
Does DNA have a specific direction?
Since the two strands of double-helical DNA run in opposite (antiparallel) directions, continuous synthesis of two new strands at the replication forkwould require that one strand be synthesized in the 5′ to 3′ direction while the other is synthesized in the opposite (3′ to 5′) direction.
What direction does DNA run in?
What direction does DNA go in? DNA is always synthesized in the 5′-to-3′ direction, meaning that nucleotides are added only to the 3′ end of the growing strand. As shown in Figure 2, the 5′-phosphate group of the new nucleotide binds to the 3′-OH group of the last nucleotide of the growing strand.
What are the 5 steps of DNA replication in order?
What are the steps of DNA replication in order quizlet?
- Starts at? DNA Replication begins at the Origin of Replication.
- Unwinds. …
- Holds strands. …
- Two types of strands added 3′ to 5′ …
- RNA Primer. …
- Add bases. …
- Fix mistakes, remove RNA Primer. …
Does DNA directly controls protein synthesis?
Most of the time when a cell is not dividing, it is performing a series of activities under the control of the DNA in its nucleus. In order to do this, information from certain portions of the DNA in the chromosomes must be taken out into the cytoplasm, to be used to make (synthesise) control proteins (enzymes, etc) for the cell.
In which direction does DNA synthesis proceed quizlet?
DNA synthesis occurs in the 5′ → 3′ direction only and requires a large suite of specialized enzymes.
What synthesizes DNA in the 5 to 3 direction?
New DNA is made by enzymes called DNA polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize DNA in the 5' to 3' direction.
What direction does DNA flow?
It synthesizes the RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, while reading the template DNA strand in the 3' to 5' direction. The template DNA strand and RNA strand are antiparallel. RNA polymerase always builds a new RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction.
How does DNA synthesis occur and what is the direction of synthesis?
How does DNA synthesis occur, and what is the direction of synthesis? DNA synthesis occurs in the 5' to 3' direction because the phosphate of an incoming dNTP is linked to the 3' OH group of the growing strand. A higher-than-normal rate of DNA synthesis errors.
Is RNA synthesized 5 to 3?
RNA polymerase synthesizes an RNA strand complementary to a template DNA strand. It synthesizes the RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, while reading the template DNA strand in the 3' to 5' direction. The template DNA strand and RNA strand are antiparallel.
Why does DNA strand grow only in the 5 to 3 direction?
Answer and Explanation: A new DNA strand only grows in the 5' to 3' direction because the enzyme that adds new bases to a growing strand requires a free 3' OH group. The sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA is made up of phosphodiester linkages between 3' OH groups and 5' phosphate groups.
How is DNA synthesized?
DNA biosynthesis occurs when a cell divides, in a process called replication. It involves separation of the DNA double helix and subsequent synthesis of complementary DNA strand, using the parent DNA chain as a template.
What are the steps of DNA replication quizlet?
Terms in this set (4)DNA primase lays down an RNA primer.DNA polymarase 3 puts together DNA nucletoids to make a long strand.DNA polymarase 1removes RNA and replaces with DNA.ligase links them together.
Which strand is synthesized towards the Replication fork?
the leading strandOne strand is synthesized continuously in the direction of the replication fork; this is called the leading strand. The other strand is synthesized in a direction away from the replication fork, in short stretches of DNA known as Okazaki fragments. This strand is known as the lagging strand.
In which direction does the DNA polymerase build a new strand?
Leading Strand and Lagging Strand The first one is called the leading strand. This is the parent strand of DNA which runs in the 3' to 5' direction toward the fork, and it's replicated continuously by DNA polymerase because DNA polymerase builds a strand that runs antiparallel to it in the 5' to 3' direction.
What direction does the DNA polymerase read the DNA template?
3'–5' directionSince DNA polymerase requires a free 3' OH group for initiation of synthesis, it can synthesize in only one direction by extending the 3' end of the preexisting nucleotide chain. Hence, DNA polymerase moves along the template strand in a 3'–5' direction, and the daughter strand is formed in a 5'–3' direction.
Why would DNA synthesis occur in both directions from an origin of replication?
Why would DNA synthesis occur in both directions from an origin of replication? DNA is double helix and DNA synthesis is 5' t0 3'. It allows DNA strands to overlap when reaching another origin of replication.
Why does DNA synthesis occur in the 5 '- 3 direction quizlet?
Why does DNA synthesis only proceed in the 5' to 3' direction? Because DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of a polynucleotide strand.
What is 5 and 3 in DNA structure?
Each end of DNA molecule has a number. One end is referred to as 5' (five prime) and the other end is referred to as 3' (three prime). The 5' and 3' designations refer to the number of carbon atom in a deoxyribose sugar molecule to which a phosphate group bonds.
Which DNA polymerase has 5 to 3 exonuclease activity?
Taq DNA polymerase has a domain at its amino terminus (residue 1 to 291) that has a 5'-3' exonuclease activity, a 3'-5' exonuclease domain in the middle (residue 292 to 423), and a domain at its C-terminus that catalyzes polymerase reactions.
What is meant by the 5 and 3 end of DNA?
The 5' and 3' specifically refer to the 5th and 3rd carbon atoms in the deoxyribose/ribose sugar ring. The phosphate group attached to the 5' end of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group at the 3' end of another nucleotide have the potential to form phospodiester bonds, and hence link adjacent nucleotides.
What is DNA Synthesis?
The biochemical method of creating a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule is known as DNA synthesis. In a cell, each of the two strands of the DNA molecule serves as a basis for a complementary strand synthesis.
How does DNA polymerase work?
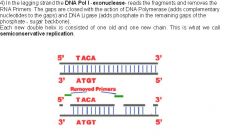
Each fragment is started with an RNA primer. Following that, DNA polymerase adds a short row of DNA bases in a 5′ to 3′ direction. The next primer will be inserted further down the lagging strand.
Why is DNA synthesis considered semiconservative?
Thus the DNA synthesis is done. DNA synthesis or replication is described as semiconservative because each DNA molecule is made up of one old and one new one.
Why is DNA synthesis important?
DNA synthesis occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, as well as in some viruses. Accurate DNA synthesis is necessary to prevent DNA mutations. In humans, mutations could lead to diseases such as DNA synthesis cancer and the machines involved in vivo have been extensively studied over the decades.
How many ends does one strand of DNA have?
One strand has a 5’ end and the other has a 3’ end. The two strands run in opposite directions. This determines the replication of each strand of DNA.
How does DNA replication work?
DNA replication also operates by using a DNA template, the DNA double helix unwinds during replication, opening unpaired bases for new nucleotides to hydrogen bonds. Gene synthesis, however, does not involve a DNA template and de novo genes are assembled.
Which enzyme eliminates all RNA primers from both strands of DNA until the new DNA has been formed?
The enzyme exonuclease eliminates all RNA primers from both strands of DNA until the new DNA has been formed.
How is DNA synthesis similar to living cells?
DNA synthesis during PCR is very similar to living cells but has very specific reagents and conditions. During PCR, DNA is chemically extracted from host chaperone proteins then heated, causing thermal dissociation of the DNA strands. Two new cDNA strands are built from the original strand, these strands can be split again to act as the template for further PCR products. The original DNA is multiplied through many rounds of PCR. More than a billion copies of the original DNA strand can be made.
How is DNA repaired?
Damaged DNA is subject to repair by several different enzymatic repair processes, where each individual process is specialized to repair particular types of damage. The DNA of humans is subject to damage from multiple natural sources and insufficient repair is associated with disease and premature aging. Most DNA repair processes form single-strand gaps in DNA during an intermediate stage of the repair, and these gaps are filled in by repair synthesis. The specific repair processes that require gap filling by DNA synthesis include nucleotide excision repair, base excision repair, mismatch repair, homologous recombinational repair, non-homologous end joining and microhomology-mediated end joining .
What is the term for the process of forming a new double stranded DNA molecule?
Complementary base pairing takes place, forming a new double-stranded DNA molecule. This is known as semi-conservative replication since one strand of the new DNA molecule is from the 'parent' strand. Continuously, eukaryotic enzymes encounter DNA damage which can perturb DNA replication.
