How much weight can a glulam beam hold?
The beams withstood a range of loads between 69,000 and 95,800 pounds. One may also ask, what is stronger glulam or LVL? Although they're much lighter than concrete and steel, they're extremely strong. Glulam is most commonly used in the construction of large buildings, including universities, airport, hotels, and museums.
What size glulam for 30 foot span?
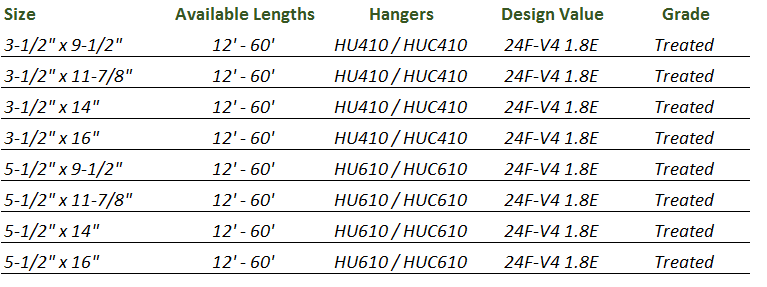
What size lvl beam for a 30 foot span:- as per general thumb rule, for a 30 foot span, size of LVL beam or GLULAM should be 16-18 inches deep and 4 inches wide, thus you need something like a 16-18″ GLULAM or LVL to span upto 30 feet used for residential building or projects.
What size beam do I need to span 20 feet?
Wood beam size for a 20 foot span :- as per general thumb rule, for a 20 foot span, size of wood beam or lumber joist should be 2×14 which placed at 16″ apart from centre used for residential building or projects or construction in which depth of section of beam is 350mm (14″) and width of beam is 50 mm or 2″.
How to determine beam size?
- The first input you need is the steel I beam load specifications or loading details on the steel I beam.
- Draw bending moment diagram for the given loads and you will find the value of maximum bending moments (say M) that the steel I beam is expected to experience.
- Choose an approximate size of steel I beam from a standard I beam table.
How many loads are in a 10 m beam?
What is the sum of moments in beam in balance?
About this website

Is a glulam stronger than a solid beam?
Today, the advancements in engineered wood construction materials with products like glulam can produce posts and beams with more added strength than from that in solid sawn lumber alone, with far less warping and extraordinary durability.
Is glulam stronger than steel?
Glulam Basics Glued laminated timber, or glulam, is a highly innovative construction material. Pound for pound, glulam is stronger than steel and has greater strength and stiffness than comparably sized dimensional lumber.
How strong is glulam?
Longstanding quality and durability In comparison to steel and concrete, wood products have a larger strength to weight ratio. For example, in the case of beam sizes, the strength of glulam is approximately 1.5 more than to double that of steel of the same load-bearing capacity.
How much weight can a beam hold?
Allowable uniform loads.Designation (Width x lbs/ft)Nominal Size - Depth x Width (inches x inches)Allowable Uniform Load (lb)Span (ft)W10 x 3010 x 5 3/423600W12 x 2612 x 6 1/224300W12 x 3012 x 6 1/22810011 more rows
How far can you span with glulam?
Glulam beams can span not more than 100 feet, even in large open spaces. Normally, people do not come in need to span in such a big measurement. To span up to 24 feet, the consumer will need a 12” (nominal) I-joist, or they could use an engineered floor truss to span the product.
Are glulam beams cheaper than steel?
How much are steel beams vs glulam beams? For a simple beam, spanning between supports, glulam is often cheaper than steel. There are also hidden savings due to the ease with which you can fix joist hangers, etc. to the beams, and the fact that you don't need to box the glulam in as you would do with steel.
What are the disadvantages of glulam?
Glulam boards have better mechanical strength than other wood products and higher resistance to rot and fire. There are some disadvantages of glulam, among them: Due to associated production costs, the Glulam price can be higher than other timber products.
What is the strongest engineered wood beam?
