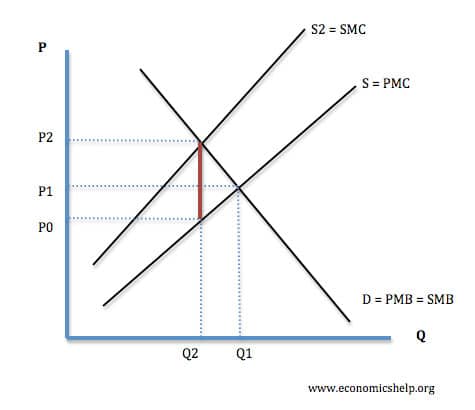
Taxes on negative externalities are intended to make consumers / producers pay the full social cost of the good. This reduces consumption and creates a more socially efficient outcome. If a good has a negative externality, without a tax, there will be over-consumption (Q1 where D=S) because people ignore the external costs.
How do taxes on negative externalities reduce consumption?
Taxes on negative externalities are intended to make consumers/producers pay the full social cost of the good. This reduces consumption and creates a more socially efficient outcome. If a good has a negative externality, without a tax, there will be over-consumption (Q1 where D=S) because people ignore the external costs.
What are the solutions to negative externalities?
Remedies for Negative Externalities One of the solutions to negative externalities is to impose taxes to change people’s behavior. The taxes can be imposed to reduce the harmful effects of certain externalities such as air pollution, smoking, and drinking alcohol.
What are the negative externalities of social cost?
The negative externalities are – pollution to other people, possible accident to other other people, and time other people sit in traffic jams Social cost is the total cost to society; it includes both private and external costs. With a negative externality the Social Cost > Private Cost
How can the government use externalities to achieve a more socially efficient?
To achieve a more socially efficient outcome, the government could try to tax the good with negative externalities. This means that consumers pay close to the full social cost. Arthur Pigou 1920 introduced the concept of externalities in The Economics of Welfare.
What are negative externalities in manufacturing?
Negative production externalities occur when the production process results in a harmful effect on unrelated third parties. For example, manufacturing plants cause noise and atmospheric pollution during the manufacturing process.
How does industrial waste affect the environment?
Water pollution. When industrial wastes are released into public waterways it pollutes and makes it harmful to humans, animals, and the plants that depend on it . Factory wastes often contain toxic chemicals that cause death to aquatic animals living in the water, and it denies fishermen a source of income.
Why are taxes imposed?
The taxes can be imposed to reduce the harmful effects of certain externalities such as air pollution, smoking, and drinking alcohol. An effective tax will equal the cost of the externality, and it is imposed with the goal of discouraging activities that cause such harmful effects.
What are the causes of air pollution?
Air pollution. Air pollution may be caused by factories, which release harmful gases to the atmosphere. Some of the gases include carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. The destructive gases cause damage to crops, buildings, and human health.
How do negative externalities affect public resources?
Negative externalities commonly affect public resources where it is difficult to hold parties accountable such as in a case of environmental pollution. Producers or consumers may create a negative externality without worrying about lawsuits or fines.
How does loud music affect the environment?
Noise pollution caused by loud music from a casino or nightclub may also affect third parties who are not part of the revelers dancing to the music. Loud music may be mentally and psychologically disruptive, especially to children who are yet to adapt to the surrounding environment.
Why do governments need to put property rights in place?
Also, since most negative externalities result from the lack of property risks, governments can introduce property rights that will help internalize the costs and benefits. Putting property rights in place will create fear among would-be offenders since they will be wary of possible legal action against them.
How does indirect tax affect the price of a product?
With an indirect tax, the supplier can shift the burden of the tax to the consumer by increasing the price of the good. When the price is elastic the producer will bear more of the tax burden. When the price is inelastic. Price elastic demand is more than one in most parts of the demand curve. The producer can pass on most of the tax to the consumer by increasing the price without losing too much sales because when a good is inelastic, the consumer still has to buy although the price increases. We now know that price elasticity of demand can be used to find the incidence or burden of a per-unit tax is falling or to predict where it will fall if there is tax.
How does tax affect supply?
Tax increases the costs of a business causing the supply curve to shift left or decreases. The distance between the original supply curve and the after tax supply curve shows the per unit tax. With an indirect tax, the supplier can pass on some or all of the tax to the consumer by increasing the price of the good. This depends on the elasticity of demand and supply and it is known as shifting the burden of the tax and
Why do we have excise taxes on tobacco?
It is a good source of revenue and the dominant opinion is that people who smoke should be responsible for paying the costs that their use imposes on society. Human being need not tobacco for survival. The reason government levied excise tax on tobacco because it can raise the revenue for government and control smoker from buying cigarettes. Higher taxes are useful in reducing the use in tobacco among the youth and lower’s income groups. However, it has an extreme control on tobacco use. As evidence, governments have increasingly using a higher tobacco taxes as a means to discourage its use.
What is the importance of deadweight loss?
Loss to society we’re represents to show the important of deadweight loss. In the sense can be view as an opportunity cost of taxation, money collect from people to obtain a dollar tax revenue actually costs society more than a dollar. The costs of the raising tax revenues include the money raise, tax collectors and government agencies to administer tax collection and deadweight loss are the example of direct cost of collection which create the incentive effect of taxes and decrease the gain of trade.
How to use price elasticity?
Price elasticity of Demand, in combination with Price elasticity of Supply, can be used to find the incidence or burden of a per-unit tax is falling or to foresee where it will fall if the tax is levied. For example, when demand is perfectly inelastic, that means that consumers need the good and that the good is a necessity, so the quantity demanded remains consistent. Suppliers usually will increase the price by the full amount of the tax, and then the consumer will bare the full amount of tax. But when demand is perfectly elastic, that means there are other substitutes for the consumer or they can buy it cheaper somewhere else, this causes consumers to stop buying the good or service in question completely. Therefore, firms cannot pass the tax at all by raising prices, so they will have to pay for the tax themselves.
Why do governments impose taxes on tobacco?
Government use such goods taxes to achieve multiple objectives. And also excise tax are used by government to generate revenues. For the most common example, tobacco, government impose three types of tax on tobacco. One of the types is excise tax. While government enforce a wide diversity of taxes on tobacco products, it is the unique taxes to tobacco products called tobacco excise taxes that straight away effects the comparative prices of tobacco products. Therefore, it has an extreme control on tobacco use. As evidence, governments using a higher tobacco taxes as a means to discourage its use after it has assembled about the health and economic consequences. Historically the elementary objective of tobacco taxes has been revenue generation.
What is the concept of effective need to be discussed in the situation of what the tax is trying to accomplish in terms of?
The concept of effective need to be discussed in the situation of what the tax is trying to accomplish in terms of government policy. For example, in the situation of non-alcoholic beverages, it can be expected that objectives of a discriminatory tax on this products would be to raise revenue or externalize perceived harm from consumption, or both.
What are the negative externalities of traffic?
The negative externalities are – pollution to other people, possible accident to other other people, and time other people sit in traffic jams
Why do we get market failure?
If goods or services have negative externalities , then we will get market failure. This is because individuals fail to take into account the costs to other people. To achieve a more socially efficient outcome, the government could try to tax the good with negative externalities.
Why is the social marginal cost greater than the private marginal cost?
Because of the external costs the social marginal cost is greater than the private marginal cost.
What does the red triangle mean in a symlink?
The red triangle is the area of deadweight welfare loss. It indicates the area of overconsumption (where SMC is greater than PMC)
What happens if you drive a car?
If you drive a car, it creates air pollution and contributes to congestion. These are both external costs imposed on other people who live in the city. Building a new road. If you build a new road, the external cost is the loss of a beautiful landscape which people can no longer enjoy.
What happens if you play loud music at night?
Loud music. If you play loud music at night, your neighbour may not be able to sleep. Pollution. If you produce chemicals and cause pollution as a side effect, then local fishermen will not be able to catch fish. This loss of income will be the negative externality. Congestion.
What is the red triangle?
The red triangle is the area of dead-weight welfare loss.
What are tradable permits?
Correcting Negative Production Externalities: Tradable Permits. Firms are issued with emission permits in proportion to their levels of pollution. Firms that can reduce pollution at a low cost may sell their spare pollution permits to other generators who have a high cost of reducing pollution.
What are the advantages of tradable permits?
Tradable Permits: Advantages. -Firms are given a profit incentive to reduce the externality. -Consumers may benefit from the sale of the permits to other companies in the form of lower prices.
How does the government persuade consumers to change their behaviour?
The govt may choose to persuade consumers to change their behaviour through advertising campaigns that encourage them to stop consuming the product or switch to another product .
What is external cost?
Refers to the external costs created by the consumers during the course of using the product or service.
What are externalities in production?
They occur when the actions of consumers or producers give rise to negative or positive side effects on third parties that are not part of these actions and whose interests are not taken into consideration. Negative Production Externalities.
Why is there a production externality?
There is a production externality because over and above the firm's private costs of production (MPC), there are additional costs that spill over onto society. Correcting Negative Production Externalities: Taxes.
What are some laws that governments can create to deter the production of goods?
Such as banning companies from dumping waste, forcing cleaner production with improved technology, limiting emission levels and ordering firms to reduce the amount of goods they produce.

Negative Production Externalities
Negative Consumption Externalities
- Negative consumption externalities arise during consumption and result in a situation where the social cost of consuming the good or service is more than the private benefit. Private benefits refer to the positive factors rewarded to the producer or the consumer involved in a transaction. Social costs are negative factors impacting third parties. For example, when a person consume…
Remedies For Negative Externalities
- One of the solutions to negative externalities is to impose taxesto change people’s behavior. The taxes can be imposed to reduce the harmful effects of certain externalities such as air pollution, smoking, and drinking alcohol. An effective tax will equal the cost of the externality, and it is imposed with the goal of discouraging activities that c...
More Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Negative Externalities. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful: 1. Environmental Liability 2. Greenwashing 3. Network Effect 4. Pigouvian Tax