How the Brain Works. Some of the nerves in the brain go right to the eyes, ears and other parts of the head. Other nerves connect the brain with other parts of the body through the spinal cord to control personality, senses and body functions from breathing to walking. Together, the brain, spinal cord and nerves form the central nervous system.
What are three things your nervous system does?
The nervous system is responsible for: Intelligence, learning and memory: your thoughts and feelings are controlled by the brain, the control centre of the nervous system. Movement: the brain sends messages that control how your body moves.
Does the nervous system control everything?
Your nervous system guides almost everything you do, think, say or feel. It controls complicated processes like movement, thought and memory. It also plays an essential role in the things your body does without thinking, such as breathing, blushing and blinking.
How fast do nerves regenerate?
When the nerve has had a rest period of 4 weeks, the healing process begins and the nerve regenerates 1 mm/day. Since sensory nerves heal faster, full regeneration and recovery is expected to be within a year. Motor nerves are a bit tricky in this matter.
What are the main parts of the nervous system?
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves attached to the brain:
- Olfactory nerves, which are sensory nerves, related to the sense of smell.
- Optic nerves, which are sensory nerves, related to the sense of sight.
- Oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nerves, which are motor nerves, responsible for regulating voluntary eye movements.

How the brain works simple explanation?
Your brain contains billions of nerve cells arranged in patterns that coordinate thought, emotion, behavior, movement and sensation. A complicated highway system of nerves connects your brain to the rest of your body, so communication can occur in split seconds.
What protects the brain in the nervous system?
The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and by a covering of three thin membranes called meninges. The brain is also cushioned and protected by cerebrospinal fluid. This watery fluid is produced by special cells in the four hollow spaces in the brain, called ventricles.
Why is the brain considered as the most complex part of the nervous system?
The brain is the most complex part of the human body. It is the center of consciousness and also controls all voluntary and involuntary movement and bodily functions. It communicates with each part of the body through the nervous system, a network of channels that carry electrochemical signals.
What 4 Things protect the brain?
12.2: Support and Protection of the BrainDura Mater.Arachnoid Mater.Pia Mater.
What are the 4 main functions of the nervous system?
The four main functions of the nervous system are:Control of body's internal environment to maintain 'homeostasis' An example of this is the regulation of body temperature. ... Programming of spinal cord reflexes. An example of this is the stretch reflex. ... Memory and learning. ... Voluntary control of movement.
How does the brain communicate with the body?
The brain is the body's control centre: it sends messages to your body through a network of nerves called “the nervous system”, which controls your muscles, so that you can walk, run and move around.
Does the brain have nerves?
The brain has no nociceptors – the nerves that detect damage or threat of damage to our body and signal this to the spinal cord and brain. This has led to the belief that the brain feels no pain. A belief that has entered popular culture.
How many nerves are in the human brain?
How many cranial nerves are there? You have 12 cranial nerve pairs. Each nerve pair splits to serve the two sides of your brain and body.
Which bones protect the brain?
The skull protects the brain and forms the shape of the face. The spinal cord, a pathway for messages between the brain and the body, is protected by the backbone, or spinal column.
How is the brain protected and nourished?
They're both cushioned by layers of membranes (called meninges) and cerebrospinal fluid. The fluid flows through hollow spaces in the brain called ventricles and around the spine in the spinal column. It protects the central nervous system, nourishes it, and takes away waste products.
How the brain is protected from shocks and jerks?
Brain is protected from shocks and jerks by the cerebrospinal fluid. It acts like a cushion and protects the brain. It is present between the spaces in the inner layers of the meninges.
What keeps harmful substances away from the brain?
A network of blood vessels and tissue that is made up of closely spaced cells and helps keep harmful substances from reaching the brain. The blood-brain barrier lets some substances, such as water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and general anesthetics, pass into the brain.
How does the nervous system develop?
Interestingly, a person’s unique nervous system develops over the course of their lifespan in a way that resembles the evolution of nervous systems in animals across vast stretches of time. For example, the human nervous system begins developing even before a person is born. It begins as a simple bundle of tissue that forms into a tube and extends along the head-to-tail plane becoming the spinal cord and brain. 25 days into its development, the embryo has a distinct spinal cord, as well as hindbrain, midbrain and forebrain ( Stiles & Jernigan, 2010 ). What, exactly, is this nervous system that is developing and what does it do?
Why is it important to understand the nervous system?
