When do profits start to decrease in the product life cycle?
Profits Start to Decrease: While this stage may be when the market as a whole makes the most profit, it is often the part of the product life cycle where a lot of manufacturers can start to see their profits decrease.
Why are the profits in the introduction stage of a product?
Nowadays successful products such as frozen foods and HDTVs lingered for many years before entering a stage of more rapid growth. Furthermore, profits in the introduction stage are negative or low due to the low sales on the one hand and high-distribution and promotion expenses on the other hand.
How do firms choose between market share and current profits?
In the growth stage, the firm must choose between a high market share and high current profits. By spending a lot of money on product improvements promotion and distribution, the firm can reach a dominant position. However, for that it needs to give up maximum current profits, hoping to make them up in the next stage.
What is the mature phase of the product life cycle?
In the mature phase of the product life cycle (PLC), the aggressive period of the growth stage is behind the market. One of the key characteristics of a mature market is that virtually all consumers have direct product experience – having previously purchased one or more products/brands.
What happens during the phase of maturity?
What is the growth phase of a company?
What is the last phase of the product life cycle?
What is the product life cycle?
What are the phases of the life cycle of a product?
Which stage of PLC aims at increasing the market share and profit?
The growth stageThe growth stage is when you should see rapidly rising sales, profits and your market share.
What is the maturity phase of PLC?
Maturity. In the maturity stage, sales slow down, indicating that the market has begun to reach saturation. This is also one of the stages of the product life cycle when pricing becomes competitive. This makes the profit margins thinner.
At what stage of growth is a business profitable?
Maturity. After several years in business, your company may hit a stage of maturity when it's more stable and profitable.
What are the 4 stages of PLC?
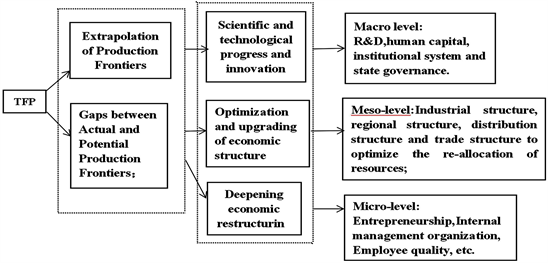
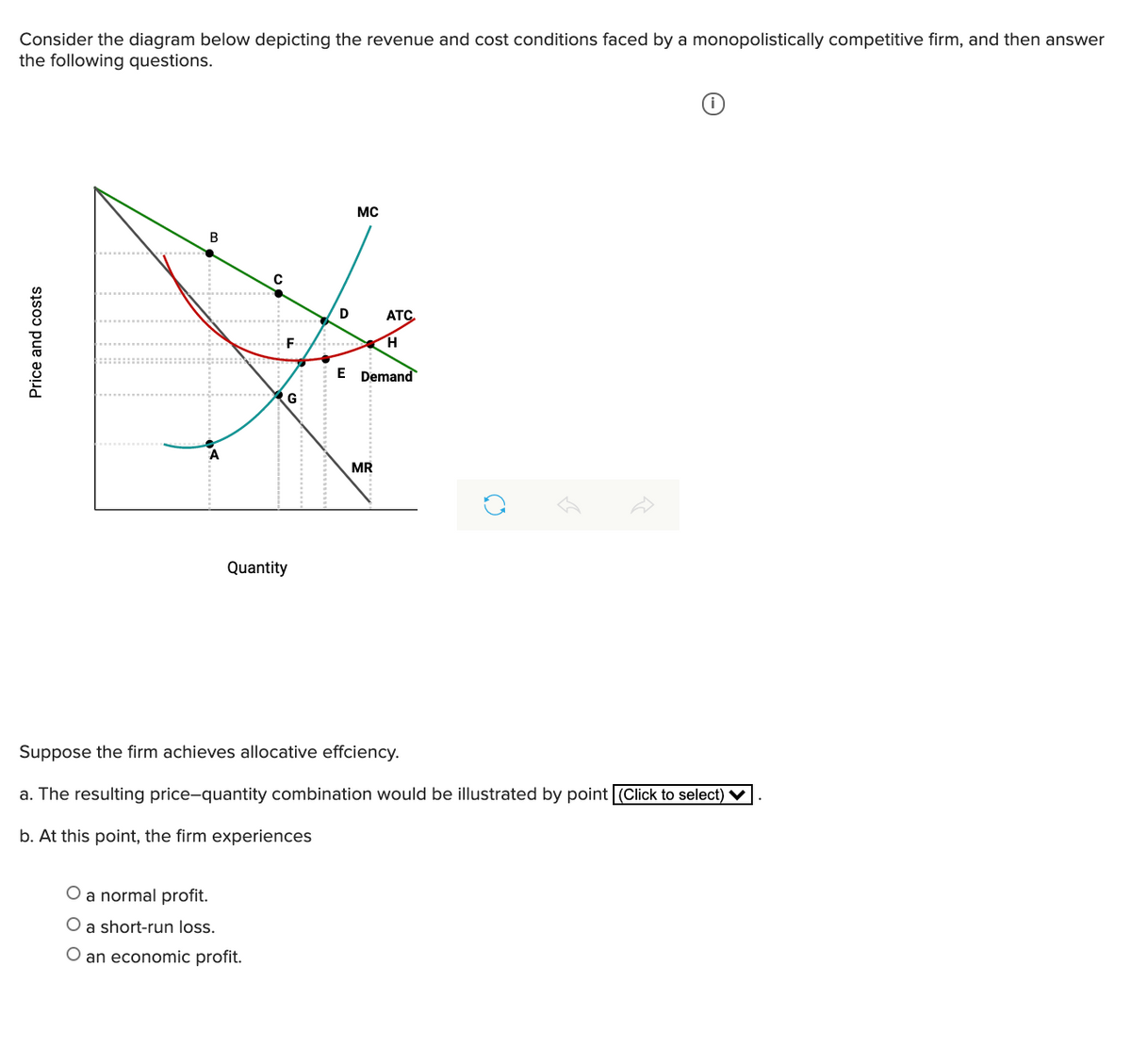
What is the Product Life Cycle? The product life cycle involves the stages through which a product goes from the time it is introduced in the market till it leaves the market. A product life cycle consists of four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
What is the meaning of maturity phase?
