
What formula is used to find constant velocity?
Where:
- x, x0: Position of the body at a given time ( x) and at the initial time ( x0 ). ...
- v, v0: Velocity of the body at a given time ( v) and at the initial time ( v0 ). ...
- a: Acceleration of the body. Its unit of measure in the International System (S.I.) is the meter per second squared (m/s 2)
How can you tell if a velocity is constant?
- Sketch and label a graph of the velocity function v(t)= 3. v ( t) = 3.
- How far did the person travel during the two hours? ...
- Find an algebraic formula, s(t), s ( t), for the position of the person at time t, t, assuming that s(0)= 0. ...
- Sketch a labeled graph of the position function y = s(t). ...
- For what values of t t is the position function s s increasing? ...
How to find instantaneous velocity on a graph?
time graph and without an equation given
- Plot a graph of displacement over time.
- Choose point A and another point B that is near to A on the line.
- Find the slope between A and B, calculate several times, moving A nearer to B.
- Calculate the slope for an infinitely small interval on the line.
- The slope obtained is instantaneous velocity. ...
What does constant acceleration look like on a graph?
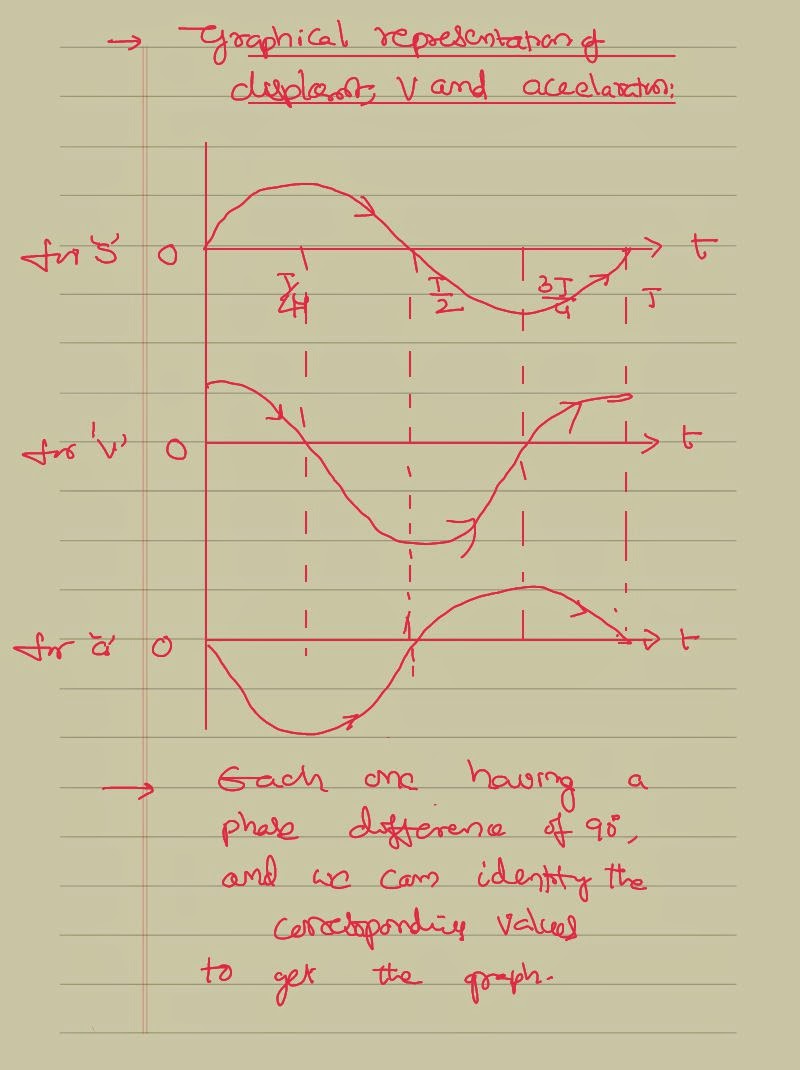
When acceleration is constant, the acceleration-time curve is a horizontal line. The rate of change of acceleration with time is a meaningless quantity so the slope of the curve on this graph is also meaningless. when two curves coincide, the two objects have the same acceleration at that time.
How do you find the constant velocity on a graph?
5:106:37Constant Velocity: Position vs. Time Graphs - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt's a horizontal line we know two things here we know that a horizontal line is a zero slope.MoreIt's a horizontal line we know two things here we know that a horizontal line is a zero slope.
What does constant velocity mean on a graph?
A constant velocity means the position graph has a constant slope (of 11.11 m/s). It's a straight line sloping up, and starting below the origin. The displacement is the area under the curve of the velocity graph.
Which line has a constant velocity?
horizontalSince the velocity is unchanging, the line is horizontal. Since the slope of a line on a v-t graph is the object's acceleration, a horizontal line (zero slope) on a v-t graph is characteristic of a motion with zeo acceleration (constant velocity).
Which part of graph shows motion with constant velocity?
Constant Velocity versus Changing Velocity Note that a motion described as a constant, positive velocity results in a line of zero slope (a horizontal line has zero slope) when plotted as a velocity-time graph.
What is constant velocity?
To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed in a constant direction. Constant direction constrains the object to motion in a straight path thus, a constant velocity means motion in a straight line at a constant speed.
Is vertical velocity constant?
This is to say that the vertical velocity changes by 9.8 m/s each second and the horizontal velocity never changes. This is indeed consistent with the fact that there is a vertical force acting upon a projectile but no horizontal force.
Is velocity constant in rectilinear path?
A body has constant velocity motion or uniform rectilinear motion when its trajectory is a straight line and its velocity is constant.
What is the graph for uniform velocity?
Hint: For a body in uniform motion, the magnitude of its velocity remains constant over time, that is, it has zero tangential acceleration that can change its speed. Hence, for uniform motion, the velocity-time graph will be a straight line.
Which of the following graph indicate uniform velocity?
A velocity-time graph with a flat line (slope of zero) indicates uniform motion.
Which graph shows an object with constant acceleration?
When acceleration is constant, the acceleration-time curve is a horizontal line.
How can you interpret that acceleration is constant from a velocity-time graph?
We can interpret the value of acceleration by observing the type of curve on the graph.
What is the slope of the velocity-time graph?
We know that we can calculate acceleration value from the typical velocity-time graph.
How to find velocity of a toy car?
The velocity can be calculated using the equation shown above where the displacement is 8 meters over a period of 5.20 seconds. Therefore, the velocity is 8 meters/5.20 seconds which is 1.54 meters/second. This data table and graph below show that the velocity of the toy car was constant. The velocity column was calculated by dividing the distance by the time.
What does cruise control do?
What cruise control does is to keep your velocity constant until you decide to either speed up (by stepping on the gas pedal) or slow down (by hitting the brakes). When cruise control was engaged, you were traveling with a constant velocity. Lesson Summary.
How to tell magnitude of velocity?
Velocity may also be represented in a diagram as an arrow like the one illustrated in the figure below. The magnitude of the vector is the length of the arrow, and the direction of the vector is where the arrow is pointing (which is 47 degrees North of East in this figure).
What is velocity in physics?
Velocity gives us information about the rate of change of your position, meaning how fast your position is changing per unit time. In physics, velocity is define d as the displacement divided by time where displacement is defined as the difference between your final and initial positions. Furthermore, when an object travels ...
What is constant velocity?
The velocity gives you information about the rate of change of your position or how fast your distance is changing per unit time. The table below lists the common units of velocity.
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
What is the direction of a velocity?
For direction, you may use any of the geographical directions (North, South, East, or West) and a positive sign or a negative sign (to represent up or to the right and down or to the left, respectively). An angle may also be used to give velocity direction.
How is the vector constant?
When you use a scalar as a constant. In that case, only the value of the scalar quantity needs to be kept unchanged over time.
What does the area between constant velocity and time graph represent?
Thus, the area between constant velocity and time graph always represents the displacement. Notice in the figure above that a particle has traveled from time a to time b with constant velocity v. And if the displacement of the particle is d
What happens to the velocity of a particle when it moves with a negative uniform velocity?
If you look closely at the graph of position-time, you will notice that first the particle moves with uniform velocity, then the velocity of the particle becomes zero and again the second time the particle moves with negative uniform velocity.
What happens to the stationary object if the force is zero?
According to Newton’s first law, if the total external applied force on a moving object is zero, then the moving object will move at constant velocity forever and the stationary object will be fixed forever.
What is constant velocity?
Constant velocity is the velocity that a particle acquires as a result of a particle crossing an equal linear path at certain time intervals.
What is acceleration in science?
Acceleration means a change in velocity in respect of time. And since the particle is moving in uniform uniformity, the change in velocity will be zero. Then the acceleration of the particle will be zero.
What happens if the total external applied force on a moving object is zero?
If the total external applied force on a moving object is zero then the object will move in uniform velocity. To prove this concept mathematically you need to take the help of Newton’s second law. Where the definition of force is given.