It is through the nervous system that we experience pleasure and pain, feel emotions, learn and use language, and plan goals, just to name a few examples.
How do neurons communicate?
Neurons communicate with one another by receiving information through the dendrites, which act as an antenna. When the dendrites channel this information to the soma, or cell body, it builds up as an electro-chemical signal. This electrical part of the signal, called an action potential shoots down the axon, a long tail that leads away from the soma and toward the next neuron. When people talk about “nerves” in the nervous system, it typically refers to bundles of axons that form long neural wires along which electrical signals can travel. Cell-to-cell communication is helped by the fact that the axon is covered by a myelin sheath —a layer of fatty cells that allow the signal to travel very rapidly from neuron to neuron ( Kandel, Schwartz & Jessell, 2000)
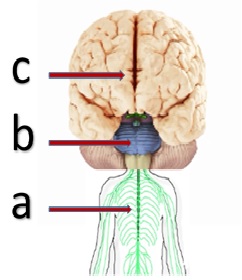
What is the central nervous system?
The Central Nervous System, or CNS for short, is made up of the brain and spinal cord (see Figure 1). The CNS is the portion of the nervous system that is encased in bone (the brain is protected by the skull and the spinal cord is protected by the spinal column). It is referred to as “central” because it is the brain and spinal cord that are primarily responsible for processing sensory information—touching a hot stove or seeing a rainbow, for example—and sending signals to the peripheral nervous system for action. It communicates largely by sending electrical signals through individual nerve cells that make up the fundamental building blocks of the nervous system, called neurons. There are approximately 86 billion neurons in the human brain and each has many contacts with other neurons, called synapses ( Herculano-Houzel, 2009 ).
What is the brain study?
This means that humans are uniquely capable of using our most sophisticated organ to understand our most sophisticated organ. Breakthroughs in the study of the brain and nervous system are among the most exciting discoveries in all of psychology. In the future, research linking neural activity to complex, real world attitudes and behavior will help us to understand human psychology and better intervene in it to help people.
Why is the central nervous system called the central nervous system?
It is referred to as “central” because it is the brain and spinal cord that are primarily responsible for processing sensory information— touching a hot stove or seeing a rainbow, for example—and sending signals to the peripheral nervous system for action.
Which part of the brain is the limbic system?
Collectively, the limbic system is a term that doesn’t have clearly defined areas as it includes forebrain regions as well as hindbrain regions. These include the amygdala, the thalamus, the hippocampus, the insula cortex, the anterior cingulate cortex, and the prefrontal cortex.
What is the central nervous system?
The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The brain lies within the skull and governs body functions by sending and receiving messages through the spinal cord . Protecting the brain and spinal cord are bones, layers of tissue, and cerebrospinal fluid. Once messages leave the central nervous system, ...
Which system sends messages to the central nervous system?
Once messages leave the central nervous system, they are carried by the peripheral nervous system . The peripheral system includes the cranial nerves (nerves branching from the brain) and the spinal nerves (nerves branching from the spinal cord). These nerves convey sensory messages from receptor cells in the body to the central nervous system.
What is the basic element of the nervous system?
The basic element of the nervous system is the nerve cell, or neuron. In combination, neurons form nerves, fibers that transmit impulses throughout the body. A protective covering of myelin, a fatty substance, insulates parts of the fibers.
What is the action of nerve cells?
The action of nerve cells is both electrical and chemical. At the ends of each nerve cell there are specialized regions called synaptic terminals, which contain large numbers of tiny membranous sacs that hold neurotransmitter chemicals. These chemicals transmit nerve impulses from one nerve cell to another.
What is the control center of the body?
The brain is the body's control center. The brain sends messages to and receives stimulation from all parts of the body. More than 10 billion interlinked brain cells regulate the functioning of the body during sleep and wakefulness.
Where does CSF go in the brain?
It then passes into the space between the innermost and second layers of the tissue covering the brain, bathing the entire outer surface of the brain in fluid before passing downward around the spinal cord.
Which system sends messages to the body?
Once messages leave the central nervous system, they are carried by the peripheral nervous system . The peripheral system includes the cranial nerves (nerves branching from the brain) and the spinal nerves (nerves branching from the spinal cord). These nerves convey sensory messages from receptor cells in the body to the central nervous system. They also transport motor impulses from the central system out to the body, where muscles and glands can respond to the impulses.
How do neurons work?
Each neuron is made up of three main parts: the cell body (also known as the soma), the axon, and the dendrites. Neurons communicate with each other using electrochemical signals. In other words, certain chemicals in the body known as ions have an electrical charge. Ions move in and out of the neuron across the cell membrane and affect the electrical charge of the neuron.
Why does the brain change?
The brain continues to change and grow throughout your lifetime because the connections between neurons are plastic. In other words, your brain can add new connections or subtract unused ones. As you grow up, your experiences and environment help your brain decide which connections are important and useful. In addition to your experiences, genetic information also influences your brain’s development. Although it is very complicated to tease apart what is inherited and what is learned, many behaviors appear to be a combination of both genetic and environmental factors
What happens when a neuron is at rest?
When a neuron is at rest, the cell body, or soma, of the neuron is negatively charged relative to the outside of the neuron. A neuron at rest has a negative charge of approximately -70 millivolts (mV) of electricity. However, when a stimulus comes along (like stubbing your toe, or hearing your name being called), it causes the neuron to take in more positive ions, and the neuron becomes more positively charged. Once the neuron reaches a certain threshold of approximately -55mV, an event known as an action potential occurs and causes the neuron to “fire.” The action potential travels down the axon where it reaches the axon terminal.
What is the transmission of information from neuron to neuron?
The transmission of information from neuron to neuron, and between networks of neurons, gives rise to everything from thinking to playing sports, solving problems, and even dreaming. Neurons in the human brain and spinal cord are organized into the central and peripheral nervous systems. The central nervous system is organized into different ...
How are neurotransmitters different from ions?
How is the brain organized? Neurotransmitters are different from ions, because instead of directly affecting the charge of the neurons, neurotransmitters communicate by activating a receptor. In other words, the neurotransmitter is like a key and the receptor is the lock.
What is the peripheral nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system is comprised of sensory and motor neurons throughout the rest of your body. The sensory neurons collect information from the outside world through the five senses, while the motor neurons allow you to move and respond to signals from the brain and spinal cord.
How many neurons are there in the human brain?
With 80-100 billion nerve cells, known as neurons, the human brain is capable of some astonishing feats. Each neuron is connected to more than 1,000 other neurons, making the total number of connections in the brain around 60 trillion!
How does the nervous system take in information?
The nervous system takes in information through our senses, processes the information and triggers reactions, such as making your muscles move or causing you to feel pain. For example, if you touch a hot plate, you reflexively pull back your hand and your nerves simultaneously send pain signals to your brain.
Which nervous system prepares the body for physical and mental activity?
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems usually do opposite things in the body. The sympathetic nervous system prepares your body for physical and mental activity.
Why does the parasympathetic nervous system help us?
The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for bodily functions when we are at rest: it stimulates digestion, activates various metabolic processes and helps us to relax.
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is made up of all the nerve cells in your body. It is through the nervous system that we communicate with the outside world and, at the same time, many mechanisms inside our body are controlled. The nervous system takes in information through our senses, processes the information and triggers reactions, ...
What is the function of dendrites in neuron?
Each neuron has a cell body and various extensions. The shorter extensions (called dendrites) act like antennae: they receive signals from, for example, other neurons and pass them on to the cell body. The signals are then passed on via a long extension (the axon), which can be up to a meter long.
Which nervous system regulates bowel motility?
The enteric nervous system is a separate nervous system for the bowel, which, to a great extent, autonomously regulates bowel motility in digestion.
Which system controls the movement of the body?
The voluntary nervous system (somatic nervous system) controls all the things that we are aware of and can consciously influence, such as moving our arms, legs and other parts of the body. The involuntary nervous system (vegetative or autonomic nervous system) regulates the processes in the body that we cannot consciously influence.
How does the nervous system work?
The rest of the nervous system is like a network that relays messages back and forth from the brain to different parts of the body. It does this via the spinal cord, which runs from the brain down through the back. It contains threadlike nerves that branch out to every organ and body part.
What Does the Brain Do?
The brain controls what we think and feel, how we learn and remember, and the way we move and talk. But it also controls things we're less aware of — like the beating of our hearts and the digestion of our food.
What Are the Parts of the Nervous System?
The nervous system is made up of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system:
What Are the Parts of the Brain?
The brain is made up of three main sections: the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain.
What is the brain stem made of?
At the base of the brain, the brain stem connects to the spinal cord and is made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. The midbrain acts like a complex switchboard, allowing the brain to communicate with the rest of the nervous system.
How much does the brain weigh?
The human brain is incredibly compact, weighing just 3 pounds. It has many folds and grooves, though. These give it the added surface area needed for storing the body's important information. The spinal cord is a long bundle of nerve tissue about 18 inches long and 1/2-inch thick.
Which part of the brain controls movement?
The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum has two hemispheres (or halves). The cerebrum controls voluntary movement, speech, intelligence, memory, emotion, and sensory processing. Print this slide. The Brain and Nervous System. Brain Stem.
How do the different brain sections connect with each other?
So, a logical question to ask is how do the different brain sections connect with each other / work with each other? How do basic nervous system ‘inputs’ become conscious thought? The answer is that each of the main sections of the brain communicate with the other sections in such a way that could be compared to that of a computer network, with the brain having a small number of “control nodes” that communicate with each other. This can all be combined to describe the most current theory of how overall thought processing occurs in the brain. Essentially, the brain processes information in a hierarchical fashion, meaning that sensory information is processed by a part of the brain with the result being passed to a “node” which is then processed by another part of the brain – with this process continuing throughout the nodes in the brain until it reaches the section (s) where it can be consciously perceived by the person. It is at this time that a “final conscious decision” is made and the responses can be generated. Note that these brain nodes communicate information in a pattern which is common to each of us (hence why they are called, “common codes”).
How do photons work?
In recent years, a growing body of evidence shows that photons play an important role in the basic functioning of cells . It turns out that many cells emit light as they work, and use this to communicate. Here is an article that supports the idea that neurons in our brains are capable of producing photons (bio-photons). It is believed that photons are conducted through microtubles, which are the internal scaffolding inside the cells that provide structural support and allow the movement of cellular material. Bio-photons appear within the visible spectrum, from near-infrared through violet. Bio-photons are created during the electrical activity of the brain, and it is now believed that they are used to help co-ordinate activities in different parts of the brain (another article here ).
Where is the thalamus located?
The thalamus is located in the middle and on both sides of the brain and acts as a relay station between the different parts of the brain, processing sensory inputs (such as vision, touch, and hearing), and is also involved in directing the focus of our attention (screening out distracting stimuli). Eventually, all processing is passed over to the cerebral cortex, which is connected to the spinal cord – so that they body can produce a reaction to all of the stimulus (inputs). Most people become conscious of their thoughts at the same ‘point’ in the brain (more detail to follow). It is interesting to note that the brain considers a number of inputs when making a decision, even those that we are not consciously aware of! For instance the act of hearing is a combined effort that includes the ears, the eyes, and the skin! (second article here ). On a bit of a side note – it is interesting that people interpret the act of thinking as listening to their ‘inner-voice’ or via imagery.
Is the brain still not well understood?
In the public eye the brain is still not very well understood, and through my research I’ve noticed that government and private funded research is far more advanced than the general public is aware. The body generates electrical signals, and uses them as a basis for ‘inner-body’ communications (a way for organs to communicate with the brain). If you had a lot of time, I’d suggest you read “ The Body Electric ” by Robert Becker and Gary Selden. The book outlines how cells, the nervous system, and the brain work electrically.
How does the nervous system work?
The nervous system works through an interconnected network of billions of neurons. These neurons transmit information in the form of nerve impulses, across the nervous system and thus, coordinate the various functions of the body.
What is the human nervous system?
The human nervous system is a highly specialized network, that contains billions of neurons, and is responsible for controlling and coordinating all the functions of the body. This system enables us to communicate with the outside world and it consists of two components, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
How many neurons are there in the nervous system?
The human nervous system contains billions of nerve cells and about 86 billion of them are found in the brain alone. Each neuron has a cell body, from where numerous branch-like projections emerge, which are known as dendrites. The dendrites usually look like the branches of a tree. At the opposite end of the cell body, a long, slender projection can be found, which is known as axon. The dendrites pick up impulses in the form of electrical signals from other neurons, which are then passed down the axon to another neuron or cell.
What are the cells that support the nervous system?
Apart from neurons, the nervous system also contain glial cell s, which support and nourish the neurons. The neurons use electrochemical signals, or neurotransmitters for transmitting impulses from one neuron to another. However, the transmission of impulses from one neuron to another is not as simple as it sounds.
How fast can the nervous system transmit impulses?