maturity stage. Definition English: Longest period in the life cycle of a firm, industry, or product, during which sales peak and start to decline. In economics, the final stage of economic growth characterized by high level of mass consumption.
What happens in the maturity phase?
The maturity stage is when the sales begin to level off from the rapid growth period. At this point, companies begin to reduce their prices so they can stay competitive amongst growing competition.
What are the three phases of maturity stage?
The maturity stage divides into three phases: growth, stable, and decaying maturity.
What are the stages of maturity?
Stages of MaturityInfant/Toddler (Newborn-4) At this level, maturity is tied to the instant gratification of needs and learning whom to trust. ... Child (5-11) ... Adolescent/Young Adult (12-18) ... Adult/Parent (19-59)
What happens during the phase of maturity?
Maturity: During the phase of maturity sales continue to increase but at a decreasing rate. When sales level off, the profit of both products and middlemen decline. The main reason is intense price competition, some firms extend their product lines with new models. Some examples are companies like Coca-cola, Dominos and other centuries-old companies still doing well but facing stiff competition from modern competitors.
What is the growth phase of a company?
Growth: Under the growth phase sales and profit rise, at a rapid pace. Competitors enter the market often in large numbers. As a result of competition, profit starts declining near the end of the growth phase. Some examples of companies under the growth stage are Uber, Airbnb etc. as they recently started getting popular.
What is the last phase of the product life cycle?
Saturation and decline: At last a point comes when it starts appearing that market has bought enough of the product. The decline in sales volume characterizes this last phase of the product life-cycle. The need or demand for product disappears. Availability of better and less costly substitutes in the market accounts for the arrival of these phases.
What is the product life cycle?
The Product Life Cycle (PLC) is the model that seeks to describe and explain the sales of a product from its introduction through to its obsolescence and withdrawal.
What are the phases of the life cycle of a product?
The life cycle of a product consists of four phases viz., introduction; Growth; Maturity; Saturation and Decline.
What is a mature market?
Mature markets provide firms with significant stability and generally provide the greatest level of profitability to the firm. In the Boston Consulting Group matrix, market leaders in a mature market are classified as “cash cows”. In other words, they are products that produce ongoing streams of income without too many challenges.
