The hazardous waste collection industry saw a 6% decrease in revenue in 2020 due to lower demand.
How many businesses provide hazardous waste services in the US?
Here are some of the most important facts to keep in mind. Hazardous Waste Statistics. There are close to 600 businesses that provide hazardous waste services (management and collection) in the US and over 8,700 employees. The hazardous waste collection industry saw a 6% decrease in revenue in 2020 due to lower demand.
How many pounds of toxics were released into the environment in 2019?
3.4 billion pounds of Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) chemicals were released into the environment in 2019.
What percentage of municipal solid waste is organic?
Organics such as paper make up 66% of the municipal solid waste stream.
How much trash does the average person produce?
The average global citizen produces 2.6 pounds of trash a day. The US produces 33% of the world's solid waste. Over thirty years ago, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) began collecting and reporting data on waste. The agency used this data to look at how much waste the U.S. generated and what municipalities choose to do with their waste.
What percentage of electronic waste is recyclable?
Only 25% of electronic waste is recyclable and 70% of metals found in US landfills come from electronic devices. Common materials found in e-waste are lead and lead-acid. Lead leaches into water and soil which can lead to devastating effects on the environment and serious health problems by entering the food chain.
How many landfills does the US have?
It is so efficient that the system can get rid of trash by throwing it in a landfill or paying another country to throw it in their landfills. The US has over 2,000 landfills and thousands of inactive ones.
How much trash does the US throw away?
The US makes up about 4% of the world’s population but produces 12% of its trash. The average American throws away 4.4 pounds of trash each day , which is almost twice as much as the global average of 2.6 pounds each day. That amounts to about 29 pounds per week, and 1,600 pounds per year from the average American.
How can we reduce waste?
There are many ways to reduce the amount of waste generated. Anyone who uses a plastic straw can switch to bamboo or stainless-steel straws. Use a reusable water bottle to fill your liquids. Gardeners may want to think about starting a compost bin to discard the fallen leaves and leftover food. School or work lunches can be packed in a reusable lunch bag or lunch box. Efforts can also be made to consume less so that there is less waste. Purchase products with less packaging so there is less trash to throw away. Each household can play a game to see how little trash each member in the household makes.
Does China take recycled paper?
Until now, China was importing America's recyclables that would be used to make shoes, bags, and other recycled products. Recently though, China put new restrictions on what they would take including not taking mixed paper, magazines, office paper, junk mail, and most plastics.
Should cities pay higher rates to get rid of recyclables?
Cities, counties, and towns must now choose between paying higher rates to get rid of recyclable products or stopping the recycling program altogether. This is also contributing to additional problems for the country.
How much of the waste generated in the 1960s was landfilled?
Landfilling of waste has decreased from 94 percent of the amount generated in 1960 to 50 percent of the amount generated in 2018.
What is the fourth largest waste?
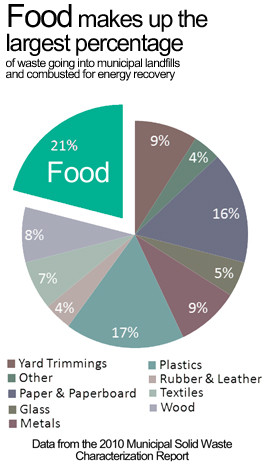
Food waste comprised the fourth largest material category, estimated at 63.1 million tons or 21.6 percent of total generation in 2018. Yard trimmings comprised the next largest material category, estimated at 35.4 million tons, or 12.1 percent of total generation, in 2018. This compares to 35 million tons (16.8 percent of total generation) in 1990. The decline in yard trimmings generation since 1990 is largely due to state legislation discouraging yard trimmings disposal in landfills, including source reduction measures such as backyard composting and leaving grass trimmings on the yard.
How much MSW was recycled?
Of the MSW generated, approximately 69 million tons were recycled and 25 million tons were composted. Together, almost 94 million tons of MSW were recycled and composted, equivalent to a 32.1 percent recycling and composting rate. An additional 17.7 million tons of food were managed by other methods.
How much compost is there in MSW?
The total MSW composted was 25 million tons. This included approximately 22.3 million tons of yard trimmings (more than a five-fold increase since 1990) and 2.6 million tons of food waste (4.1 percent of generation of wasted food).
What percentage of MSW is recycled?
It decreased to 32.1 percent in 2018.
How many tons of MSW were produced in 2018?
Generation. The total generation of MSW in 2018 was 292.4 million tons, which was approximately 23.7 million tons more than the amount generated in 2017. This is an increase from the 268.7 million tons generated in 2017 and the 208.3 million tons in 1990. Created with Highcharts 4.2.7.
What is EPA trash?
EPA refers to trash, or MSW, as various items consumers throw away after they are used. These items include bottles and corrugated boxes, food, grass clippings, sofas, computers, tires and refrigerators. However, MSW does not include everything that may be landfilled at the local level, such as construction and demolition (C&D) debris, municipal wastewater sludge, and other non-hazardous industrial wastes. While the analysis in Facts and Figures focuses primarily on MSW, EPA has been including estimates of C&D generation and management as a separate non-hazardous waste stream in recent years.
How much of the world's e-waste is recycled?
Only 17.4% of total global e-waste is known to have been collected and properly recycled. This figure has fallen in the last 5 years as a percentage of total waste generated.
How much has the global e-waste generation increased over the last decade?
On average, the global e-waste generation has increased by 2 Mt annually over the last decade
What happens when you dispose of chemicals improperly?
When disposed of improperly, these chemicals can be released indefinitely into the air, soil or water which is detrimental to ecosystems as well as human populations.
Why don't people recycle electronic equipment?
The fact that so many people don’t do this is down to either a lack of education or sheer laziness.
How much of e-waste goes to landfill?
It is estimated that 8% of e-waste is discarded in the trash, and subsequently goes to landfill or gets incinerated. This consists mostly of smaller electrical and It items (tablets, mobile phones etc).
Why is the e-waste market growing?
That’s why the global e-waste management market is likely to grow, due to financial reasons as well as environmental ones.
What are the raw materials in e-waste?
There are several high value raw materials in e-waste, including gold, copper and iron. It is estimated that the 53.6 Mt of e-waste generated in 2019 contained raw materials worth around $57 billion.

Overview
Developed nations
Developed countries produce more waste per capita because they have higher levels of consumption. There are higher proportions of plastics, metals, and paper in the municipal solid waste stream and there are higher labour costs. As countries continue developing, there is a reduction in biological solid waste and ash. Per capita waste generation in OECD countries has increased by 14% since 1990, and 35% since 1980. Waste generation generally grows at a rate sl…
Developing nations
Developing nations produce lower levels of waste per capita with a higher proportion of organic material in the municipal solid waste stream. If measured by weight, organic (biodegradable) residue constitutes at least 50% of waste in developing countries. Labour costs are relatively low but waste management is generally a higher proportion of municipal expenditure. As urbanization continues, municipal solid waste grows faster than urban populations because of increasing con…
Transboundary issues with waste
Waste is shipped between countries for disposal and this can create problems in the target country.
Electronic waste is commonly shipped to developing countries for recycling, reuse or disposal. The Basel Convention is a Multilateral Environmental Agreement to prevent problematic waste disposal in countries that have weaker environmental protection laws. The Convention has not p…
Waste by country
• Waste in New Zealand
• Waste in the United Kingdom
• Waste in the United States
• Waste management in India
See also
• Litter
• Fly-tipping
• Environmental dumping
• Marine pollution
• Marine debris
External links
• Municipal waste generation by country