Why is DNA replication so important in eukaryotic cells?
DNA replication machinery is therefore highly controlled in order to prevent collapse when encountering damage. Control of the DNA replication system ensures that the genome is replicated only once per cycle; over-replication induces DNA damage. Deregulation of DNA replication is a key factor in genomic instability during cancer development.
How does DNA replication occur?
In nature, DNA molecules are synthesised by all living cells through the process of DNA replication. This typically occurs as a part of cell division. DNA replication occurs so, during cell division, each daughter cell contains an accurate copy of the genetic material of the cell.
What is double stranded DNA?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. Structure of double-stranded DNA, the product of DNA synthesis, showing individual nucleotide units and bonds. DNA synthesis is the natural or artificial creation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules. DNA is a macromolecule made up of nucleotide units, which are linked by covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds, ...
What is DNA replication?
DNA replication occurs so, during cell division, each daughter cell contains an accurate copy of the genetic material of the cell. In vivo DNA synthesis (DNA replication) is dependent on a complex set of enzymes which have evolved to act during the S phase of the cell cycle, in a concerted fashion.
Why does DNA synthesis only proceed in the 5' to 3' direction?
Why does DNA synthesis only proceed in the 5' to 3' direction? 1.Because that is the direction in which the two strands of DNA unzip. 2.Because that is the only direction that the polymerase can be oriented. 3.Because the chromosomes are always aligned in the 5'to 3'direction in the nucleus. 4.Because the 3'end of the polynucleotide molecule is more electronegative than the 5'end. 5.Because DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 3'end of a polynucleotide strand.
Which direction does DNA ligase work?
d. DNA ligase works only in the 3'-> 5' direction
What is the final product of DNA replication?
The final product of DNA replication is: two DNA molecules, each of which contains one new and one old DNA strand. The information carried by DNA is incorporated in a code specified by the: specific nucleotide sequence of the DNA molecule. The enzyme DNA ligase is responsible for: linking short DNA segments.
Which end of a polynucleotide can DNA polymerases add nucleotides?
Because DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of a polynucleotide strand.
When can transcription begin?
d. Transcription can begin as soon as translation has begun even a little
Which type of chromosome has a single origin of replication?
b. Prokaryotic chromosomes have a single origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes have many.

Overview
DNA synthesis is the natural or artificial creation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules. DNA is a macromolecule made up of nucleotide units, which are linked by covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds, in a repeating structure. DNA synthesis occurs when these nucleotide units are joined to form DNA; this can occur artificially (in vitro) or naturally (in vivo). Nucleotide units are made up of a nitro…
DNA replication
In nature, DNA molecules are synthesised by all living cells through the process of DNA replication. This typically occurs as a part of cell division. DNA replication occurs so, during cell division, each daughter cell contains an accurate copy of the genetic material of the cell. In vivo DNA synthesis (DNA replication) is dependent on a complex set of enzymes which have evolved to …
Reverse Transcription
Reverse transcription is part of the replication cycle of particular virus families, including retroviruses. It involves copying RNA into double-stranded complementary DNA (cDNA), using reverse transcriptase enzymes. In retroviruses, viral RNA is inserted into a host cell nucleus. There, a viral reverse transcriptase enzyme adds DNA nucleotides onto the RNA sequence, generating cDNA that is inserted into the host cell genome by the enzyme integrase, encoding vi…
Polymerase chain reaction
A polymerase chain reaction is a form of enzymatic DNA synthesis in the laboratory, using cycles of repeated heating and cooling of the reaction for DNA melting and enzymatic replication of the DNA.
DNA synthesis during PCR is very similar to living cells but has very specific reagents and conditions. During PCR, DNA is chemically extracted from host c…
Gene synthesis
Artificial gene synthesis is the process of synthesizing a gene in vitro without the need for initial template DNA samples. In 2010 J. Craig Venter and his team were the first to use entirely synthesized DNA to create a self-replicating microbe, dubbed Mycoplasma laboratorium.
Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of sequences of nucleic acids. The majority of biological research and bioengineering involves synthetic DNA, which can include oligonucleotides, …