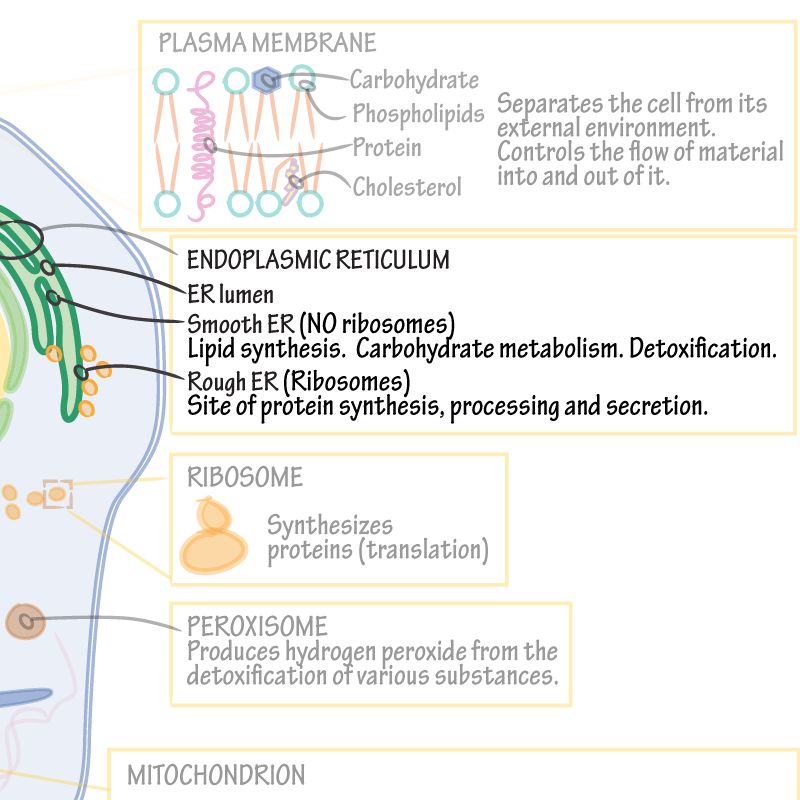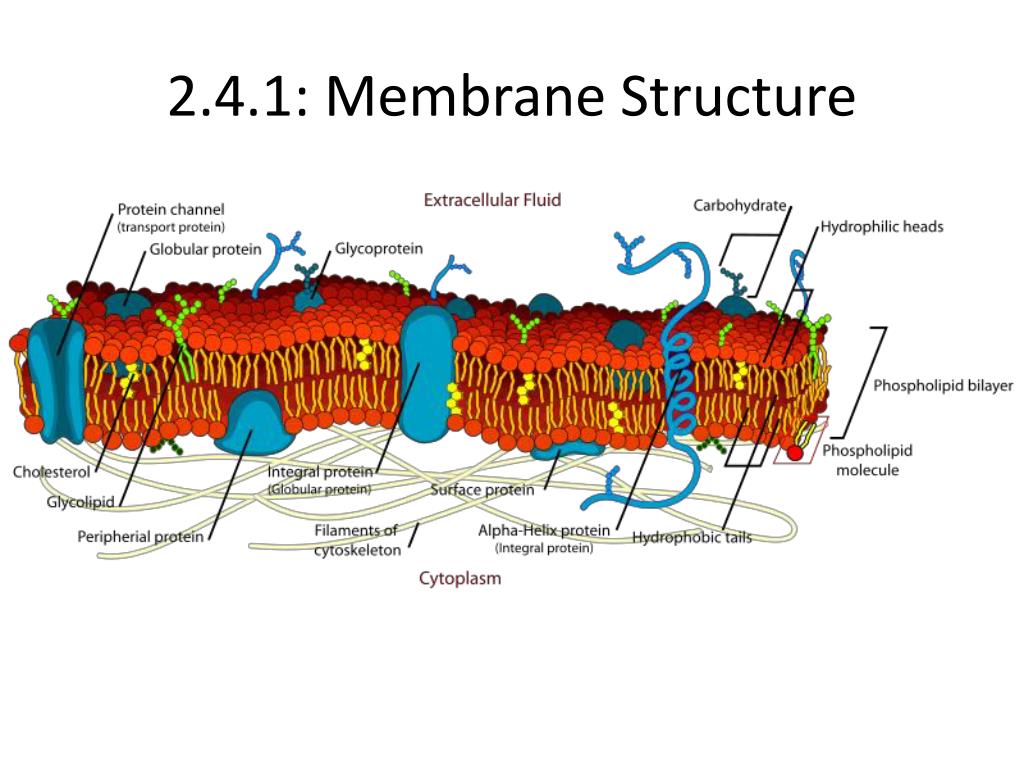
Phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids that are a major component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. The structure of the phospholipid molecule generally consists of two hydrophobic fatty acid "tails" and a hydrophilic "head" consisti…
What are the primary functions of phospholipids?