Power Beam® is the strongest engineered wood product (EWP) on the market with design values of 3000Fb - 2.1E - 300Fv. Power Beam® is manufactured with superior strength southern yellow pine MSR Lumber.
Why would you use a glulam beam instead of a standard lumber beam?
Glulam construction offers superior strength and stiffness over dimensional lumber, and pound-for-pound it is stronger than steel. Connections for glulam beams are typically made with bolts or steel dowels and steel plates.
How do you calculate beam load capacity?
Calculate the maximum bending moment for the wooden beams. The bending moment is the length of the span times the weight to be supported divided by 8. For a beam spanning a 12-foot room and supporting a weight of 600 lbs., the maximum bending moment would be 12 x 600/8 = 900 foot-pounds.
Which is stronger H beam or I beam?
The cross section of the H beam is stronger than the cross section of the I beam, meaning it can bear a greater load. In comparison, the cross section of an I beam can bear direct load and tensile but cannot resist twisting because the cross section is so narrow. This means that it can only bear force in one direction.
How do you calculate load bearing beam size?
1:313:31Beam Calculator Tutorial - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAssuming. That the joists. Are running perpendicular out from the house towards us okay so you'reMoreAssuming. That the joists. Are running perpendicular out from the house towards us okay so you're standing in front of the house looking at the house and this is what you would you won't actually see
Is laminated timber stronger than steel?
GLUE-LAMINATED TIMBER (GLT) BEAMS ARE STRONGER THAN STEEL.
Is glulam considered heavy timber?
However, in consideration of engineered wood products, IBC Table 2304.11 (IBC 2015 Table 602.4) provides equivalent glulam and SCL sizes that qualify as heavy timber. For most building elements other than heavy timber, passive fire-resistive requirements are in the form of a required fire- resistance rating (FRR).
Can glulam be used as posts?
TimberLab Glulam timber beams are load-bearing structural members for roofs, floors and other construction situations, e.g. bridges, posts, etc. Glulam uses stress rated, seasoned and selected timbers – usually Radiata Pine or Douglas Fir.
What are glulam beams used for?
They are commonly used for large curved or arching members to build vaulted roofs, domes, and even bridges. Glulam construction offers superior strength and stiffness over dimensional lumber, and pound-for-pound it is stronger than steel.
How many loads are in a 10 m beam?
A 10 m long beam with two supports is loaded with two loads, 500 kg is located 1 m from the end ( R1 ), and the other load of 1000 kg is located 6 m from the same end. The balance of forces can be expressed as
What is the sum of moments in beam in balance?
In addition for a beam in balance the algebraic sum of moments equals zero. The moment balance can be expressed as
How much does an 8 foot tall wall weigh?
Loads are contributed to the lower header by the roof, upper walls and 2nd floor system. The Architectural Graphic Standards lists the weight of an exterior 2×6 wall as 16 pounds per ft 2. So an 8-foot tall wall weighs 8 ft x 16 pounds/ft 2 = 128 pounds per lineal foot. The loads delivered to the header are:
How do headers and beams work?
The job of headers and beams is a simple one. They transfer loads from above to the foundation below through a network of structural elements. The idea behind sizing headers and beams is straight-forward: Add together all live loads and dead loads that act on the member and then choose a material that will resist the load. The beam must be strong enough so it doesn’t break (Fb value) and stiff enough so that it doesn’t deflect excessively under the load (E value). However, the process for sizing these structural elements can be complicated if you are not an engineer. Here is a simplified approach that will help you specify the appropriate material for many applications.
How much load does a roof carry?
Here, each square foot of roof system delivers 50 pounds of live load and 15 pounds of dead load (65 psf total) to the structural support system . Remember, these loads are distributed uniformly over the entire surface of the roof. The exterior wall (and the headers within) will carry all loads from the mid-point of the house (between the supporting walls) to the outside of the house (including the roof overhang). The distance in this case is 12 ft+ 2 ft = 14 ft. So, each lineal foot of wall must carry the loads imposed by a 1-foot wide strip in that 14 ft region. In technical terms, the wall has a tributary width of 14 ft. From this we can readily see that each lineal foot of wall supports:
What is a distributed load?
Loads are considered to be either distributed or point loads. A layer of sand spread evenly over a surface is an example of a pure distributed load. Each square foot of the surface feels the same load. Live and dead loads listed in the building code for roofs and floors are approximations of distributed loads. Point loads occur when a weight is imposed on one spot in a structure, like a column. The load is not shared equally by the supporting structure. Analysis of point loading is best left to engineers. We will consider only distributed loads. This will enable us to size beams for most common applications.
Why is it important to list live load, dead load and total load separately?
It is important to list live load, dead load and total load separately because live load is used to compute stiffness and total load is used to calculate strength.
Can you beat sawn lumber for window headers?
Too often builders gang together 2-inch dimension lumber to support roof and floor loads without considering other options. You can’t beat sawn lumber for most small window headers, but as spans and loads increase, stronger materials are a better choice.
How to size engineered beams?
To size engineered beams and headers you begin with load per foot of beam. With engineered wood, you use both live load and dead load values. Live load determines stiffness and total load is used to determine strength. The sizing steps are: determine the total load and live load per foot of beam.
What is the width of a parallam?
The wood fiber used is strong and stiff. Several widths from 1 ¾” – 7″ are available in depths of 9 ¼” – 18″. Parallam dimensions are compatible with the other engineered wood products like I-joists and LVL. Parallam has been around for a while, but still — not all sizes are available in all regions.
What is parallam lumber?
Parallam, manufactured by Trus Joist MacMillan (TJM), virtually defines the term: parallel strand lumber (PSL). PSL is an assembly of long, thin strands of wood veneer glued together to form continuous lengths of beam. The wood fiber used is strong and stiff. Several widths from 1 ¾” – 7″ are available in depths of 9 ¼” – 18″. Parallam dimensions are compatible with the other engineered wood products like I-joists and LVL. Parallam has been around for a while, but still — not all sizes are available in all regions. It is best to plan your design well ahead of schedule. Like APB, Parallam comes fully assembled and is comparably heavy. It is a good choice for long clear spans where sawn lumber is impractical.
What is LVL laminate?
Laminated Veneer Lumber ( LVL) is strong, stiff and versatile. It spans long distances. I was able to use LVL for every application in the case-house. Typically, LVL comes 1 ¾” thick and ranges in depth from 7 ¼” up to 18″. To fine-tune the load-carrying potential of a LVL beam, just add another ply to the side of a beam. Labor is a factor. It takes time to laminate multiple layers of LVL. But the upside is that 2 workers can usually handle the weight of each lamination as it is assembled. LVL is carried as a stock item in most lumber yards and it is familiar to most building code officials and designers.
How much lumber does a 2x6 double header hold?
Note: a single 2×6 will support 347 pounds per lineal foot of beam. Therefore, a double 2×6 carries 2 x 347 = 694 pounds per lineal foot.
What is the next step in calculating structural beams?
Once the loads acting on structural beams are calculated, the next step is to size and select the appropriate beam.
What is the deflection limit for a roof beam?
The table lists spans with a deflection limit of L/360 , normal for floor loads. If you size a roof beam like a structural ridge that has a L/240 limitation, you would multiply the minimum E-value by 0.666 (785,000 x 0.666 = 522,810 in this case). For L/180 multiply by 0.5.
How many loads are in a 10 m beam?
A 10 m long beam with two supports is loaded with two loads, 500 kg is located 1 m from the end ( R1 ), and the other load of 1000 kg is located 6 m from the same end. The balance of forces can be expressed as
What is the sum of moments in beam in balance?
In addition for a beam in balance the algebraic sum of moments equals zero. The moment balance can be expressed as