The nervous system can transmit impulses at the speed of 100 meters per second, and the transmission of impulses across electrical synapses is much faster and energy efficient than chemical synapses. But, the impulses get weaker as they travel from one neuron to another through electrical synapses. On the other hand, chemical signaling is ...
Which part of the brain processes sensory signals?
The sensory neurons transmit the stimuli or impulses received from the sensory organs, like the eyes, nose or skin, to the central nervous system, i.e., to the brain and the spinal cord. The brain in turn, processes these stimuli and sends them back to other parts of the body, telling them how to react to a particular type of stimulus. The motor neurons are responsible for receiving signals from the brain and spinal cord, and sending them to other parts of the body.
What are the parts of the brain?
The human brain can be divided into three parts, forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain .

Mechanism
- The brain is the most complex part of the human body. It is the center of consciousness and also controls all voluntary and involuntary movement and bodily functions. It communicates with each part of the body through the nervous system, a network of channels that carry electrochemical signals.
Research
- In the 1800s a German scientist by the name of Ernst Weber conducted several experiments meant to investigate how people perceive the world via their own bodies (Hernstein & Boring, 1966). It is obvious that we use our sensory organsour eyes, and ears, and noseto take in and understand the world around us. Weber was particularly interested in the sense of touch. Using …
Introduction
- It is worth mentioning here, at the start, that an introduction to the biological aspects of psychology can be both the most interesting and most frustrating of all topics for new students of psychology. This is, in large part, due to the fact that there is so much new information to learn and new vocabulary associated with all the various parts of the brain and nervous system. In fac…
Evolution
- As a species, humans have evolved a complex nervous system and brain over millions of years. Comparisons of our nervous systems with those of other animals, such as chimpanzees, show some similarities (Darwin, 1859). Researchers can also use fossils to study the relationship between brain volume and human behavior over the course of evolutionary history. Homo habili…
Example
- If we were to zoom in still further we could take a closer look at the synapse, the space between neurons (see Figure 3). Here, we would see that there is a space between neurons, called the synaptic gap. To give you a sense of scale we can compare the synaptic gap to the thickness of a dime, the thinnest of all American coins (about 1.35 mm). You could stack approximately 70,00…
Quotes
- It is amazing to realize that when you thinkwhen you reach out to grab a glass of water, when you realize that your best friend is happy, when you try to remember the name of the parts of a neuronwhat you are experiencing is actually electro-chemical impulses shooting between nerves!
Structure
- It is helpful to examine the various parts of the brain and to understand their unique functions to get a better sense of the role the brain plays. We will start by looking at very general areas of the brain and then we will zoom in and look at more specific parts. Anatomists and neuroscientists often divide the brain into portions based on the location and function of various brain parts. Am…
Function
- The brain stem is the most basic structure of the brain and is located at the top of the spine and bottom of the brain. It is sometimes considered the oldest part of the brain because we can see similar structures in other, less evolved animals such as crocodiles. It is in charge of a wide range of very basic life support functions for the human body including breathing, digestion, and the be…
Definition
- The cerebellum is a structure at the very back of the brain. Aristotle referred to it as the small brain based on its appearance and it is principally involved with movement and posture although it is also associated with a variety of other thinking processes. The cerebellum, like the brain stem, coordinates actions without the need for any conscious awareness.
Causes
- In addition to the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) there is also a complex network of nerves that travel to every part of the body. This is called the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and it carries the signals necessary for the body to survive (see Figure 7). Some of the signals carried by the PNS are related to voluntary actions. If you want to type a message to …
Pathophysiology
- The brain is difficult to study because it is housed inside the thick bone of the skull. Whats more, it is difficult to access the brain without hurting or killing the owner of the brain. As a result, many of the earliest studies of the brain (and indeed this is still true today) focused on unfortunate people who happened to have damage to some particular area of their brain. For instance, in the 1880s …
Other animals
- An alternative to examining the brains or behaviors of humans with brain damage or surgical lesions can be found in the instance of animals. Some researchers examine the brains of other animals such as rats, dogs and monkeys. Although animals brains differ from human brains in both size and structure there are many similarities as well. The use of animals for study can yiel…
Diagnosis
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) records metabolic activity in the brain by detecting the amount of radioactive substances, which are injected into a persons bloodstream, the brain is consuming. This technique allows us to see how much an individual uses a particular part of the brain while at rest, or not performing a task. Another technique, known as Functional Magnetic R…