What Are the Primary Functions of Phospholipids?. Phospholipids are molecules comprised of a water-loving phosphate head and a water-repellent lipid tail. This amphiphilic nature yields the formation of phospholipid bilayers. Phospholipid bilayers provide structure and stability to cellular membranes while maintaining dynamic cellular processes.
How do phospholipids benefit you?
Phospholipids. Phospholipids are essential in the body. In the most basic sense they are fat molecules. They are found in every cell in the human body and are a necessary building block. They form the cell membranes that allow nutrients to pass into the cells. EPA and DHA, the omega 3 fatty acids, are not absorbable by the human body in pure form.
What are phospholipids and why should you care?
Properties Of Phospholipids
- They are signal mediators.
- They are amphipathic molecules.
- They anchor proteins within the cell membranes.
- They are the major constituents of cell membranes.
- They are the components of bile and lipoproteins.
What are the health benefits of phospholipids?
What are the potential benefits of phospholipids?
- Protection of the gastrointestinal mucosa. ...
- Supporting cell membrane structure and function. ...
- Supplying choline for acetylcholine (ACh) PC is an excellent source of choline for the neurotransmitter ACh. ...
- Prostaglandin production. ...
- Emulsification of fat and bile. ...
- Increasing cholesterol solubility. ...

How do phospholipids maintain cell membranes?
Phospholipids spontaneously form stable bilayers, with their polar head groups exposed to water and their hydrophobic tails buried in the interior of the membrane. Lipids constitute approximately 50% of the mass of most cell membranes, although this proportion varies depending on the type of membrane.
How the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids help to maintain the structure of cell membranes?
Cell membranes are made up of a double layer of these phospholipid molecules. This is because in water the hydrophilic heads will face the water while the hydrophobic tails will be in the center because they face away from the water. The phospholipid bilayer makes the membrane very stable but also allows flexibility.
How do the properties of phospholipids related to their function?
Phospholipids consist of a hydrophilic (or 'water loving') head and a hydrophobic (or 'water fearing') tail. Phospholipids like to line up and arrange themselves into two parallel layers, called a phospholipid bilayer. This layer makes up your cell membranes and is critical to a cell's ability to function.
How the amphipathic properties of phospholipids play a role in membrane structure?
The phosphate group on the phospholipid head is charged making it hydrophilic. This amphipathic nature allows for the bi- layer to form with the hydrophobic tails turning inwards away from the aqueous environment of the inside and outside of the cell with the hydrophilic phosphate head being in contact with the water.
How phospholipids maintain fluidity of the cell membrane?
If saturated fatty acids are compressed by decreasing temperatures, they press in on each other, making a dense and fairly rigid membrane. If unsaturated fatty acids are compressed, the “kinks” in their tails push adjacent phospholipid molecules away, which helps maintain fluidity in the membrane.
Which characteristic of a phospholipid contributes to the fluidity of the membrane?
Double bonds in fatty acid tail. So cholesterol does provide fluidity, but the answer is actually D because the double bonds and the fatty acid tails contribute the most the fluidity of the membrane because it's a hydrocarbon tail, so it's got carbons with hydrogen bonded to it.
What are the properties of phospholipids?
Properties of the Phospholipid Bilayer: The bilayer is held together by weak hydrophobic interactions between the tails. Hydrophilic / hydrophobic layers restrict the passage of many substances. Individual phospholipids can move within the bilayer, allowing for membrane fluidity and flexibility.
Why are phospholipids important for cells?
Phospholipids are natural, integral parts of cells. They are structural components of cell surface membranes and the membranes within the cells, because they help maintain their strength, flexibility, and integrity.
Why are phospholipids so important to living cells?
Phospholipids provide barriers in cellular membranes to protect the cell, and they make barriers for the organelles within those cells. Phospholipids work to provide pathways for various substances across membranes.
What is a property of phospholipids that explains why lipids self assemble into a bilayer?
Phospholipids have the ability to spontaneously form complex structures such as lipid bilayers. What is a property of phospholipids that explains why lipids self-assemble into a bilayer? 1. The hydrophobic tails of lipids are buried in the membrane and are pointed toward each other.
Which property of phospholipid molecules helps them to form bilayers in water?
amphipathic propertiesPhospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules. Membrane proteins are diverse in terms of structure, position in the membrane and function. Cholesterol is a component of animal cell membranes.
Why does the cell membrane have hydrophobic and hydrophilic characteristics?
This is because they are two-faced molecules, with hydrophilic (water-loving) phosphate heads and hydrophobic (water-fearing) hydrocarbon tails of fatty acids. In water, these molecules spontaneously align — with their heads facing outward and their tails lining up in the bilayer's interior.
Why are phospholipids hydrophilic and hydrophobic?
1: A phospholipid consists of a head and a tail. The "head" of the molecule contains the phosphate group and is hydrophilic, meaning that it will dissolve in water. The "tail" of the molecule is made up of two fatty acids, which are hydrophobic and do not dissolve in water.
How do hydrophobic tails contribute to the stability of the plasma membrane?
The fatty acid, hydrocarbon tails are non-polar and are hydrophobic so face inwards to the centre of the membrane. Due to the interactions between the hydrophobic tails in the centre and between the hydrophilic heads and water on the outside, it creates a very stable membrane.
What is are the major roles of the phospholipid bilayer in the cellular membrane?
Phospholipid bilayers are critical components of cell membranes. The lipid bilayer acts as a barrier to the passage of molecules and ions into and out of the cell. However, an important function of the cell membrane is to allow selective passage of certain substances into and out of cells.
What are phospholipids made of?
Phospholipid molecules make up the cell membrane and are hydrophilic (attracted to water) as well as hydrophobic (not attracted to water but are attracted to other hydrophobic tails). They have a hydrophilic phosphate head and two hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails. Cell membranes are made up of a double layer of these phospholipid molecules. This is because in water the hydrophilic heads will face the water while the hydrophobic tails will be in the center because they face away from the water. The phospholipid bilayer makes the membrane very stable but also allows flexibility. The phospholipid in the membrane are in a fluid state which allows the cell to change it's shape easily.
What is found in animal cell membranes and functions to improve stability and reduce fluidity?
2. Cholesterol - Found in animal cell membranes and functions to improve stability and reduce fluidity
How is the bilayer held together?
1. The bilayer is held together by weak hydrophobic interactions between the tails
Why are phospholipids classified as amphipathic?
3. Because phospholipids contain both hydrophilic (water-loving) and lipophilic (fat-loving) regions, they are classed as amphipathic
Which bilayer is viscous?
1. Fluid - the phospholipid bilayer is viscous and individual phospholipids can move position
What property does the squid use to self-organize?
They use the emergent property , which allows them to self-organize their heads to stay wet and their tails to stay dry.
Do membrane proteins move?
It showed that membrane proteins are free to move within the membrane rather that be fixed in a peripheral layer.
Why do phospholipids form cell membranes?
Phospholipids are able to form cell membranes because the phosphate group head is hydrophilic (water-loving) while the fatty acid tails are hydrophobic (water-hating). They automatically arrange themselves in a certain pattern in water because of these properties, and form cell membranes. To form membranes, phospholipids line up next ...
What are the functions of phospholipids?
Functions of Phospholipids. As membrane components, phospholipids are selectively permeable (also called semi-permeable), meaning that only certain molecules can pass through them to enter or exit the cell. Molecules that dissolve in fat can pass through easily, while molecules that dissolve in water cannot. Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and urea are ...
What is the difference between hydrophobic and lipid bilayer?
Hydrophobic – a molecule that “hates water”; it is not attracted to water, but will usually dissolve in oils or fats. Lipid bilayer – a double layer of phospholipids that makes up the cell membrane and other membranes, like the nuclear envelope and the outside of mitochondria.
What is the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope, a membrane surrounding a cell’s nucleus, is also made up of phospholipids arranged in a lipid bilayer, as is the membrane of mitochondria, the part of the cell that produces energy. This figure depicts the lipid bilayer and the structure of a phospholipid:
What are phosphates made of?
Fatty acids are long chains that are mostly made up of hydrogen and carbon, while phosphate groups consist of a phosphorus molecule with four oxygen molecules attached. These two components of the phospholipid are connected via a third molecule, glycerol. Phospholipids are able to form cell membranes because the phosphate group head is hydrophilic ...
What is a phospholipid?
Phospholipid Definition. A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane. Lipids are molecules that include fats, waxes, and some vitamins, among others. Each phospholipid is made up of two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a glycerol molecule. When many phospholipids line up, ...
What is the double layer of the cell membrane?
In this way, a double layer is formed with phosphate group heads on the outside, and fatty acid tails on the inside. This double layer, called a lipid bilayer, forms the main part of the cell membrane. The nuclear envelope, a membrane surrounding a cell’s nucleus, is also made up of phospholipids arranged in a lipid bilayer, ...
What are the molecules in the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is comprised of molecules with a phosphate head and hydrocarbon tail. The phosphate heads are polar, therfore they are hydrophilic and form favourable interactions with water, so line the outside of the membrane. The fatty acid, hydrocarbon tails are non-polar and are hydrophobic so face inwards to the centre of the membrane.
Why is the hydrophobic tail of a membrane stable?
Due to the interactions between the hydrophobic tails in the centre and between the hydrophilic heads and water on the outside, it creates a very stable membrane.