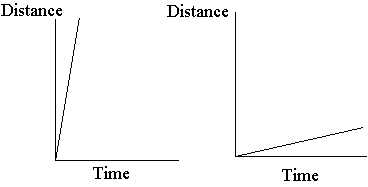
What happens when you have a high velocity?
If we have a high velocity, the graph has a steep slope. If we have a low velocity the graph has a shallow slope (assuming the vertical and horizontal scale of each graph is the same).
What is the formula for displacement s and time t?
a. `s = 12t` , for displacement s and time t.
What is the equation for y?
y = mx (where m is a constant and x is a variable).
Is velocity a constant or a variable?
Velocity is constant and time is a variable.
How to tell if an object is speeding up or slowing down?
Now how can one tell if the object is speeding up or slowing down? Speeding up means that the magnitude (or numerical value) of the velocity is getting large. For instance, an object with a velocity changing from +3 m/s to + 9 m/s is speeding up. Similarly, an object with a velocity changing from -3 m/s to -9 m/s is also speeding up. In each case, the magnitude of the velocity (the number itself, not the sign or direction) is increasing; the speed is getting bigger. Given this fact, one would believe that an object is speeding up if the line on a velocity-time graph is changing from near the 0-velocity point to a location further away from the 0-velocity point. That is, if the line is getting further away from the x-axis (the 0-velocity point), then the object is speeding up. And conversely, if the line is approaching the x-axis, then the object is slowing down.
How to tell if a graph is positive or negative?
The answers to these questions hinge on one's ability to read a graph. Since the graph is a velocity-time graph, the velocity would be positive whenever the line lies in the positive region (above the x-axis) of the graph. Similarly, the velocity would be negative whenever the line lies in the negative region (below the x-axis) of the graph. As learned in Lesson 1, a positive velocity means the object is moving in the positive direction; and a negative velocity means the object is moving in the negative direction. So one knows an object is moving in the positive direction if the line is located in the positive region of the graph (whether it is sloping up or sloping down). And one knows that an object is moving in the negative direction if the line is located in the negative region of the graph (whether it is sloping up or sloping down). And finally, if a line crosses over the x-axis from the positive region to the negative region of the graph (or vice versa), then the object has changed directions.
What is the lesson 4 of kinematics?
Lesson 4 focuses on the use of velocity versus time graphs to describe motion. As we will learn, the specific features of the motion of objects are demonstrated by the shape and the slope of the lines on a velocity vs. time graph. The first part of this lesson involves a study of the relationship between the shape of a v-t graph and the motion of the object.
How to find the speed of a graph?
1. Consider the graph at the right. The object whose motion is represented by this graph is ... (include all that are true): 1 moving in the positive direction. 2 moving with a constant velocity. 3 moving with a negative velocity. 4 slowing down. 5 changing directions. 6 speeding up. 7 moving with a positive acceleration. 8 moving with a constant acceleration.
What is the slope of a velocity time graph?
The principle is that the slope of the line on a velocity-time graph reveals useful information about the acceleration of the object. If the acceleration is zero, then the slope is zero (i.e., a horizontal line). If the acceleration is positive, then the slope is positive (i.e., an upward sloping line).
What does a positive slope mean on a velocity time graph?
This very principle can be extended to any conceivable motion. The slope of a velocity-time graph reveals information about an object's acceleration.
What does it mean when a velocity is negative?
As learned in Lesson 1, a positive velocity means the object is moving in the positive direction; and a negative velocity means the object is moving in the negative direction.
What happens if the acceleration function is zero?
If you are given an acceleration function or graph and it is zero (green line below), then the velocity is constant. If it is anything but zero, then the velocity is not constant. Answer link.
Is velocity constant if it is a curve?
If it is strictly a curve, then velocity is not constant. If you are given a velocity function and it is constant, then the velocity is constant. If you are given a velocity graph and it is horizontal (blue and green lines below), then the velocity is constant.
What Is Constant Velocity on A graph?
Velocity-Time Graph
What Is Constantly Variable on The Velocity-Time graph?
What Is Not Constant in Velocity-Time graph?
When Does The Velocity of The Object Is constant?
Is Acceleration Constant in The Velocity-Time graph?
- The y-axis represents velocity and the x-axis denotes time, hence the slope of the velocity-time graph gives acceleration. If the velocity increases at a consistent rate then the slope of the graph is found to be constant.
Is The Velocity of The Object Constant in The Velocity-Time graph?