
The Hudson Bay - Arctic Lowlands
- It is typically split into two sub-regions: The Hudson Bay Lowlands and Arctic Lowlands
- It is located more specifically in Ontario, Quebec, Manitoba, Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut
- This region formed in the Paleozoic Era, when the enormous weight of a glacier sunk the Canadian Shield and the area became lowlands when the glaciers retreated
How were the Hudson Bay-Artic lowlands formed?
The Hudson Bay - Artic Lowlands were formed during the last ice age when the glaciers were rubbed against the Earth's surface. The region have great vegetation considering the fact that the growing season is less than five months - there are over 800 plant species.
Where is the Hudson Bay Lowlands?
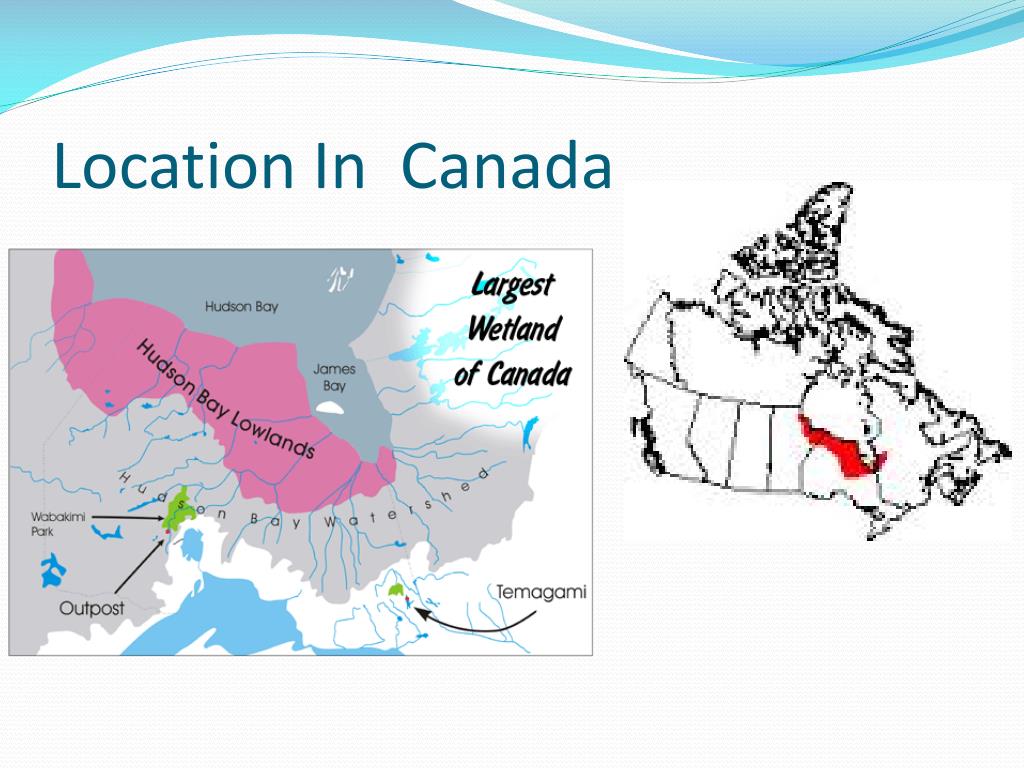
The Hudson Bay Lowlands is a vast wetland located between the Canadian Shield and southern shores of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Most of the area lies within the province of Ontario, with smaller portions reaching into Manitoba and Quebec.
What is the geology of Hudson Bay?
Hudson Bay is in the region of the most rapid uplift. Hudson Bay and the associated structural basin lies within the centre of a large free-air gravity anomaly that lies within the Canadian Shield.
What are the biggest problems in the Hudson Bay-Arctic Lowlands?
Like mentioned, mining is one of the biggest economic industries in the Hudson Bay - Arctic Lowlands, therefore deforestation, air pollution and destroying of animals' habitats are big problems. However, this doesn't just negatively affect the nature, but affects the miners' health, as well.

When was the Hudson Bay lowland formed?
