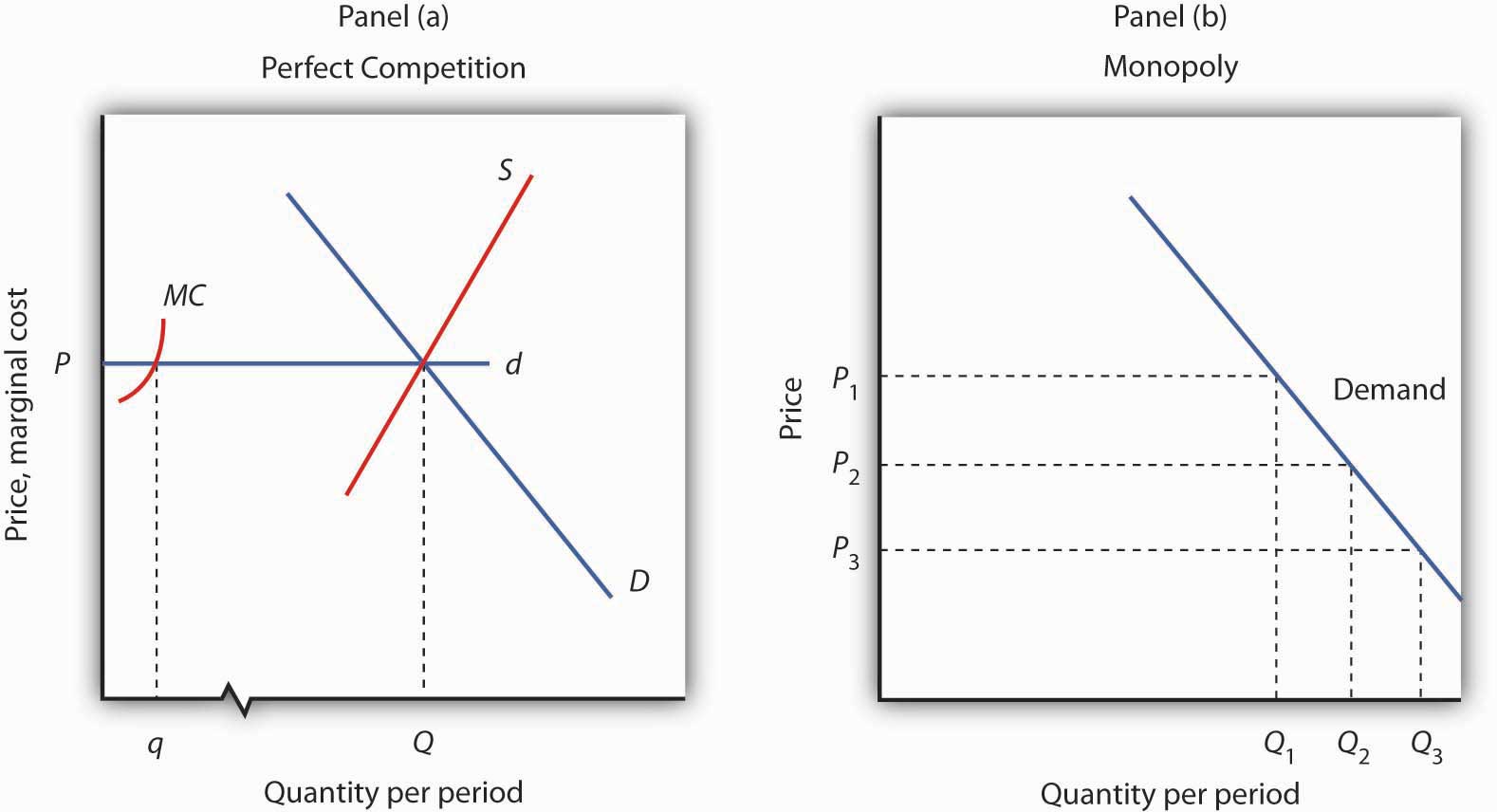
Under monopoly, prices are higher and output lower than they would be under Perfect Competition. The power of the monopolist derives from the fact that demand for his product is not perfectly elastic, so that when price rises, sales largely hold up.
What is the difference between perfect competition and monopoly?
Under perfect competition price is equal to marginal cost at the equilibrium output. While under monopoly, the price is greater than average cost. 2. Equilibrium: Under perfect competition equilibrium is possible only when MR = MC and MC cuts the MR curve from below.
What determines the price output of a monopoly?
Note that the price and output under monopoly are determined by equality between marginal cost and marginal revenue and not by the intersection of demand and supply curves. Price-output equilibrium under perfect competition and monopoly are graphically shown in a single diagram (Fig. 26.11).
Why do monopolies have lower marginal and average costs?
If he can derive the advantages of large-scale production, then his marginal and average costs would be lower than those of a perfectly competitive seller. If this is so, monopoly price will be lower and output higher than under perfect competition.
How does a monopolist increase his profits by discriminating prices?
The monopolist will be increasing his total profits by discriminating prices if he finds that elasticities of demand at the single monopoly price are different in different markets. But it is not possible for a firm under perfect competition to charge different prices from different buyers.
How will the price and output of a monopolist compare with perfect competition quizlet?
Monopolists charge higher prices than firms in a perfectly competitive market. Monoplists exploit their monopoly power and charge consumers high prices. Monopoly market output is much lower than output in the perfectly competitive market because Monopololists restrict output to a low level in order to keep prices high.
How does the price and output of a monopolist differ from that of the perfectly competitive industry?
The key difference with a perfectly competitive firm is that in the case of perfect competition, marginal revenue is equal to price (MR = P), while for a monopolist, marginal revenue is not equal to the price, because changes in quantity of output affect the price.
How does perfect competition compare to monopolistic?
In a monopolistic market, there is only one firm that dictates the price and supply levels of goods and services. A perfectly competitive market is composed of many firms, where no one firm has market control. In the real world, no market is purely monopolistic or perfectly competitive.
How will the price and output policy of an unregulated monopolist compare with a perfectly competitive market?
Following the assumption that firms maximize profits, how will the price and output policy of an unregulated monopolist compare with ideal market of perfect competition? output will be too small and its price too high.
When comparing perfect competition to monopoly What is the output for monopolies?
Comparison of Output: Perfect competition output is higher than monopoly price. Under perfect competition the firm is in equilibrium at point M1 (As shown in Fig. 11 (a)), AR = MR = AC = MC are equal. The equilibrium output is ON1.
What is the difference between the perfectly competitive equilibrium level of output and the pure monopoly equilibrium level of output?
A significant difference between the two is that while under perfect competition price equals marginal cost at the equilibrium output, under monopoly equilibrium price is greater than marginal cost.
Which price is for perfect competition and which is for monopoly?
In a perfectly competitive market, price equals marginal cost and firms earn an economic profit of zero. In a monopoly, the price is set above marginal cost and the firm earns a positive economic profit.
Why is perfect competition more efficient than monopoly?
Perfectly competitive firms have the least market power (i.e., perfectly competitive firms are price takers), which yields the most efficient outcome. Monopolies have the most market power, which yields the least efficient outcome.
How price and output is determined in monopolistic competition?
, In monopolistic competition, firms make price/output decisions as if they were a monopoly. In other words, they will produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. , Free entry into the market may ultimately shrink the economic profits of monopolistically competitive firms.
Can a perfectly monopolist maximize profit along the inelastic part of the demand curve Why or why not?
It is that a profit maximizing monopoly would not produce on the inelastic portion. THis is because, when the demand curve is inelastic, a rise in quantity will lead to a relatively larger fall in price, and hence total revenue will actually fall.
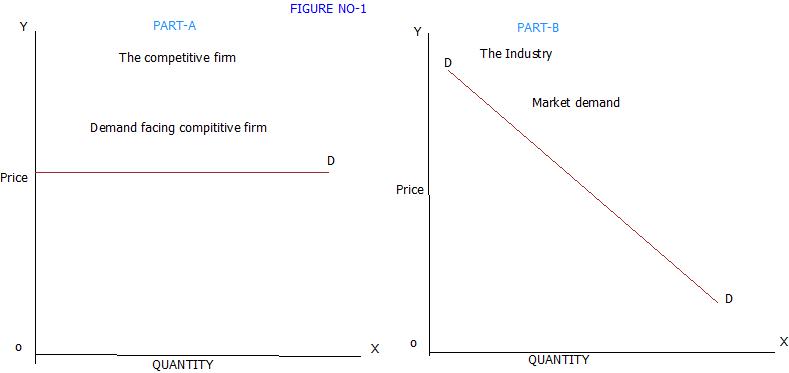
How does the demand curve faced by the monopolist differ from that confronting the perfect competitor why do they differ?
The demand curve facing a pure monopolist is downward sloping; that facing the purely competitive firm is horizontal, perfectly elastic. This is so for the pure competitor because the firm faces a multitude of competitors, all producing perfect substitutes.
When a monopolist increases the amount of output that it produces and sells its average revenue?
Question: When a monopolist increases the amount of output that it produces and sells, what happens to its average revenue and its marginal revenue? Its average revenue increases and its marginal revenue increases.
How do perfectly competitive firms and monopolists differ quizlet?
What is the key difference between a monopolist and a perfect competitor? A perfectly competitive firm does not take into account the effect of its output decision on the price it receives, whereas a monopolistic firm takes into account that its output decision can affect price.
What is the key difference between a perfectly competitive firm and a monopoly firm quizlet?
What is the key difference between a competitive firm and a monopoly? A monopoly firm has market power, the ability to influence the market price of the product it sells. A competitive firm has no market power.
Does a monopolist the market price as given Why or why not?
Unlike a perfectly competitive firm, the monopolist does not have to simply take the market price as given. Instead, the monopolist is a price searcher; it searches the market demand curve for the profit maximizing price.
What is the relationship between marginal revenue and price in a monopoly?
In a monopoly, because the price changes as the quantity sold changes, marginal revenue diminishes with each additional unit and will always be equal to or less than average revenue.
What is the difference between a monopolistic market and a perfectly competitive market?
In a monopolistic market, there is only one firm that dictates the price and supply levels of goods and services, and that firm has total market control. In contrast to a monopolistic market, a perfectly competitive market is composed of many firms, where no one firm has market control.
What is monopolistic competition?
In monopolistic competition, there are many producers and consumers in the marketplace, and all firms only have a degree of market control. In contrast, whereas a monopolist in a monopolistic market has total control of the market, monopolistic competition offers very few barriers to entry.
Why are firms in a perfectly competitive market all price takers?
Firms in a perfectly competitive market are all price takers because no one firm has enough market control. Unlike a monopolistic market, firms in a perfectly competitive market have a small market share. Barriers to entry are relatively low, and firms can enter and exit the market easily.
What is perfectly competitive market?
A perfectly competitive market is composed of many firms, where no one firm has market control. In the real world, no market is purely monopolistic or perfectly competitive. In between a monopolistic market and perfect competition lies monopolistic competition or imperfect competition.
Why are firms able to enter a market?
All firms are able to enter into a market if they feel the profits are attractive enough. This makes monopolistic competition similar to perfect competition. However, in a monopolist competitive market, there is product differentiation.
Why are prices high in monopolistic markets?
Monopolistic Markets. In a monopolistic market, firms are price makers because they control the prices of goods and services. In this type of market, prices are generally high for goods and services because firms have total control of the market. Firms have total market share, which creates difficult entry and exit points.
Is monopoly a rare thing?
Purely monopolistic markets are extremely rare and perhaps even impossible in the absence of absolute barriers to entry, such as a ban on competition or sole possession of all natural resources.
Why is a monopolist a very large firm?
Because the monopolist is the only producer of the commodity, he is likely to be a very large firm that can secure economies of scale. If he can derive the advantages of large-scale production, then his marginal and average costs would be lower than those of a perfectly competitive seller. If this is so, monopoly price will be lower ...
Why does a monopolist refrain from raising prices?
A monopolist may refrain from raising price as far as he can because he does not want to encourage the entry of new firms into the industry. If the excess profits are very high, potential new entrants may try to find ways of overcoming whatever barriers have hitherto kept them out of the industry.
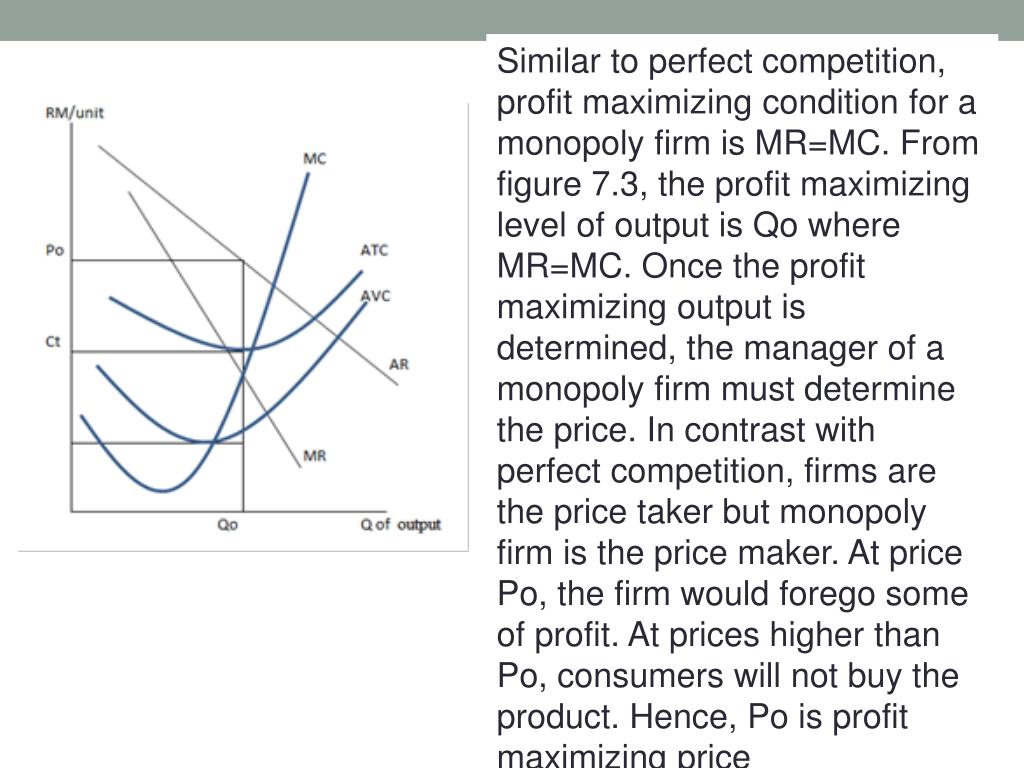
What is the equilibrium output of a monopoly?
If, however, the diagram were to represent a monopoly situation, the equilibrium output would be OQ 1 (where MR = MC) and the price would be OP 1. Thus monopoly output is less than competitive output but monopoly price is higher than competitive price. This supply means that if a firm does not have any competitors to fear, then it is in a position to raise its price.
What happens when a commodity is concentrating production into one firm?
If by concentrating production into one firm economies of scale are secured, the benefits arising from this may be passed on to the consumers. In other words, price can be reduced when costs fall. This is possible only when a commodity is produced on a very large scale in a single plant.
What are the drawbacks of monopoly?
Another drawback of monopoly, again from the consumer’s welfare point of view, is the lack of choice. The monopolist is the sole supplier of the commodity. So the consumer cannot express dissatisfaction by turning to a competitor’s product.
Why are restaurants in monopoly?
Such restaurants find themselves in a monopoly position because customers have nowhere else to go unless they bring their own food. If there were two or three suppliers in the same station in competition with one another, one might expect the complaints about standards to be reduced as each of the competitors would try to ensure that the customers come to them again and again.
Is a monopoly price higher than a competitive price?
Monopoly price is likely to be higher than competitive price. This is one major argument against monopoly. A monopolist usually charges as much as the traffic will bear. So consumers are exploited and there is loss of consumer welfare.
What is the difference between perfect competition and monopoly?
Under perfect competition price is equal to marginal cost at the equilibrium output. While under monopoly, the price is greater than average cost.
Why is the supply curve of a firm known?
It is so because all firms can sell desired quantity at the prevailing price. Moreover, there is no price discrimination. Under monopoly, supply curve cannot be known. MC curve is not the supply curve of the monopolist.
Why is demand curve elastic?
Under perfect competition, demand curve is perfectly elastic. It is due to the existence of large number of firms. Price of the product is determined by the industry and each firm has to accept that price. On the other hand, under monopoly, average revenue curve slopes downward.
Which firm aims at maximising its profits?
Under perfect competition and monopoly the firm aims at to maximize its profits. The firm which aims at to maximize its profits is known as rational firm.
Can a monopolist charge different prices?
Under simple monopoly, a monopolist can charge different prices from the different groups of buyers. But, in the perfectly competitive market, it is absent by definition.
Is perfect competition higher than monopoly price?
Perfect competition output is higher than monopoly price. Under perfect competition the firm is in equilibrium at point M 1 (As shown in Fig. 11 (a)), AR = MR = AC = MC are equal. The equilibrium output is ON 1. On the other hand monopoly firm is in equilibrium at point M where MC=MR. The equilibrium output is ON. The monopoly output is lower than perfectly competitive firm output.
What is the difference between monopoly and perfect competition?
A significant difference between the two is that while under perfect competition price equals marginal cost at the equilibrium output, under monopoly equilibrium price is greater than marginal cost. Why? Under perfect competition average revenue curve is a horizontal straight line and therefore marginal revenue curve coincides with average revenue curve and as a result marginal revenue and average revenue are equal to each other at all levels of output.
What is the similarity between perfect competition and monopoly?
Only similarity between the two is that a firm under both perfect competition and monopoly is in equilibrium at the level of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost. But there are many important points of difference which we spell out below.
What does OP mean in a monopolist?
In Fig. 26.10 monopolist is in equilibrium when marginal cost is falling at and near the point of equilibrium. In all these three cases, OP represents the price determined, OM represents the equilibrium output, and RNQP represents total positive profits made, though their amount differs in different cases.
What happens to the marginal cost curve when a monopolist comes into existence?
26.11 will shift to a downward position when monopoly comes into existence. If these economies are large enough so that there is substantial fall in the cost curve, the monopoly price may be lower than the competitive price MP and monopoly output will be larger than the competitive output.
What is the difference between monopoly equilibrium and perfectly competitive equilibrium?
Another important difference between monopoly equilibrium and perfectly competitive equilibrium is that under monopoly price is higher and output smaller than under perfect competition, assuming cost conditions in the two cases to be the same. ADVERTISEMENTS:
Why does a monopolist firm stop short of the optimum size?
This is so because it pays a competitive firm to expand production so long as average cost is falling since average revenue and marginal revenue remain constant but it does not pay a monopolist firm ...
Which curve is the supply curve of perfectly competitive industry?
The curve SS which is the supply curve of perfectly competitive industry will be the marginal cost curve under monopoly. It will be seen from Fig. 26.11 that the marginal revenue curve MR cuts the marginal cost (MC) curve SS of the monopolist at point F and as a consequence monopoly price O’ P’ and monopoly output OM’ are determined.
What is the intersection of marginal revenue and marginal cost curves?
The intersection of a firm's marginal revenue and marginal cost curves determines the level of output at which
Why would a D. firm have to take a lower price?
d. firm will have to take a lower price if it wants to increase the number of units that it sells.
Monopolistic Market vs. Perfect Competition: An Overview
- A monopolistic market and a perfectly competitive market are two market structures that have several key distinctions in terms of market share, price control, and barriers to entry. In a monopolistic market, there is only one firm that dictates the price and supply levels of goods and services, and that firm has total market control. In contrast to a monopolistic market, a perfectl…
Monopolistic Markets
- In a monopolistic market, firms are price makers because they control the prices of goods and services. In this type of market, prices are generally high for goods and services because firms have total control of the market. Firms have total market share, which creates difficult entry and exit points. Since barriers to entry in a monopolistic market are high, firms that manage to enter …
Perfect Competition
- In a market that experiences perfect competition, prices are dictated by supply and demand. Firms in a perfectly competitive market are all price takersbecause no one firm has enough market control. Unlike a monopolistic market, firms in a perfectly competitive market have a small market share. Barriers to entry are relatively low, and firms can en...
Special Considerations
- According to economic theory, when there is perfect competition, the prices of goods will approach their marginal cost of production(i.e., the cost to produce one more unit). This is because any firm that tries to sell at a higher price in an attempt to earn excess profits will be undercut by a competitor seeking to grab market share. This also promotes a sort of technologi…