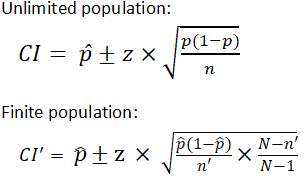
A good maximum sample size is usually 10% as long as it does not exceed 1000. A good maximum sample size is usually around 10% of the population, as long as this does not exceed 1000. For example, in a population of 5000, 10% would be 500.
Why is 30 statistically significant?
When the sample size approaches 30, the sampling distribution approaches normality regardless of the original distribution. Now for intereval estimation, the big leap that is made in practice is to assume that the sample standard deviation is a sufficient estimate for the population standard deviation.
How do you calculate Sample Size in statistics?
- determine the sample size needed to detect an effect of a given size with a given probability
- be aware of the magnitude of the effect that can be detected with a certain sample size and power
- calculate the power for a given sample size and effect size of interest
How to calculate sample proportion?
x: The count of individuals in the sample with a certain characteristic. n: The total number of individuals in the sample. We would then use this sample proportion to estimate the population proportion. For example, if 367 of the 1,000 residents in the sample supported the new law, the sample proportion would be calculated as 367 / 1,000 = 0.367.
How to pick sample size?
Sample size determination: In summary, the steps involved in estimating a sample size are: There must be a statement about what is expected of the sample. We must determine what is it we are trying to estimate, how precise we want the estimate to be, and what are we going to do with the estimate once we have it. This should easily be derived ...
What is the assumption used for nearly every statistical test?
Can we add a finite population correction to the confidence interval?
About this website

Is 10 percent a representative sample?
For populations under 1,000, a minimum ratio of 30 percent (300 individuals) is advisable to ensure representativeness of the sample. For larger populations, such as a population of 10,000, a comparatively small minimum ratio of 10 percent (1,000) of individuals is required to ensure representativeness of the sample.
What is the 10% rule in statistics?
The 10% condition states that sample sizes should be no more than 10% of the population. Whenever samples are involved in statistics, check the condition to ensure you have sound results. Some statisticians argue that a 5% condition is better than 10% if you want to use a standard normal model.
Why should the sample size be less than 10% of the population?
If the sample size is less than 10% of the population size, then the trials can be treated as if they are independent, even if they are not. Independent trials are trials in which the outcome of one trial does not influence the outcome of another.
What is a good effective sample size?
The sample size measures the number of individual samples measured or observations used in a survey or experiment. It is believed that a sample size of 30 is required for an analysis to be valid, then the effective sample size – rather than the actual sample size – is used in such an assessment.
Why do we use the 10% condition?
Conclusion. The 10% Condition says that our sample size should be less than or equal to 10% of the population size in order to safely make the assumption that a set of Bernoulli trials is independent.
Why is it important to check the 10% condition?
It's important to check the 10% condition before calculating probabilities involving x because we want to ensure that the observations in the sample are close to independent.
What is considered a small sample size?
There are appropriate statistical methods to deal with small sample sizes. Although one researcher's “small” is another's large, when I refer to small sample sizes I mean studies that have typically between 5 and 30 users total—a size very common in usability studies.
What is a minimum sample size?
Your minimum sample size is the minimum number of respondents you need to get survey results that reflect the population you are studying, whilst adhering to your desired confidence interval (margin of error) and confidence level.
What is a good sample?
What makes a good sample? A good sample should be a representative subset of the population we are interested in studying, therefore, with each participant having equal chance of being randomly selected into the study.
What is best a large or small sample size?
The first reason to understand why a large sample size is beneficial is simple. Larger samples more closely approximate the population. Because the primary goal of inferential statistics is to generalize from a sample to a population, it is less of an inference if the sample size is large.
What law is the 10% rule?
Lindemann gave the ten percent law in 1942. This law states that only 10 percent of energy in a food chain out of the total energy is transferred from one trophic level to another. The rest of the energy is utilized for other metabolic processes and some are released as heat.
What is the 10 rule quizlet?
When a consumer eats a producer, 10 percent of the producer's energy is passed on to the consumer trophic level.
Why does the 10% condition exist for normal sample distribution?
To convince yourself that something is going to go wrong when the sample gets too large compared to the population, consider the extreme case in which the sample size is the same as the population size: then there is only one possible sample mean, so the sampling distribution isn't really normal in any meaningful sense.. As for what exactly goes wrong: The CLT is an asymptotic result that ...
SAMPLE SIZE: HOW MANY IS ENOUGH? - Griffith University
1 SAMPLE SIZE: HOW MANY IS ENOUGH? Elizabeth Burmeister BN MSc Nurse Researcher Nursing Practice Development Unit, Princess Alexandra Hospital and Research Centre for Clinical and
What is the minimum sample size?
The minimum sample size is 100 . Most statisticians agree that the minimum sample size to get any kind of meaningful result is 100. If your population is less than 100 then you really need to survey all of them.
How big is the sample size for a population of more than 5000?
You will see on this table that the smallest samples are still around 100, and the biggest sample (for a population of more than 5000) is still around 1000. The same general principles apply as before – if you plan to divide the results into lots of sub-groups, or the decisions to be made are very important, you should pick a bigger sample.
How accurate is a sample of 1000 people?
Even in a population of 200,000, sampling 1000 people will normally give a fairly accurate result. Sampling more than 1000 people won’t add much to the accuracy given the extra time and money it would cost.
What is a basic survey?
Basic surveys such as feedback forms, needs assessments, opinion surveys, etc. conducted as part of a program.
What is the limiting factor in a survey?
In practice most people normally want the results to be as accurate as possible, so the limiting factor is usually time and money .
Can you calculate sample size using a formula?
That means you shouldn’t worry too much if you can’t use fancy maths to choose your sample size – you’re in good company.
Do you need a rough estimate of the results of a sample?
You only need a rough estimate of the results. You don’t plan to divide the sample into different groups during the analysis, or you only plan to use a few large subgroups (e.g. males / females). You think most people will give similar answers.
Why is a sample size smaller than necessary?
A sample that is larger than necessary will be better representative of the population and will hence provide more accurate results. However, beyond a certain point, the increase in accuracy will be small and hence not worth the effort and expense involved in recruiting the extra patients. Furthermore, an overly large sample would inconvenience more patients than might be necessary for the study objectives; this is unethical. In contrast, a sample that is smaller than necessary would have insufficient statistical power to answer the primary research question, and a statistically nonsignificant result could merely be because of inadequate sample size (Type 2 or false negative error). Thus, a small sample could result in the patients in the study being inconvenienced with no benefit to future patients or to science. This is also unethical.
How large should a sample be for a hypothesis?
So how large should a sample be? In hypothesis testing studies, this is mathematically calculated, conventionally, as the sample size necessary to be 80% certain of identifying a statistically significant outcome should the hypothesis be true for the population, with Pfor statistical significance set at 0.05. Some investigators power their studies for 90% instead of 80%, and some set the threshold for significance at 0.01 rather than 0.05. Both choices are uncommon because the necessary sample size becomes large, and the study becomes more expensive and more difficult to conduct. Many investigators increase the sample size by 10%, or by whatever proportion they can justify, to compensate for expected dropout, incomplete records, biological specimens that do not meet laboratory requirements for testing, and other study-related problems.
What is sample size calculation?
Sample size calculations require assumptions about expected means and standard deviations, or event risks, in different groups; or, upon expected effect sizes. For example, a study may be powered to detect an effect size of 0.5; or a response rate of 60% with drug vs. 40% with placebo.[1] When no guesstimates or expectations are possible, pilot studies are conducted on a sample that is arbitrary in size but what might be considered reasonable for the field.
Why is sample size important in multicenter studies?
The sample size may need to be larger in multicenter studies because of statistical noise (due to variations in patient characteristics, nonspecific treatment characteristics, rating practices, environments, etc. between study centers).[2] Sample size calculations can be performed manually or using statistical software; online calculators that provide free service can easily be identified by search engines. G*Power is an example of a free, downloadable program for sample size estimation. The manual and tutorial for G*Power can also be downloaded.
Why are studies conducted on samples?
Studies are conducted on samples because it is usually impossible to study the entire population. Conclusions drawn from samples are intended to be generalized to the population, and sometimes to the future as well. The sample must therefore be representative of the population. This is best ensured by the use of proper methods of sampling. The sample must also be adequate in size – in fact, no more and no less.
Is the population null in schizophrenia?
On a parting note, it is unlikely that population values will be null. That is, for example, that the response rate to the drug will be exactly the same as that to placebo, or that the correlation between height and age at onset of schizophrenia will be zero. If the sample size is large enough, even such small differences between groups, or trivial correlations, would be detected as being statistically significant. This does not mean that the findings are clinically significant.
What is a group of samples used for?
A group of samples can be used to generate a normal distribution that approximates the population distribution (central limit theorem). Repeating this process many times generates a cloud of curves whose spread is a representation of their standard error. For example,
Do statisticians use the term "normally distributed"?
They often use it in the context of assumptions of Linear Regression. I have seen many use the wording "The errors must be normally distributed".
Is having a large sample size bad?
This is not to say abandon hope, all ye who enter here --having a large sample size is certainly not bad! More samples is better, and you shouldn't limit yourself to small samples just to avoid having to deal with the divergence between the infinite population theory and the finite population reality. You just have to be a bit smarter with things like the finite population correction.
Do you need 30,000 samples for a parameter estimate?
First, you do NOT need a sample of 30,000 for good parameter estimates (i.e., estimates of the population characteristics) if you have good sampling.
Can you take a larger sample?
There's nothing stopping you taking a larger sample. What changes is the formulas for variances/standard errors of estimates (such as the standard error of the mean). If you take a small fraction of the population, you can ignore the difference between the formulas for sampling with replacement (e.g. the usual σ/√n for a standard error of a mean, which is estimated by s/√n) and without replacement (which is smaller), but once you get above a few percent of the population, they become noticeably different. See the finite population correction.
Should residuals be normally distributed?
I think it actually should be 'The residuals must be normally distributed'. Since there is no way one could know for sure about the Errors and whether they follow normal distribution or not.
What is sample size?
The sample size of a survey is the total number of complete responses that were received during the survey process. It is referred to as a sample because it does not include the full target population; it represents a selection of that population.
What is population size?
Population Size: The population size is the total number of people in the target population. For example, if you were performing research that was based on the people living in the UK, the full population would be approximately 66 million. Likewise, if you were conducting research on an organization, the total size of the population would be the number of employees who work for that organization.
What is confidence level?
Confidence level: The level of confidence of a sample is expressed as a percentage and describes the extent to which you can be sure it is representative of the target population; that is, how frequently the true percentage of the population who would select a response lies within the confidence interval. For example, if you have a confidence level of 90%, if you were to conduct the survey 100 times, the survey would yield the exact same results 90 times out of those 100 times.
What is population size?
N is population size. Within statistics, a population is a set of events or elements that have some relevance regarding a given question or experiment. It can refer to an existing group of objects, systems, or even a hypothetical group of objects.
What is a confidence interval in statistics?
In statistics, a confidence interval is an estimated range of likely values for a population parameter, for example 40 ± 2 or 40 ± 5%. Taking the commonly used 95% confidence level as an example, if the same population were sampled multiple times, and interval estimates made on each occasion, in approximately 95% of the cases, the true population parameter would be contained within the interval. Note that the 95% probability refers to the reliability of the estimation procedure and not to a specific interval. Once an interval is calculated, it either contains or does not contain the population parameter of interest. Some factors that affect the width of a confidence interval include: size of the sample, confidence level, and variability within the sample.
What are the factors that affect the width of a confidence interval?
Some factors that affect the width of a confidence interval include: size of the sample, confidence level, and variability within the sample.
What is confidence level?
The confidence level is a measure of certainty regarding how accurately a sample reflects the population being studied within a chosen confidence interval. The most commonly used confidence levels are 90%, 95%, and 99% which each have their own corresponding z-scores (which can be found using an equation or widely available tables like the one provided below) based on the chosen confidence level. Note that using z-scores assumes that the sampling distribution is normally distributed, as described above in "Statistics of a Random Sample." Given that an experiment or survey is repeated many times, the confidence level essentially indicates the percentage of the time that the resulting interval found from repeated tests will contain the true result.
What is the assumption used for nearly every statistical test?
In an introductory stats book by Nicole Radziwell "Statistics the easy way with R" , an assumption used for nearly every statistical test (e.g.t-tets, anova, etc) is that the sample size should not be more than 10% of the population size (where the population size in known).
Can we add a finite population correction to the confidence interval?
However, we can add a "finite population correction" term to this formula to obtain a confidence interval for the mean of a finite population of N units:
