
Full Answer
How did the Roman Empire expand its empire?
In reality, Roman expansion was mostly accomplished under the Republic, though parts of northern Europe were conquered in the 1st century AD, when Roman control in Europe, Africa, and Asia was strengthened.
What is the Roman Empire?
Roman Empire, the ancient empire, centred on the city of Rome, that was established in 27 bce following the demise of the Roman Republic and continuing to the final eclipse of the Empire of the West in the 5th century ce.
How long did it take for Rome to become an empire?
After 450 years as a republic, Rome became an empire in the wake of Julius Caesar’s rise and fall in the first century B.C. The long and triumphant reign of its first emperor, Augustus, began a golden age of peace and prosperity; by contrast, the Roman Empire’s decline and fall by the fifth century A.D.
Why did Rome split into eastern and Western empires?
The Western Empire, suffering from repeated invasions and the flight of the peasants into the cities, had grown weak compared with the East, where spices and other exports virtually guaranteed wealth and stability. When Theodosius died, in 395, Rome split into Eastern and Western empires.
See more
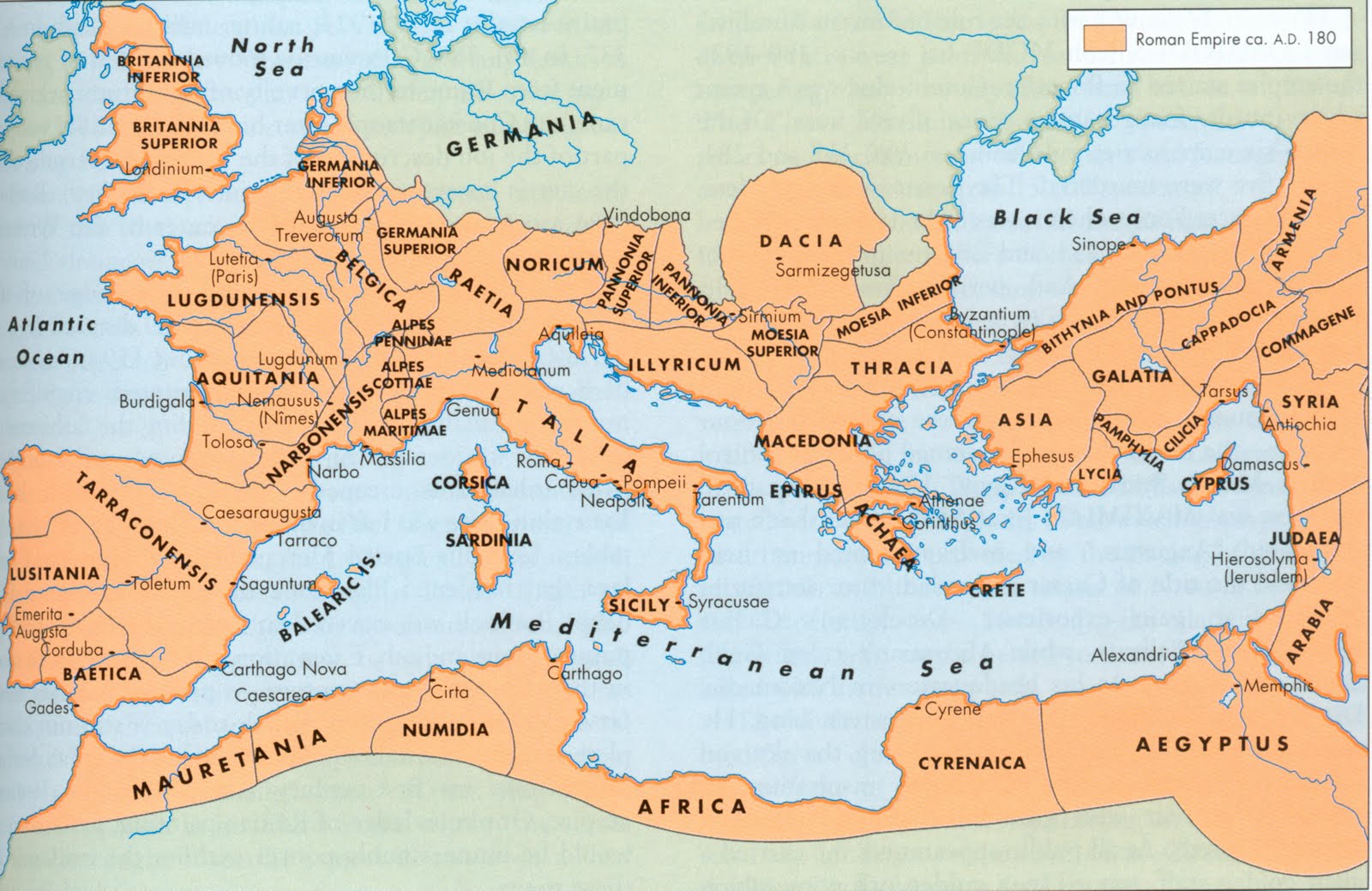
How did Rome connect its empire?
