The body tightly regulates pH levels through; blood buffers, kidneys and breathing through out lungs. When we breathe out air, we breath out acidic carbon dioxide, this helps to regulate blood acidity levels. Besides you wouldn’t want the body to change pH that easily, because your cells would die.
How to naturally balance pH in your body?
How to Support Proper pH balance
- Reduce Intake of Acidic Foods. If you currently eat a “Standard American Diet,” you’ll likely need to give certain things up in order to eat a diet that’s lower ...
- Eat an Alkaline Diet. If there’s such thing as a pH balance diet, it’s one that includes lots of green plants and other alkalizing foods.
- Drink Alkaline Water. ...
What drink will increase the pH level of my body?
Drink lemon water once or twice daily to help restore the pH balance in your body. To make lemon water, mix the juice of ½ lemon to a glass of warm water and add a little raw honey for taste. Does apple cider vinegar make your body alkaline?
How to lower body pH naturally?
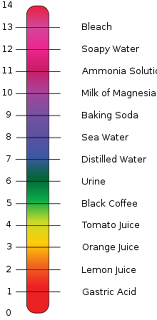
- Highly Acidic: Lemon juice, vinegar (pH 2)
- Highly Acidic: Sodas, energy drinks, carbonated water (pH 3)
- Medium Acidity: Alcohol, coffee, black tea, cheese, milk, yogurt, distilled water, chocolate, roasted nuts, beef, pork, wheat, pastas, pastries, breads, crackers (pH 4-5)
How does the body maintain a stable pH level?
- Foods you eat can help you achieve acid/alkaline balance.
- To maintain pH balance, eat a variety of fruits, vegetables and grains that are middle alkaline or acidic and choose highly acidic foods when you have high alkaline pH.
- Hydrate with water daily, limit your alcohol use and follow medication instructions on the label to prevent high acid pH.

Which organ controls pH?
The lungs may seem like a strange place for controlling pH however, if we consider how CO2 is transported from the tissues (read more here ), we see that CO2 dissociates into carbonic acid. Hence, the higher the CO2 levels in the tissues, the lower the pH gets (more acidic).
What does the body like to do when it comes to pH?
When it comes to pH, your body likes to keep a tight control of the balance between acidity and alkalinity.
Why is the pH of Eg 2 higher?
The pH is higher Eg. 1 because the kidneys are retaining bicarbonate and excreting H+ to try and bring the pH back to normal.
How to determine if you have acidosis or alkylosis?
Firstly, we must deduce whether we have an Acidosis or an Alkylosis by measuring the pH. Once we have done this, we need to work out whether we have a respiratory (lungs) or a metabolic (kidney) cause and an easy way to remember this is ROME.
What organ controls the excretion and retention of bicarbonate?
The kidneys deal in acids and bases, they can excrete/retain H+ if needed and they also control the excretion/retention of bicarbonate (HCO3-).
Is alkalosis metabolic or uncompensated?
Eg. 3: High pH, Normal CO2 and High bicarbonate – This is an alkalosis, it is metabolic and it is uncompensated.
How does the respiratory system regulate pH?
The respiratory system helps regulate blood pH or acid-base status by altering the circulating concentrations of carbonic acid. CO2 and H2O can form carbonic acid in the blood, as detailed above. However, this reaction is only favored up to the point when levels of CO2 and carbonic acid form a steady-state equilibrium.
What is the pH of the body?
Throughout the body, it is ideal to maintain a neutral pH of 7.4. Several buffer systems exist to help maintain this pH in bodily fluids, especially blood, and organ systems. Ones we will consider in this section include those in the blood: 1 Proteins 2 Phosphates 3 Bicarbonate
How does carbonic anhydrase affect blood pH?
In the kidneys, carbonic anhydrase regulates blood pH as increased production of bicarbonate ions enters the bloodstream to raise pH. Too much bicarbonate ion can result in metabolic alkalosis, whereas reductions in bicarbonate ions or too much hydrogen ion can result in metabolic acidosis.
What is metabolic acidosis?
Metabolic acidosis - due to decreased renal reabsorption of bicarbonate ion, loss of bicarbonate ion (such as can occur by the intestines), or the decreased ability of the kidneys to excrete hydrogen ion. These four conditions are not mutually exclusive and can occur together.
How does the kidney regulate pH?
The kidneys primarily act to regulate pH in these bodily fluids by adjusting the amount of bicarbonate ion that results from the carbonic anhydrase reaction within the kidney. As in the blood, carbonic anhydrase converts CO2 and water to bicarbonate ion and HCL.
How does the body compensate for CO2 build up?
Once one is able to breathe again, the body will compensate by taking deeper breaths and/or increasing the rate of respiration to exhale the excess CO2 built-up , and the blood pH is allowed to return to a neutral value as this will also reduce the amount of carbonic acid in the blood.
What is the buffer system of phosphates?
Phosphate buffer system - Phosphates exist in the blood in two forms: Na2H2PO4- (a weak acid) and Na2HPO4-2 (a weak base). Na2HPO4- binds to hydrogen from HCL, which results in the formation of Na2H2PO4- and NaCl. Conversely, NaH2PO4- binds to NaOH to form Na2H2PO4- and water.
How is pH maintained in the body?
pH is maintained in the body using primarily three mechanisms: buffer systems, respiratory control, and renal control. pH Level of the Mouth & Body. Play.
Which region of the body maintains pH?
Maintaining the pH values of different regions is critical for their function. pH of the gastrointestinal tract. Esophagus, stomach, duodenum, small intestine, colon. Image Credit: Timonina / Shutterstock.
How does the renal system regulate pH?
The renal system regulates the pH of extracellular fluid. The changes in pH induced by the respiratory system are in minutes, while the changes induced by the renal system are in the order of days. If the acidity of the fluids is high, kidney secretes H+ ions, while if the carbonate ion levels are high it retains H+ ions and secretes HCO3 ions. Although this process is slow but it can prove an effective mode to regulate pH. One limitation of renal regulation is that the pH of urine cannot be below 4.4. Thus, strong acids can be removed by reacting with basic salts of phosphoric acid or by addition of base (NH3) to urine.
Why does alkalosis cause acidosis?
Acidosis and alkalosis may be caused either due to imbalance of acid-base secretion by the kidneys or altered levels of CO2 in the blood due to breathing disorders. Overview of Acid-Base Balance ( https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/hormonal-and-metabolic-disorders/acid-base-balance/overview-of-acid-base-balance) ...
Why is breathing slow during alkalosis?
On the other hand during alkalosis or increased pH, the breathing may get slow in order to increase the CO2 levels and reduce the alkalinity. However, low breathing rate could also lead to low oxygen levels which could be detrimental. Thus, respiration provides an important control to regulate the pH levels.
Why does CO2 make my blood acidic?
Thus, presence of more CO2 makes the blood more acidic. That is the reason when we hold the breath for long durations, the CO2 levels increase in the blood lowering our pH leading to fainting.
What are the two types of abnormalities in acid-base balance?
Abnormalities in Acid-Base Balance. The abnormalities in acid-base balance are of two types: acidosis and alkalosis. In acidosis, the blood pH is low or there is too much acid in the blood, while in alkalosis, the blood pH is high or there is too much base in the blood. Acidosis and alkalosis may be caused either due to imbalance ...
How does blood pH work?
Blood pH is maintained via the lungs and the kidneys. Lungs alter the amount of carbon dioxide expelled to maintain blood pH. Consider the reaction below.
What does it mean when your pH is reduced?
Decreased blood pH. Correct answer: Decreased blood pH. Explanation: Diabetic ketoacidosis is a condition that can occur in people who have diabetes. In this situation, there is a deficiency in insulin production. Consequently, the glucose that is present in the blood has no way of entering cells.
Why is blood acidic?
The energy deficit that cells experience as a result of not having access to glucose causes significant production of these acidic ketone bodies. In fact, so many of these ketone bodies are produced that it overwhelms the body's normal pH buffering capacity, and thus the blood can become dangerously acidic.
How does the body control carbon dioxide?
Body controls carbon dioxide levels via breathing. Hyperventilation refers to increased breathing whereas hypoventilation refers to decreased breathing. During hyperventilation the person breathes out excess carbon dioxide (decreasing the hydrogen ion concentration). During hypoventilation, on the other hand, a person breathes slowly and retains carbon dioxide (increasing the hydrogen ion concentration). The patient in this question has low blood pH (high hydrogen ion concentration); therefore, of the options, the patient must be hypoventilating.
Why does the body think it is energy starved?
Glucagon output is also increased because, as explained above, the body "thinks" it is energy starved due to there not being enough glucose even though there is plenty.
How does the body control the amount of hydrogen ions in the blood?
One way the body controls the amount of hydrogen ions in the blood is by altering the amount of carbon dioxide. Recall that, according to Le Chatelier’s principle, increasing carbon dioxide will push the reaction the right and increase hydrogen ion concentration whereas decreasing carbon dioxide will decrease hydrogen ion concentration.
What does low pH mean in blood?
Explanation: Low blood pH suggests that the patient has high concentration of hydrogen ions. To solve this question, we need to look at the following reaction, which represents the major blood buffer system: One way the body controls the amount of hydrogen ions in the blood is by altering the amount of carbon dioxide.
What is the pH balance of the body?
What is pH balance? Your body’s pH balance, also referred to as its acid-base balance, is the level of acids and bases in your blood at which your body functions best. The human body is built to naturally maintain a healthy balance of acidity and alkalinity. The lungs and kidneys play a key role in this process.
Why is pH important?
Your pH balance is important for your health , and you can trust that your body is equipped to maintain that balance on its own. However, if your doctor finds your balance to be off through blood and urine testing, they will do additional tests to determine the exact cause.
How do the kidneys and lungs maintain pH?
How the lungs and kidneys maintain the pH balance. The lungs control your body’s pH balance by releasing carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a slightly acidic compound. It’s also a waste product produced by cells in the body as they use oxygen. The cells release it into your blood, and it’s taken to your lungs.
How do kidneys help the body maintain pH balance?
Your brain constantly monitors this in order to maintain the proper pH balance in your body. The kidneys help the lungs maintain acid-base balance by excreting acids or bases into the blood. The kidneys’ effect on acidity works much more slowly than that of the lungs.
What happens if your blood pH is too low?
If the lungs or kidneys are malfunctioning, your blood’s pH level can become imbalanced. Disruption in your acid-base balance can lead to medical conditions known as acidosis and alkalosis. Both conditions require treatment from a medical professional, not simply dietary changes.
What are the two conditions that can lead to a blood pH imbalance?
A blood pH imbalance can lead to two conditions: acidosis and alkalosis.
What causes metabolic alkalosis?
Other conditions that can lead to metabolic alkalosis are kidney damage caused by a severe loss of fluids or ingestion of a large amount of baking soda.
Why is it important to maintain pH balance?
Because so many different factors — gut health, stress, sleep, medications and medical history — also affect how hard your body has to work to maintain its appropriate pH level, other lifestyle habits can also be helpful for restoring balance.
Why is pH important?
Most of us never consider the acid/alkaline balance of our blood, but a proper pH is a crucial aspect to overall health. Many doctors stress the importance of reducing acidity and increasing alkalinity with an alkaline diet because a balanced pH helps protect us from the inside out.
What causes pH imbalance?
The Merck Manual’s definition of acidosis is “An overproduction of acid in the blood or an excessive loss of bicarbonate from the blood (metabolic acidosis), or a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood that results from poor lung function or depressed breathing (respiratory acidosis).” ( 8)
How to maintain pH balance?
( 1) The most effective way to support a balanced pH is to eat lot of nutrient-dense, alkalizing plant foods and to limit your intake of processed foods.
What is the best diet for pH balance?
If there’s such thing as a pH balance diet, it’s one that includes lots of green plants and other alkalizing foods. It’s also smart to purchase as much organic food as possible, since crops that are grown in organic, mineral-dense soil tend to be more alkalizing and have higher vitamin and mineral content. Here are foods that are included in a well-rounded alkaline diet:
What foods are good for pH balance?
The keto diet and its foods are also supportive of pH balance include: healthy fats and oils, all types of leafy greens, powdered greens/drink mixes and superfoods. Most high protein foods are acid forming, so if you’re eating lots of meat and animal foods, it’s important to balance these with alkalizing plant foods.
What does pH balance mean?
What is the meaning of “pH balance”? Do you know if your pH levels are off? Well, pH balance refers to a proper balance in the body between acidity and alkalinity. Your body does a great job of keeping its pH balanced in most cases, but by eating an alkaline diet may help prevent unhealthy microbes and organisms from flourishing, tissues and organs from becoming damaged, minerals from being depleted, and your immune system from being compromised. Why? You’ll have to read on to find out!
How does the lungs regulate blood pH?
The lungs can help regulate blood pH rapidly through the process of exhaling carbon dioxide, sometimes producing changes within seconds. For example, when someone exercises, they produce more carbon dioxide, so they breathe faster to prevent the blood from becoming too acidic.
What happens when pH changes?
When a change happens in one direction, there are mechanisms to move the acid-base balance the other way. For example, if a person has respiratory acidosis, there should be a metabolic response from the kidneys to reset the balance. If the body does not reset the pH balance, it can lead to more severe illness.
Why does respiratory alkalosis occur?
Respiratory alkalosis often occurs due to situations or conditions that make people breathe quicker or deeper than usual . These include:
What is metabolic acidosis?
Metabolic acidosis: This occurs due to reduced bicarbonate or increased acid levels.
What does the pH of blood mean?
The pH of blood refers to how acidic it is. Changes to blood pH can signal underlying medical issues. The pH scale, otherwise known as the acid-base scale, runs from 0 to 14. It measures how acidic a solution of a substance in water is. For example, pure water has a pH of 7. Solutions with a low pH have a high concentration ...
How to find out if someone has acid or base?
Blood pH tests. There are two main types of tests that doctors can use to find out the pH of someone’s blood: arterial blood gas testing and electrolyte testing. Knowing the pH of a person’s blood can help a doctor find out if that person has an acid-base disorder.
What does it mean when your pH is suddenly changing?
A sudden change in blood pH may indicate an underlying health problem. The pH of blood in the arteries should be between 7.35 and 7.45 for the body’s metabolic processes and other systems to work well. These processes produce acids, so the body has a complex system of feedback and regulation to maintain healthy pH levels.

Ph of Different Body Fluids
Impact of Altering The Ph Balance
Maintaining The Body Ph
- pH is maintained in the body using primarily three mechanisms: buffer systems, respiratory control, and renal control.
Buffer Systems
- Proteins form a part of the buffer system to regulate the pH levels. These proteins can act as H+ acceptors or donors because of the presence of basic or acidic groups. Similarly phosphate buffers also help in moderating the levels of pH. Buffers may help in regulating pH during minor physiological changes, such as during breath holding (which increases the CO2 in the blood), ex…
Respiratory Control
- The pH of blood during normal conditions is 7.4. However, CO2 dissociates into carbonic acid in the tissues. Thus, presence of more CO2 makes the blood more acidic. That is the reason when we hold the breath for long durations, the CO2 levels increase in the blood lowering our pH leading to fainting. On the other hand during alkalosis or increased ...
Renal Control
- The renal system regulates the pH of extracellular fluid. The changes in pH induced by the respiratory system are in minutes, while the changes induced by the renal system are in the order of days. If the acidity of the fluids is high, kidney secretes H+ ions, while if the carbonate ion levels are high it retains H+ ions and secretes HCO3 ions. Although this process is slow but it can prov…
Abnormalities in Acid-Base Balance
- The abnormalities in acid-base balance are of two types: acidosis and alkalosis. In acidosis, the blood pH is low or there is too much acid in the blood, while in alkalosis, the blood pH is high or there is too much base in the blood. Acidosis and alkalosis may be caused either due to imbalance of acid-base secretion by the kidneys or altered levels of CO2 in the blood due to brea…
Further Reading