
What is a diagnostic test for genetic disorders?
Diagnostic testing. If you have symptoms of a disease that may be caused by genetic changes, sometimes called mutated genes, genetic testing can reveal if you have the suspected disorder. For example, genetic testing may be used to confirm a diagnosis of cystic fibrosis or Huntington's disease.
Can genetic tests determine whether or not you will get a disease?
However, DTC tests cannot definitely determine whether or not you will get a disease and should not be used alone for decisions about your treatment or medical care. There are many different kinds of genetic tests. There is no single genetic test that can detect all genetic conditions.
What is the difference between genetic screening and diagnostic tests?
Screening tests evaluate an individual’s risk of developing a genetic condition, while diagnostic tests identify genetic conditions. All genetic tests have both benefits and limitations. Genetic screening tests are generally used in people who do not have signs or symptoms of a disorder.
What are the reasons for genetic testing?
Reasons for Genetic Testing. To learn whether you have a genetic condition that runs in your family before you have symptoms. To learn about the chance a current or future pregnancy will have a genetic condition. To diagnose a genetic condition if you or your child has symptoms.
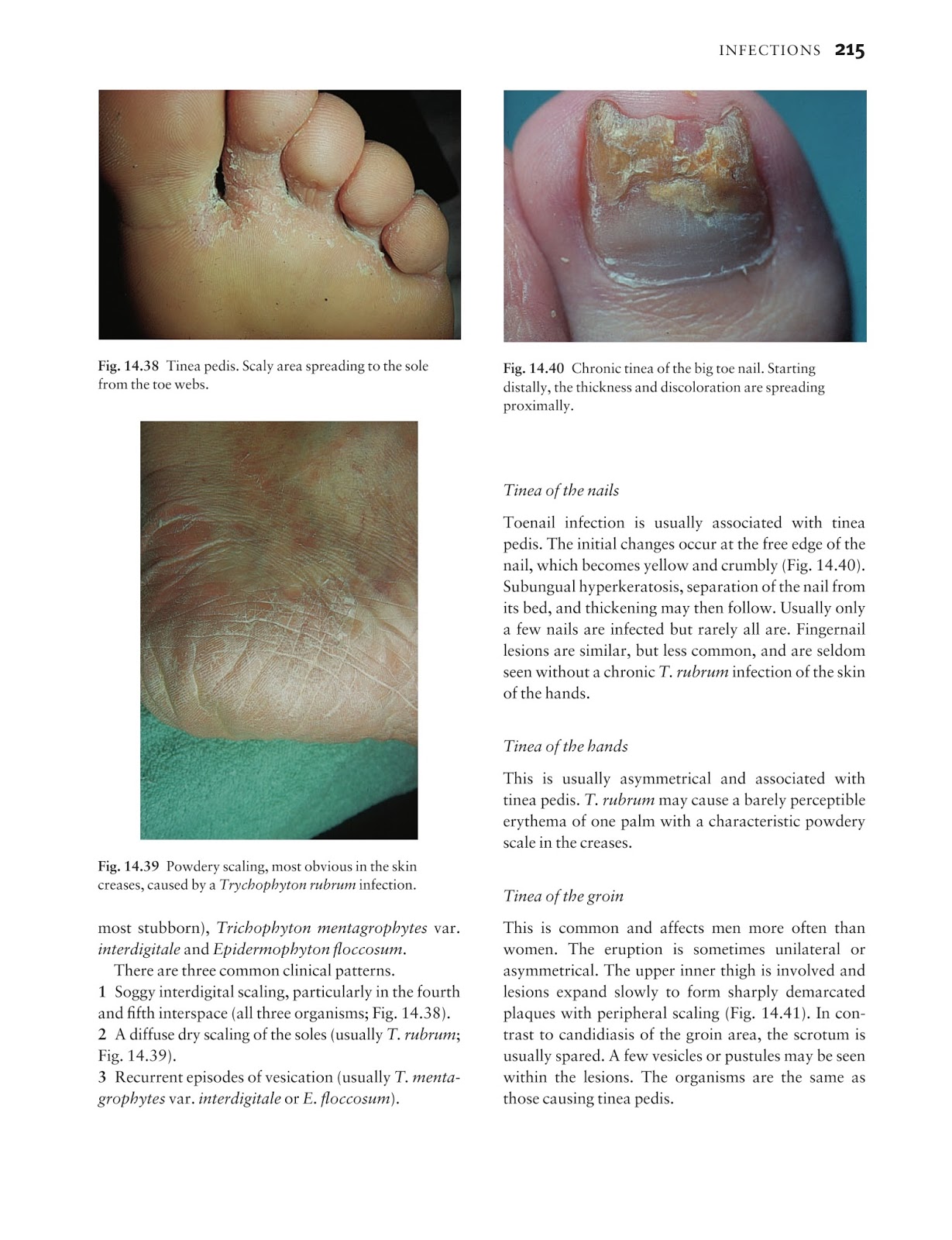
What is a diagnostic test to search for genetic abnormalities in the developing fetus?
Amniocentesis Amniocentesis Prenatal diagnostic testing involves testing the fetus before birth (prenatally) to determine whether the fetus has certain abnormalities, including certain hereditary or spontaneous genetic... read more is done if further testing is needed.
Which is a test that is looking for genetic abnormalities?
Genetic testing is a type of medical test that identifies changes in genes, chromosomes, or proteins. The results of a genetic test can confirm or rule out a suspected genetic condition or help determine a person's chance of developing or passing on a genetic disorder.
Is diagnostic testing genetic testing?
Diagnostic testing is used to identify or rule out a specific genetic or chromosomal condition. In many cases, genetic testing is used to confirm a diagnosis when a particular condition is suspected based on physical signs and symptoms.
What are the types of diagnostic genetic testing?
The following information describes the three main types of genetic testing: chromosome studies, DNA studies, and biochemical genetic studies. Tests for cancer susceptibility genes are usually done by DNA studies.
What is the meaning of genetic testing?
(jeh-NEH-tik TES-ting) The process of analyzing cells or tissue to look for changes in genes, chromosomes, or proteins that may be a sign of a disease or condition, such as cancer. These changes may also be a sign that a person has an increased risk of developing a specific disease or condition.
What is the meaning of DNA test?
Definition of DNA test : a test that examines DNA and that is used to identify someone or to show that people are relatives.
What is a diagnostic test for?
Diagnostic tests are used to confirm or rule out conditions and diseases. Before creating a treatment plan, your doctor needs critical information for a correct diagnosis, which a diagnostic test can provide.
What is screening and diagnostic tests?
Screening tests evaluate an individual's risk of developing a genetic condition, while diagnostic tests identify genetic conditions.
Is genetic screening and genetic testing the same?
Genetic testing is focused on an individual; genetic screening is really focused on a whole population of people, trying to identify those specifically who are [at] increased risk to develop it or to have children with a condition in question or the condition being screened for.
What tests are used to diagnose genetic disorders?
Laboratory tests, including genetic testing: Molecular, chromosomal, and biochemical genetic or genomic testing are used to diagnose genetic disorders. Other laboratory tests that measure the levels of certain substances in blood and urine can also help suggest a diagnosis.
What is genetic testing?
Genetic testing is one of several tools that doctors use to diagnose genetic conditions. The approaches to making a genetic diagnosis include: A physical examination: Certain physical characteristics, such as distinctive facial features, can suggest the diagnosis of a genetic disorder.
What does a genetic counselor ask about?
A doctor or genetic counselor will ask about health conditions in an individual's parents, siblings, children, and possibly more distant relatives. This information can give clues about the diagnosis and inheritance pattern of a genetic condition in a family.
When can you get a genetic diagnosis?
A diagnosis of a genetic disorder can be made anytime during life, from before birth to old age, depending on when the features of the condition appear and the availability of testing. Sometimes, having a diagnosis can guide treatment and management decisions.
Is genetic testing available?
Genetic testing is currently available for many genetic conditions. However, some conditions do not have a genetic test; either the genetic cause of the condition is unknown or a test has not yet been developed. In these cases, sequencing the entire genome may result in locating the responsible genetic variant.
Is diagnostic genetic testing only used for rare diseases
Simply, no. While rare diseases are what you might imagine this type of testing is designed for, diagnostic genetic testing is also often recommended for those who may have very common diseases and health conditions.
Benefits of early diagnostic genetic testing for children
An early diagnosis can make all the difference to children born with a genetic health disorder. Diagnostic genetic testing is crucial to ensuring your child receives the best and most helpful treatment and care.
My test came back positive, what does that mean for me?
Results for your diagnostic genetic testing may indicate you have an above-average risk for contracting a disease, but that doesn’t mean you will absolutely contract this disease. In the same way, results showing no markers for risk can’t guarantee that you won’t.
Why do people get genetic testing?
Someone may be offered diagnostic genetic testing if they were exhibiting symptoms that suggested a specific genetic condition. This type of testing can be carried out on individuals of any age to help establish a diagnosis.
What can a doctor do if a person has a genetic disorder?
If a doctor suspects that a person’s health problems are as a result of a genetic disorder, they can arrange for genetic testing to be performed to clarify the diagnosis. Diagnostic testing may also be arranged by a specialist e.g. a paediatrician who would send a blood sample to a genetics laboratory or by a clinical geneticist ...
Is genetic testing important?
It is important to remember, however, that establishing a diagnosis in an individual may have implications for other family members as well. When considering having diagnostic genetic testing, it is important to meet with a genetic counsellor who will help explain the varied implications for you and other family members.
What is a clinical genetic test?
Clinical genetic tests are different from direct-to-consumer (DTC) genetic tests, which can give some information about medical and non-medical traits. Clinical genetic tests are ordered by your doctor for a specific medical reason. DTC tests are usually purchased by healthy individuals who are interested in learning more about traits like ancestry, responses to medications, or risk for developing certain complex conditions. DTC test results can be used to make decisions about lifestyle choices or provide issues to discuss with your doctor. However, DTC tests cannot definitely determine whether or not you will get a disease and should not be used alone for decisions about your treatment or medical care.
What is the name of the test that looks at all the genes in the DNA?
external icon. looks at all the genes in the DNA (whole exome) or just the genes that are related to medical conditions (clinical exome). Genome sequencing. external icon. is the largest genetic test and looks at all of a person’s DNA, not just the genes.
What are some examples of DNA tests?
DNA is packaged into structures called chromosomes. Some tests look for changes in chromosomes rather than gene changes. Examples of these tests are karyotype and chromosomal microarrays. Gene expression. Genes are expressed, or turned on, at different levels in different types of cells.
What are some examples of genetic panel tests?
Some examples of genetic panel tests are low muscle tone, short stature, or epilepsy. Panel genetic tests can also be grouped into genes that are all associated with higher risk of developing certain kinds of cancer, like breast or colorectal (colon) cancer. Large-scale genetic or genomic testing. There are two different kinds ...
What can I do before and after genetic testing?
Genetic counseling before and after genetic testing can help make sure that you are the right person in your family to get a genetic test, you’re getting the right genetic test, and that you understand your results.
Why do gene expression tests compare cells?
Gene expression tests compare these levels between normal cells and diseased cells because knowing about the difference can provide important information for treating the disease.
Why is genetic testing important?
Genetic testing is useful in many areas of medicine and can change the medical care you or your family member receives. For example, genetic testing can provide a diagnosis for a genetic condition such as Fragile X or information about your risk to develop cancer. There are many different kinds of genetic tests.
What are chromosomal abnormalities?
Every cell in the body, or at least almost every cell, contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. This gives each person 46 chromosomes in total. Half of these come from the Mother, with the remaining half coming from the Father.
Genetic syndromes caused by chromosomal abnormalities
Down syndrome or Trisomy 21: caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21 in affected individuals. This chromosomal abnormality is one of the main chromosome diseases by prevalence and it occurs in 1 in every 700 live births in the US. Symptoms include unique facial features, developmental delay, and congenital heart defects.
The diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities process
The standard chromosome test is a type of genetic analysis known as karyotype testing which looks at the size, shape, and number of chromosomes within an individual.
When is testing recommended
During pregnancy. Some individuals opt for full genetic screening during pregnancy, regardless of whether they are believed to be at high risk for having a baby with chromosomal abnormalities. As awareness about rare diseases and genetic screening grows, more people are opting to undergo genetic analysis to rule out any genetic or health issues.
Genetic counseling first
Before anyone begins the process of diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities, the first step should be to consult with a genetic counselor. A genetic counselor will explain exactly what the process will involve, what it will look like, and what answers it may or may not provide.
Overview
Why It's Done
- Genetic testing plays a vital role in determining the risk of developing certain diseases as well as screening and sometimes medical treatment. Different types of genetic testing are done for different reasons: 1. Diagnostic testing.If you have symptoms of a disease that may be caused by genetic changes, sometimes called mutated genes, genetic test...
Risks
- Generally genetic tests have little physical risk. Blood and cheek swab tests have almost no risk. However, prenatal testing such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling has a small risk of pregnancy loss (miscarriage). Genetic testing can have emotional, social and financial risks as well. Discuss all risks and benefits of genetic testing with your doctor, a medical geneticist or a …
How You Prepare
- Before you have genetic testing, gather as much information as you can about your family's medical history. Then, talk with your doctor or a genetic counselor about your personal and family medical history to better understand your risk. Ask questions and discuss any concerns about genetic testing at that meeting. Also, talk about your options, depending on the test results. If yo…
What You Can Expect
- Depending on the type of test, a sample of your blood, skin, amniotic fluid or other tissue will be collected and sent to a lab for analysis. 1. Blood sample.A member of your health care team takes the sample by inserting a needle into a vein in your arm. For newborn screening tests, a blood sample is taken by pricking your baby's heel. 2. Cheek swab.For some tests, a swab sample fro…
Results
- The amount of time it takes for you to receive your genetic test results depends on the type of test and your health care facility. Talk to your doctor, medical geneticist or genetic counselor before the test about when you can expect the results and have a discussion about them.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.