Rome was able to gain its empire in large part by extending some form of citizenship to many of the people it conquered. Military expansion drove economic development, bringing enslaved people and loot back to Rome, which in turn transformed the city of Rome and Roman culture.
Is Rome connected to the Roman Empire?
Roman Empire, the ancient empire, centred on the city of Rome, that was established in 27 bce following the demise of the Roman Republic and continuing to the final eclipse of the empire of the West in the 5th century ce.
How did the Romans communicate with each other?
Writing was a useful tool for the ancient Romans - the written word could communicate ideas to the people of Rome and to Roman subjects throughout the Empire. Only a fraction of the huge number of texts written by the Romans have survived.
Why did the Roman Empire split in two?
In short, the empire's vast size played a role — its colossal borders made it challenging to govern — but other factors, such as political and social instability, revolts, invasions and incursions into the empire, also led to the split.
Who has the biggest empire in history?
1) The British Empire was the largest empire the world has ever seen. The British Empire covered 13.01 million square miles of land - more than 22% of the earth's landmass. The empire had 458 million people in 1938 — more than 20% of the world's population.
Which empire lasted the longest?
15 longest uninterrupted empires in historyEmpire of Japan: minimum 1703 years to date (see above)Byzantine Empire: 874 years (uninterrupted from 330 to 1204)Holy Roman Empire: 844 years (962-1806)Zhou Empire: 790 years (1046–256 BCE)Ethiopian Empire: 666 years (1270-1936)Khmer Empire: 629 years (802–1431)More items...
Who actually spoke Latin?
Originally spoken by small groups of people living along the lower Tiber River, Latin spread with the increase of Roman political power, first throughout Italy and then throughout most of western and southern Europe and the central and western Mediterranean coastal regions of Africa.
What language did Romans speak?
LatinLatin is the language that was spoken by the ancient Romans. As the Romans extended their empire throughout the Mediterranean, the Latin language spread. By the time of Julius Caesar, Latin was spoken in Italy, France, and Spain.
When did Romans stop speaking Latin?
To oversimplify the matter, Latin began to die out in the 6th century shortly after the fall of Rome in 476 A.D. The fall of Rome precipitated the fragmentation of the empire, which allowed distinct local Latin dialects to develop, dialects which eventually transformed into the modern Romance languages.
What made Rome fall?
Invasions by Barbarian tribes The most straightforward theory for Western Rome's collapse pins the fall on a string of military losses sustained against outside forces. Rome had tangled with Germanic tribes for centuries, but by the 300s “barbarian” groups like the Goths had encroached beyond the Empire's borders.
Who destroyed Roman Empire?
the VisigothsThe West was severely shaken in 410, when the city of Rome was sacked by the Visigoths, a wandering nation of Germanic peoples from the northeast. The fall of Rome was completed in 476, when the German chieftain Odoacer deposed the last Roman emperor of the West, Romulus Augustulus.
What group defeated Rome?
The Sack of Rome on 24 August 410 AD was undertaken by the Visigoths led by their king, Alaric. At that time, Rome was no longer the capital of the Western Roman Empire, having been replaced in that position first by Mediolanum (now Milan) in 286 and then by Ravenna in 402.
What broke the Roman Empire?
Invasions by Barbarian tribes The most straightforward theory for Western Rome's collapse pins the fall on a string of military losses sustained against outside forces. Rome had tangled with Germanic tribes for centuries, but by the 300s “barbarian” groups like the Goths had encroached beyond the Empire's borders.
Who started the Roman Empire?
The Roman Empire was founded when Augustus Caesar proclaimed himself the first emperor of Rome in 31BC and came to an end with the fall of Constantinople in 1453CE. An empire is a political system in which a group of people are ruled by a single individual, an emperor or empress.
What was before the Roman Empire?
Before the glory of Rome, the Etruscans ruled much of what is now Italy. Some of Rome's first kings were from Etruria, and Etruscans may have founded the city-state that would dominate much of the known world for centuries.
Who defeated the Roman Empire?
chieftain OdoacerThe West was severely shaken in 410, when the city of Rome was sacked by the Visigoths, a wandering nation of Germanic peoples from the northeast. The fall of Rome was completed in 476, when the German chieftain Odoacer deposed the last Roman emperor of the West, Romulus Augustulus.
What happened to the Roman Empire in the 3rd century?
In the 3rd century the Empire underwent a crisis that threatened its existence , as the Gallic Empire and Palmyrene Empire broke away from the Roman state, and a series of short-lived emperors, often from the legions, led the empire. The empire was reunified under Aurelian ( r. 270–275 ).