The basin was inundated by seawater after the retreat of glaciation some 7500 years ago. The bay is generally shallow, and the land is rising steadily at around 60 cm per 100 years because of isostatic uplift, exposing more and more of the coast.
What is Hudson Bay Lowlands made of?
The Hudson Bay Lowlands are mostly muskeg or peat-forming wetland. There are long marshes along the coastline of Hudson Bay and James Bay. In the southwestern part of the Hudson Bay Lowlands, there are thick forests of trees such as white spruce, white birch, and balsam poplar.
What landforms are in Hudson Bay Lowlands?
Wetland landforms are the main features in the landscape. These include open and forested bogs and peat plateaus; flat fen meadows, and stringed and palsa fens; and swamps, marsh, and open water. Local relief is commonly <2 m. The landscape of the lowlands is the product of its geologic history and present conditions.
Where is Hudson Bay Lowlands?
The Hudson Bay Lowlands is a vast wetland located between the Canadian Shield and southern shores of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Most of the area lies within the province of Ontario, with smaller portions reaching into Manitoba and Quebec.
What are two main landform features of the Hudson Bay Lowlands?
Wetland landforms are the main features in the landscape. These include open and forested bogs and peat plateaus; flat fen meadows, and stringed and palsa fens; and swamps, marsh, and open water. Local relief is commonly <2 m.
Why is Hudson Bay Lowland important?
Furthermore the coastal zone of the Lowland is a major staging and breeding ground for polar bears, migratory birds and other species. Perhaps assurance of preservation of the still pristine natural Hudson Bay Lowland should be achieved by establishing it as an international heritage park.
How deep is the water in Hudson Bay?
886′Hudson Bay / Max depthHudson Bay has a shallow and quite smooth floor, averaging 330 feet (100 metres) in depth, with a maximum around 900 feet (270 metres). The coast, situated in a region of permanently frozen earth layers, or permafrost, is a marsh-ridden lowland fed by lake waters and turbulent rivers.
What type of rock is in the Hudson Bay Lowlands?
Most of the bedrock in the Hudson Bay lowlands is composed of limestone and carbonate-dominated sedimentary rock.
Is Hudson Bay salt or fresh water?
saltwaterHudson Bay (Southern East Cree: ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, romanized: Wînipekw; Southern East Cree: ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, romanized: Wînipâkw; Inuktitut: ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, romanized: Kangiqsualuk ilua or Inuktitut: ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, romanized: Tasiujarjuaq; French: baie d'Hudson), sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of saltwater in ...
How old is the Hudson Bay region?
Hudson's Bay Company. The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), famous for their iconic Point Blankets and their role in starting the fur trade industry in Canada, is named after this large body of water. HBC was incorporated on May 2nd 1670 and is the oldest corporation in North America (and is among the oldest in the world).
Does anyone live near Hudson Bay?
Population. The area around Hudson Bay is very sparsely populated. The biggest sector of the population is the Inuit, who have largely given up their traditional way of life as hunters and now live from fishing and handicrafts in the few small communities dotted along the coast.
What kind of rock is the Hudson Bay Lowlands made out of?
Most of the bedrock in the Hudson Bay lowlands is composed of limestone and carbonate-dominated sedimentary rock.
What minerals are in the Hudson Bay Lowlands?
The Hudson Bay Lowlands stretch through northern Ontario and northeastern Manitoba. They are geologically characterized by volcanic and sedimentary rocks, and contain scattered deposits of copper, zinc, gold and nickel.
What animals are in the Hudson Bay Lowlands?
The Hudson Bay Lowlands region provides vital habitat for a variety of unique mammals and migratory birds including: woodland caribou, polar bear, arctic fox, and arctic hare. Canada geese, snow geese, willow ptarmigan and various species of sea ducks.
What is the name of the bay in the Hudson Bay region?
The region is named after the nearby inland sea, Hudson Bay, the second largest in the world. The entire area drains into the bay through rivers such as the Churchill, Severn, and Attawapiskat. The region is located in the extreme north of Ontario, extending into both Manitoba to the west and Quebec in the east, and covers around 25 percent of Ontario's total land area (approximately 228,400 km 2 ). The area was covered in ice during the last glacial maximum, and then flooded as the ice receded, leaving behind plains that are slowly rising out of the ocean due to post-glacial rebound. Peatlands, both bogs and fens now cover much of the landscape, with other kinds of wetlands along rivers and the coast. The climate of the region depends largely on the water surface of the bay, which heats rapidly in the summer, breaking the ice and bringing rains to the lowlands. In the winter, the bay freezes over again, bringing freezing temperatures and winds. The vegetation is mostly conifer forest and peatland, with typical subarctic and boreal plants.
What province is Hudson Bay in?
Most of the area lies within the province of Ontario, with smaller portions reaching into Manitoba and Quebec. Many wide and slow-moving rivers flow through this area toward the saltwater of Hudson Bay: these include the Churchill, Nelson and Hayes in Manitoba, Severn, Fawn, Winisk, Asheweig, Ekwan, Attawapiskat, and Albany in Ontario, ...
Why did the Ojibwa not populate the Hudson Bay?
The local Ojibwa and Cree most likely came into contact with the region but did not populate the region due to the harsh, undesirable conditions and poor drainage patterns of the area . When Europeans arrived in the area, the Hudson's Bay Company set up trading posts such as Rankin Inlet, some of which remain populated today. However, these never grew into sizable towns, again because of the poor living conditions and climate. To this day, not all of the lowlands have been properly explored. There are a few small First Nations settlements on the southern shore of Hudson Bay Lowlands at places like Moose Factory, Moosonee, Attawapiskat, and Fort Severn .
What is the climate of the bay?
The climate of the region depends largely on the water surface of the bay, which heats rapidly in the summer, breaking the ice and bringing rains to the lowlands. In the winter, the bay freezes over again, bringing freezing temperatures and winds. The vegetation is mostly conifer forest and peatland, with typical subarctic and boreal plants.
Why is Hudson Bay so low in salinity?
Hudson Bay has a lower average salinity level than that of ocean water. The main causes are the low rate of evaporation (the bay is ice-covered for much of the year), the large volume of terrestrial runoff entering the bay (about 700 km 3 (170 cu mi) annually, the Hudson Bay watershed covering much of Canada, many rivers and streams discharging into the bay), and the limited connection with the Atlantic Ocean and its higher salinity. Sea ice is about three times the annual river flow into the bay, and its annual freezing and thawing significantly alters the salinity of the surface layer.
What is Hudson Bay called?
states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay .
What is the average temperature in James Bay?
(Köppen: Dfb) The average annual temperature in almost the entire bay is around 0 °C (32 °F) or below.
What is the climate of Hudson Bay?
Northern Hudson Bay has a polar climate ( Köppen: ET) being one of the few places in the world where this type of climate is found south of 60 °N, going farther south towards Quebec, where Inukjuak is still dominated by the tundra. From Arviat, Nunavut, to the west to the south and southeast prevails the subarctic climate (Köppen: Dfc ). This is because in the central summer months, heat waves can advance from the hot land and make the weather milder, with the result that the average temperature surpasses 10 °C or 50 °F. At the extreme southern tip of the extension known as James Bay arises a humid continental climate with a longer and generally hotter summer. (Köppen: Dfb) The average annual temperature in almost the entire bay is around 0 °C (32 °F) or below. In the extreme northeast, winter temperatures average as low as −29 °C or −20.2 °F.
What was the name of the company that negotiated a monopoly on the Hudson Bay watershed?
In 1668, Nonsuch reached the bay and traded for beaver pelts, leading to the creation of the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) which still bears the historic name. The HBC negotiated a trading monopoly from the English crown for the Hudson Bay watershed, called Rupert's Land. : 4 France contested this grant by sending several military expeditions to the region, but abandoned its claim in the Treaty of Utrecht (April 1713).
What is the name of the southern arm of Hudson Bay?
Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay . The Eastern Cree name for Hudson and James Bay is Wînipekw (Southern dialect) or Wînipâkw (Northern dialect), meaning muddy or brackish water. Lake Winnipeg is similarly named by the local Cree, as is the location for the city of Winnipeg .
How deep is the Bay of Bengal?