What is the mature phase of the product life cycle?
In the mature phase of the product life cycle (PLC), the aggressive period of the growth stage is behind the market. One of the key characteristics of a mature market is that virtually all consumers have direct product experience – having previously purchased one or more products/brands. This direct buying experience provides them with a good understanding of the various offerings, leading to stronger attitudes and more consistent loyalty and repeat purchase behavior.
What is the key market condition of a mature stage market?
As a result, a key market condition of a mature stage market is the stability of market shares. While there are some historical exceptions (primarily due to innovation), this principle generally holds in most markets. Therefore, existing competitors tend to develop “a holding pattern” of competitive behavior in order to protect their profitability, customer base, and market shares.
Why is there limited incentive to overly invest in a market share grab?
This is because there is limited incentive to overly invest in a “market share grab” because it is generally quite difficult and expensive to deliver on in a large scale. For example, in the 1980s, there were the “Cola Wars” between Coca-Cola and Pepsi-Cola. During this period of very aggressive promotions, product innovation, and retailer relationships battles – there was limited change in overall market share (some slight shift to Pepsi), resulting in an overall reduced profitability for both firms.
What happens to the market after the growth period?
Following the period of growth, a market will reach the maturity stage of its product life cycle. This means that there is limited growth – usually in line with the economy – left in the market. Sales have maximized and are unlikely, generally, to change significantly in the foreseeable future. In other words, the market has stabilized in terms of its sales volume.
Why are sales unlikely to change significantly?
The reason that sales are unlikely to change significantly (and continue strong growth) is that we have the absence of significant numbers of first-time consumers. First-time consumers – typically consumers switching from an older product offering to the new product offering – are the main reason that markets grow. Once we have a situation where “virtually every consumer” who is likely to buy the product, it is buying the product, then we have no “natural” growth left in the market.
Is profitability a key goal?
Most established firms realize that profitability is the key goal, in most cases, rather than a constant battle for market share. Therefore, in mature stage markets, there is a willingness to be less aggressive in terms of competitive rivalry.
How do profits decrease in product life cycle?
Profits Start to Decrease: While this stage may be when the market as a whole makes the most profit, it is often the part of the product life cycle where a lot of manufacturers can start to see their profits decrease. Profits will have to be shared amongst all of the competitors in the market, and with sales likely to peak during this stage, any manufacturer that loses market share, and experiences a fall in sales, is likely to see a subsequent fall in profits. This decrease in profits could be compounded by the falling prices that are often seen when the sheer number of competitors forces some of them to try attracting more customers by competing on price.
What is the decline in market share?
Decreasing Market Share: Another characteristic of the Maturity stage is the large volume of manufacturers who are all competing for a share of the market. With this stage of the product life cycle often seeing the highest levels of competition, it becomes increasingly challenging for companies to maintain their market share.
What is the maturity stage of a product?
The Maturity stage of the product life cycle presents manufacturers with a wide range of challenges. With sales reaching their peak and the market becoming saturated, it can be very difficult for companies to maintain their profits, let alone continue trying to increase them, especially in the face of what is usually fairly intense competition. During this stage, it is organizations that look for innovative ways to make their product more appealing to the consumer that will maintain, and perhaps even increase, their market share.
What happens after the introduction and growth stages?
After the Introduction and Growth stages, a product passes into the Maturity stage. The third of the product life cycle stages can be quite a challenging time for manufacturers. In the first two stages companies try to establish a market and then grow sales of their product to achieve as large a share of that market as possible. However, during the Maturity stage, the primary focus for most companies will be maintaining their market share in the face of a number of different challenges.
What happens to profits when a manufacturer loses market share?
Profits will have to be shared amongst all of the competitors in the market, and with sales likely to peak during this stage, any manufacturer that loses market share, and experiences a fall in sales, is likely to see a subsequent fall in profits.
What happens to sales volume during growth stage?
Sales Volumes Peak: After the steady increase in sales during the Growth stage, the market starts to become saturated as there are fewer new customers. The majority of the consumers who are ever going to purchase the product have already done so.
How does economies of scale help reduce costs?
Continued Reduction in Costs: Just as economies of scale in the Growth stage helped to reduce costs, developments in production can lead to more efficient ways to manufacture high volumes of a particular product, helping to lower costs even further.
Why is product life cycle strategy important?
Most important may be the fact that carrying a weak product delays the search for replacements and creates a lopsided product mix. It also hurts current profits and weakens the company’s foothold on the future. Therefore, proper product life cycle strategies are critical.
What happens when you drop a product from a product line?
Dropping the product from the product line may involve selling it to another firm or simply liquidate it at salvage value.
Why is it important to carry a weak product?
The reason is that carrying a weak product can be very costly to the firm, not just in profit terms. There are also many hidden costs. For instance, a weak product may take up too much of management’s time.
How to sustain rapid market growth?
Several product life cycle strategies for the growth stage can be used to sustain rapid market growth as long as possible. Product quality should be improved and new product features and models added. The firm can also enter new market segments and new distribution channels with the product. Prices remain where they are or decrease to penetrate the market. The company should keep the promotion spending at the same or an even higher level. Now, there is more than one main goal: educating the market is still important, but meeting the competition is likewise important. At the same time, some advertising must be shifted from building product awareness to building product conviction and purchase.
What is the growth stage of a product?
The growth stage is the stage in which the product’s sales start climbing quickly. The reason is that early adopters will continue to buy, and later buyers will start following their lead, in particular if they hear favourable word of mouth. This rise in sales also attracts more competitors that enter the market.
Why should cost plus pricing be used?
Cost-plus pricing should be used to recover the costs incurred.
How many stages are there in the product life cycle?
The Product Life Cycle contains mainly four distinct stages. For the four stages introduction, growth, maturity and decline, we can identify specific product life cycle strategies. These are based on the characteristics of each PLC stage. Which product life cycle strategies should be applied in each stage is crucial to know in order to manage the PLC properly.
What happens during the phase of maturity?
Maturity: During the phase of maturity sales continue to increase but at a decreasing rate. When sales level off, the profit of both products and middlemen decline. The main reason is intense price competition, some firms extend their product lines with new models. Some examples are companies like Coca-cola, Dominos and other centuries-old companies still doing well but facing stiff competition from modern competitors.
What is the growth phase of a company?
Growth: Under the growth phase sales and profit rise, at a rapid pace. Competitors enter the market often in large numbers. As a result of competition, profit starts declining near the end of the growth phase. Some examples of companies under the growth stage are Uber, Airbnb etc. as they recently started getting popular.
What is the last phase of the product life cycle?
Saturation and decline: At last a point comes when it starts appearing that market has bought enough of the product. The decline in sales volume characterizes this last phase of the product life-cycle. The need or demand for product disappears. Availability of better and less costly substitutes in the market accounts for the arrival of these phases.
What is the product life cycle?
The Product Life Cycle (PLC) is the model that seeks to describe and explain the sales of a product from its introduction through to its obsolescence and withdrawal.
What are the phases of the life cycle of a product?
The life cycle of a product consists of four phases viz., introduction; Growth; Maturity; Saturation and Decline.
Introduction Stage
- The introduction stage of a product’s life cycle is the initial phase. The introduction phase is identical to commercialisation’s last phase of the new product development process. This level often has larger marketing expenses than the preceding phases. As an illustration, consider the difference between the quantity of fuel a plane requires for t...
Growth Stage
- If a product is recognized by the market, its life cycle advances to the growth phase. The growth phase is characterised by rising sales, increased competition, and increased profitability. Unfortunately for the company, the boom phase attracts swiftly entering competitors. For instance, after Diet Coke’s tremendous popularity, Diet Pepsi was introduced by Pepsi. Coca-Col…
Maturity Stage
- After a large number of competitors enter the market and the number of prospective new customers decreases, the sales of a product often tend to stabilise. This denotes that a product’s life cycle has reached its maturity stage. The majority of consumer goods are at the mature phase of their life cycle, and the majority of their consumers are repeat customers as opposed to new …
Saturation and Decline Stage
- When sales begin to decline and continue to fall, a product has reached the decline phase of its product life cycle. Changes in customer preferences, technological advancements, and substitutes that satisfy the same need can contribute to a fall in product demand during the decline phase. How many of you do you believe have used a typewriter, a calculator, or a slide ru…