When did the Roman Empire end?
Most chronologies place the end of the Western Roman Empire in 476 , when Romulus Augustulus was forced to abdicate to the Germanic warlord Odoacer. By placing himself under the rule of the Eastern Emperor, rather than naming a puppet emperor of his own, Odoacer ended the Western Empire.
What did freeborn Roman women do?
Freeborn Roman women were considered citizens throughout the Republic and Empire, but did not vote, hold political office, or serve in the military . A mother's citizen status determined that of her children, as indicated by the phrase ex duobus civibus Romanis natos ("children born of two Roman citizens"). A Roman woman kept her own family name (nomen) for life. Children most often took the father's name, but in the Imperial period sometimes made their mother's name part of theirs, or even used it instead.
What was the Roman Empire's cultural diversity?
The Roman Empire was remarkably multicultural, with "a rather astonishing cohesive capacity" to create a sense of shared identity while encompassing diverse peoples within its political system over a long span of time. The Roman attention to creating public monuments and communal spaces open to all—such as forums, amphitheatres, racetracks and baths —helped foster a sense of "Romanness".
What happened to the Severan Dynasty?
But despite this gesture of universality, the Severan dynasty was tumultuous—an emperor's reign was ended routinely by his murder or execution—and, following its collapse, the Roman Empire was engulfed by the Crisis of the Third Century, a period of invasions, civil strife, economic disorder, and plague.
What was the Barbarian invasion?
The Barbarian Invasions consisted of the movement of (mainly) ancient Germanic peoples into Roman territory. Even though northern invasions took place throughout the life of the Empire, this period officially began in the 4th century and lasted for many centuries, during which the western territory was under the dominion of foreign northern rulers, a notable one being Charlemagne. Historically, this event marked the transition between classical antiquity and the Middle Ages.
What was the Roman Empire's prosperity during the 200 years of Augustus?
During this period, the cohesion of the empire was furthered by a degree of social stability and economic prosperity that Rome had never before experienced. Uprisings in the provinces were infrequent but put down "mercilessly and swiftly" when they occurred. The success of Augustus in establishing principles of dynastic succession was limited by his outliving a number of talented potential heirs. The Julio-Claudian dynasty lasted for four more emperors— Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, and Nero —before it yielded in 69 AD to the strife-torn Year of Four Emperors, from which Vespasian emerged as victor. Vespasian became the founder of the brief Flavian dynasty, to be followed by the Nerva–Antonine dynasty which produced the " Five Good Emperors ": Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and the philosophically-inclined Marcus Aurelius .
How was Cleopatra connected to the Roman Empire?
How was Cleopatra connected with the Roman Empire? Cleopatra is one of the most well-known figures in history, but her connection to the Roman Empire is still a bit hazy to some. She was seen as cunning, charming and beautiful, an overly captivating individual.
What was Cleopatra's influence on Rome?
Cleopatra’s influence on Rome. With her infant son as co-regent, Cleopatra’s power over Egypt was more secure than ever. Still, this was not to be the last of Cleopatra’s interactions with Rome. With unreliable flooding of the Nile resulting in failing crops, and conflict raging in Rome, the two regions were again brought together in their troubles.
What happened to Antony and Cleopatra?
After losing the battle Antony heard rumours that Cleopatra had committed suicide, the news causing him to fall on his sword and die just as news arrived that the rumour was false. After burying Antony, Cleopatra locked herself in her chambers and joined her lover in death. Her cause of death is unknown, but Plutarch and other writers proposed the story that she used to a poisonous snake, a symbol of divine royalty, to commit suicide at age 39.
What happened to Cleopatra after she ran out of Egypt?
After attempting to take sole possession of the throne, Ptolemy XIII ran her out of Egypt, which ended in the famous civil war between them. Whilst in Syria, Cleopatra raised an army of mercenaries and returned the following year to face her brother’s forces.
What happened to Cleopatra after she buried Antony?
After burying Antony, Cleopatra locked herself in her chambers and joined her lover in death. Her cause of death is unknown, but Plutarch and other writers proposed the story that she used to a poisonous snake, a symbol of divine royalty, to commit suicide at age 39.
When did Cleopatra return to Egypt?
The family moved briefly to Rome, but when Ceasar was murdered in 44 BC, Cleopatra returned to Egypt, where her youngest brother died soon after. And so, little Ptolemy Caesar at 3 years old became co-regent of Egypt with his mother.
Who was Ceasar's brother?
Ceasar returned the throne to Cleopatra and her youngest brother Ptolemy XIV (then only 13 years old). It is believed that Cleopatra and Ceasar lived together for a while, having an affair. In around 47 BC, Cleopatra gave birth to a son, Ptolemy Caesar.
What was the Roman Empire?
After 450 years as a republic , Rome became an empire in the wake of Julius Caesar’s rise and fall in the first century B.C. The long and triumphant reign of its first emperor, Augustus, began a golden age of peace and prosperity; by contrast, the Roman Empire’s decline and fall by the fifth century A.D. was one of the most dramatic implosions in the history of human civilization.
When did Rome become an empire?
After 450 years as a republic, Rome became an empire in the wake of Julius Caesar’s rise and fall in the first century B.C. The long and triumphant reign of its first emperor, Augustus, began a golden age of peace and prosperity; by contrast, the Roman Empire’s decline and fall by the fifth century A.D.
How many kings were there in Rome?
There are seven legendary kings of Rome: Romulus, Numa Pompilius, Tullus Hostilius, Ancus Martius, Lucius Tarquinius Priscus (Tarquin the Elder), Servius Tullius and Tarquinius Superbus, or Tarquin the Proud (534-510 B.C.). While they were referred to as “Rex,” or “King” in Latin, all the kings after Romulus were elected by the senate.
How many miles of roads were built in the Roman Empire?
They included such modern-seeming innovations as mile markers and drainage. Over 50,000 miles of road were built by 200 B.C. and several are still in use today.
What was the first law in Rome?
In 450 B.C., the first Roman law code was inscribed on 12 bronze tablets–known as the Twelve Tables–and publicly displayed in the Roman Forum. These laws included issues of legal procedure, civil rights and property rights and provided the basis for all future Roman civil law. By around 300 B.C., real political power in Rome was centered in the Senate, which at the time included only members of patrician and wealthy plebeian families.
How did Augustus rule Rome?
Augustus’ rule restored morale in Rome after a century of discord and corruption and ushered in the famous pax Romana –two full centuries of peace and prosperity. He instituted various social reforms, won numerous military victories and allowed Roman literature, art, architecture and religion to flourish. Augustus ruled for 56 years, supported by his great army and by a growing cult of devotion to the emperor. When he died, the Senate elevated Augustus to the status of a god, beginning a long-running tradition of deification for popular emperors.
What languages did Rome use?
Among the many legacies of Roman dominance are the widespread use of the Romance languages (Italian, French, Spanish, Portuguese and Romanian) derived from Latin, the modern Western alphabet and calendar and the emergence of Christianity as a major world religion. After 450 years as a republic, Rome became an empire in the wake ...

Overview
Economy
Scholar Moses Finley was the chief proponent of the primitivist view that the Roman economy was "underdeveloped and underachieving," characterized by subsistence agriculture; urban centres that consumed more than they produced in terms of trade and industry; low-status artisans; slowly developing technology; and a "lack of economic rationality." Current views are more compl…
History
Rome had begun expanding shortly after the founding of the republic in the 6th century BC, though it did not expand outside the Italian peninsula until the 3rd century BC. Then, it was an "empire" (i.e. a great power) long before it had an emperor. The Roman Republic was not a nation-state in the modern sense, but a network of towns left to rule themselves (though with varying degrees of indep…
Geography and demography
The Roman Empire was one of the largest in history, with contiguous territories throughout Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. The Latin phrase imperium sine fine ("empire without end" ) expressed the ideology that neither time nor space limited the Empire. In Virgil's epic poem the Aeneid, limitless empire is said to be granted to the Romans by their supreme deity Jupiter. Thi…
Health and disease
Epidemics were common in the ancient world, and occasional pandemics in the Roman Empire killed millions of people. The Roman population was unhealthy. About 20 percent of the population—a large percentage by ancient standards—lived in one of hundreds of cities, Rome, with a population estimated at one million, being the largest. The cities were a "demographic sink," even in the best of times. The death rate exceeded the birth rate and a constant in-migration of n…
Languages
The language of the Romans was Latin, which Virgil emphasized as a source of Roman unity and tradition. Until the time of Alexander Severus (reigned 222–235), the birth certificates and wills of Roman citizens had to be written in Latin. Latin was the language of the law courts in the West and of the military throughout the Empire, but was not imposed officially on peoples brought under Roman ru…
Society
The Roman Empire was remarkably multicultural, with "a rather astonishing cohesive capacity" to create a sense of shared identity while encompassing diverse peoples within its political system over a long span of time. The Roman attention to creating public monuments and communal spaces open to all—such as forums, amphitheatres, racetracks and baths—helped foster a sens…
Government and military
The three major elements of the Imperial Roman state were the central government, the military, and the provincial government. The military established control of a territory through war, but after a city or people was brought under treaty, the military mission turned to policing: protecting Roman citizens (after 212 AD, all freeborn inhabitants of the Empire), the agricultural fi…