The bay is relatively shallow and is considered an epicontinental sea, with an average depth of about 100 m (330 ft) (compared to 2,600 m (8,500 ft) in the Bay of Bengal). It is about 1,370 km (850 mi) long and 1,050 km (650 mi) wide.
What are the lowlands of the Hudson Bay?
The Hudson Bay lowlands consists of swampy plains and lots of small lakes and ponds, while the Arctic lowlands are made of islands with gently rolling hills. Both are made of mainly sedimentary rocks, along with igneous and metamorphic rocks. The Hudson Bay - Artic Lowlands were formed during the last ice age when the glaciers were rubbed against the Earth's surface. The region have great vegetation considering the fact that the growing season is less than five months - there are over 800 plant species. However, the soil is very poorly drained.
What are the problems with mining in the Hudson Bay?
Like mentioned, mining is one of the biggest economic industries in the Hudson Bay - Arctic Lowlands, therefore deforestation, air pollution and destroying of animals' habitats are big problems. However, this doesn't just negatively affect the nature, but affects the miners' health, as well.
What are the two regions of the Hudson Bay?
The Hudson Bay - Arctic Lowlands. It is typically split into two sub-regions: The Hudson Bay Lowlands and Arctic Lowlands. It is located more specifically in Ontario, Quebec, Manitoba, Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. This region formed in the Paleozoic Era, when the enormous weight of a glacier sunk the Canadian Shield and ...
How many islands are there in the Hudson Bay?
It also consists of part of the Arctic Archipelago which has 94 major islands and 34, 369 minor islands. Vegetation: Hudson Bay Lowlands: he Hudson Bay Lowlands are covered by a swampy forest and it’s vegetation includes bushes,trees that are spread apart, stunted tamarack, and black spruce as its in mainly transitional forest.
What is the poor vegetation in the Arctic Lowlands?
Arctic Lowlands: It has poor vegetation with low growing shrubs and seeds (no trees).the Arctic Lowlands only consist of low growing shrubs and seeds (no trees) as most is barren land with some tundar forest. Poor vegetation in arctic lowlands can also be attributed to the continuous permafrost that is part of the arctic archipelago.
What ecosystem is the Canadian shield dominated by?
Vegetation: The Canadian Shield is dominated by the boreal forest ecosystem. It's elevation varies.
What era was the Canadian Shield formed?
This region formed in the Paleozoic Era, when the enormous weight of a glacier sunk the Canadian Shield and the area became lowlands when the glaciers retreated. This region consists of sedimentary (~40%), igneous and metamorphic rocks. A few major waterways near this region include Hudson Bay and James Bay.
Overview
The Hudson Bay Lowlands is a vast wetland located between the Canadian Shield and southern shores of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Most of the area lies within the province of Ontario, with smaller portions reaching into Manitoba and Quebec. Many wide and slow-moving rivers flow through this area toward the saltwater of Hudson Bay: these include the Churchill, Nelson and Hayes in Manitoba, Severn, F…
Early discoveries and exploration
The local Ojibwa and Cree most likely came into contact with the region but did not populate the region due to the harsh, undesirable conditions and poor drainage patterns of the area. When Europeans arrived in the area, the Hudson's Bay Company set up trading posts such as Rankin Inlet, some of which remain populated today. However, these never grew into sizable towns, again because of the poor living conditions and climate. To this day, not all of the lowlands have been …
Geography
The region is named after the nearby inland sea, Hudson Bay, the second largest in the world. The entire area drains into the bay through rivers such as the Churchill, Severn, and Attawapiskat. The region is located in the extreme north of Ontario, extending into both Manitoba to the west and Quebec in the east, and covers around 25 percent of Ontario's total land area (approximately 228,400 km ). The area was covered in ice during the last glacial maximum, and then flooded as …
Industries
The forestry industry is present in the coniferous forests of the region. There is a growing tourist industry which includes fly-fishing and beluga and seal-watching excursions.
See also
• Geology of Ontario
External links
• Map of the Hudson Plains Ecoregions
• An Introduction to Ecozones
• Map of major rivers draining into southern Hudson Bay
• Hudson Bay Lowlands - Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources