Which enzymes break down proteins?
- Diastases: Break down starch into maltose
- Amylases: Break down starch into sugars like glucose and maltose
- Invertases: Break down sucrose, a type of sugar, into glucose and fructose
- Proteases: Break down proteins into amino acids
What is proteins function to break down other proteins?
Proteins that are intact and folded correctly will not be broken down, essentially acting as a cellular quality control function. Proteolysis is a key component of nutrient digestion, breaking down any protein ingested so that the nutrients are available to be taken up by the organism. In this process the proteins are completely broken down ...
What combines amino acids to make proteins?
• Amino acids are linked together by ‘amide groups’ called peptide bonds. • During protein synthesis, the carboxyl group of amino acid at the end of the growing polypeptide chain reacts with the amino group of an incoming amino acid, releasing a molecule of water. The resulting bond between the amino acids is a peptide bond.
Does trypsin break down proteins?
Trypsin is an enzyme that helps us digest protein. In the small intestine, trypsin breaks down proteins, continuing the process of digestion that began in the stomach. It may also be referred to as a proteolytic enzyme, or proteinase. Trypsin is produced by the pancreas in an inactive form called trypsinogen.

Are all proteins broken down into amino acids?
Because amino acids are building blocks that the body reserves in order to synthesize other proteins, more than 90 percent of the protein ingested does not get broken down further than the amino acid monomers.
What splits proteins into amino acids?
proteaseproteolytic enzyme, also called protease, proteinase, or peptidase, any of a group of enzymes that break the long chainlike molecules of proteins into shorter fragments (peptides) and eventually into their components, amino acids.
How are proteins broken down?
During digestion, proteins are broken down into amino acids through hydrolysis. The amino acids dissolve in our blood and are carried to tissues and organs. There, the amino acids are either used as a source of energy or are assembled into proteins through condensation polymerization.
What enzyme is used to break down protein?
Of these five components, pepsin is the principal enzyme involved in protein digestion. It breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids that can be easily absorbed in the small intestine.
What is the process of breaking down proteins called?
Introduction. Protein catabolism is the breakdown of proteins into absorbable monomers for further degradation or reassembly. Protein catabolism in the intestinal lumen is important for several reasons, one of which is mobilizing essential amino acids for absorption.
What are enzymes that break down substances called?
There are three main types of digestive enzymes: Proteases: Break down protein into small peptides and amino acids. Lipases: Break down fat into three fatty acids plus a glycerol molecule. Amylases: Break down carbs like starch into simple sugars.
How does protein get metabolized?
Protein is digested and broken down to amino acids which are absorbed into the circulation and taken to cells throughout the body, primarily the liver and quickly become combined by peptide linkages. The plasma level of amino acids is tightly controlled and maintained near a constant level.
What is the process of protein metabolism?
Protein metabolism involves the synthesis of proteins and amino acids, i.e. anabolism and breakdown of proteins into amino acids, i.e. catabolism. Proteins are synthesised by ribosomes using the mRNA template in the translation process followed by post-translational modifications.
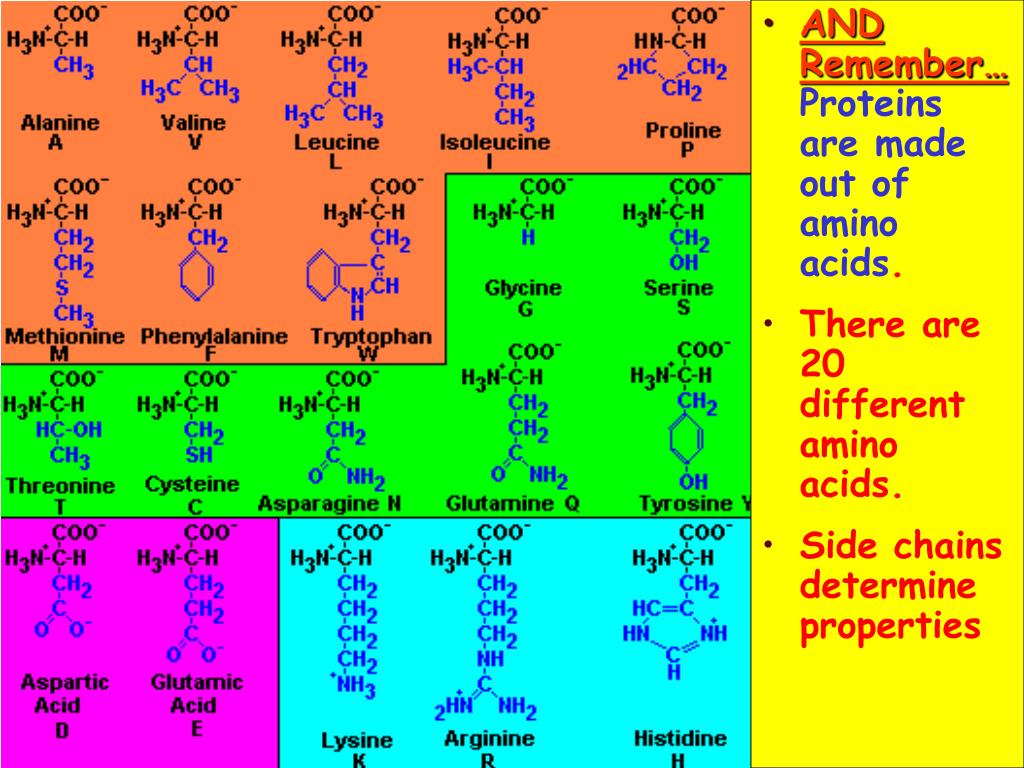
How many amino acids are in a protein?
All proteins are made up of different arrangements of the same 20 amino acids. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a variable “R” group ( Figure 3.5).
How are polymers broken down?
Polymers are broken down into monomers in a process known as hydrolysis, which means “to split water.”. ( Figure 3.3 ). During these reactions, the polymer is broken into two components: one part gains a hydrogen atom (H+) and the other gains a hydroxyl molecule (OH–) from a split water molecule.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
The same 20 common amino acids are present in proteins from all species of life. Ten of these are considered essential amino acids in humans because the human body cannot produce them and they must be obtained from the diet. Each amino acid differs only in the R group (or side chain). The chemical nature of the R group determines the nature of the amino acid (that is, whether it is acidic, basic, polar, or nonpolar). For example, amino acids such as valine, methionine, and alanine are nonpolar or hydrophobic in nature, while amino acids such as serine, threonine, and cysteine are polar and have hydrophilic side chains. The side chains of lysine and arginine are positively charged, while the side chains of aspartate and glutamate are negatively charged. ( Figure 3.6 ).
What are macromolecules made of?
Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. This type of reaction is known as dehydration synthesis (also known as condensation ), which means “to make while losing water.”
How is water formed in dehydration?
In a dehydration synthesis reaction, the hydrogen of one monomer combines with the hydroxyl group of another monomer, releasing a molecule of water ( Figure 3.2 ). At the same time, the monomers share electrons and form covalent bonds.
What are the structures of a cell?
Each cell in a living system may contain thousands of proteins, each with a unique function. Their structures, like their functions, vary greatly. Structural proteins make up the cytoskeleton inside cells and the scaffold outside of cells. They include the keratin of our skin and the collagen of our connective tissue.
What enzyme breaks down carbohydrates?
Each macromolecule is broken down by a specific enzyme. For instance, carbohydrates are broken down by amylase, sucrase, lactase, or maltase. Proteins are broken down by the enzymes pepsin and peptidase, and by hydrochloric acid.
