A nucleus of an atom
Atom
An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small; typical sizes are around 100 picometers (1×10⁻¹⁰ m, a ten-milliont…
Is the nucleus of an atom positive?
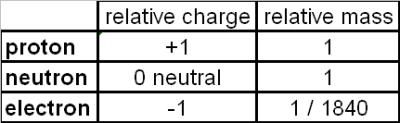
Yes. By definition the nucleus of an atom consists only of protons and neutrons. The electrons buzz around the nucleus in sort of fuzzy orbits a way off from the nucleus. Protons have a +1 positive electric charge and neutrons carry no charge, so by definition, a nucleus is always positive.
What is the charge of the nucleus of an atom?
2 Answers. The nucleus of an atom is constituted only by nucleons that can be protons or neutrons, in a number that is reported by the periodic table. Now, the charge of protons is always positive, the neutrons have no net charge (charge zero) then the total resulting charge of nucleus is positive, due only to the protons contribute. Nam D.
How do electrons move around the nucleus?
The electrons buzz around the nucleus in sort of fuzzy orbits a way off from the nucleus. Protons have a +1 positive electric charge and neutrons carry no charge, so by definition, a nucleus is always positive.
Is it possible for an atom to have an antimatter nucleus?
Atoms made of antimatter have a negatively charged nucleus. Atoms by definition have at least one proton and at least one electron orbiting it, so, yes. An interesting possible exception would be a neutron star, which would consist of a ginormous nucleus consisting of nothing but neutrons! Yes if it is matter.

Is a nucleus positive or negative?
positively chargedAn atom consists of a positively charged nucleus, surrounded by one or more negatively charged particles called electrons. The positive charges equal the negative charges, so the atom has no overall charge; it is electrically neutral.
Can nucleus be negative?
Explanation: Protons, massive, positively charged nuclear particles, have an opposite electronic charge to electrons, extra-nuclear particles of negligible mass. The positive/negative charge convention is entirely arbitrary.
Does a nucleus have positive charge?
Composition of the Atom. The atom consists of a tiny nucleus surrounded by moving electrons. The nucleus contains protons, which have a positive charge equal in magnitude to the electron's negative charge. The nucleus may also contain neutrons, which have virtually the same mass but no charge.
Is nucleus positively charged or neutral?
Because the nucleus is only made up of protons and neutrons it is positively charged. Was this answer helpful?
Why is the cell nucleus negatively charged?
DNA is negatively charged because of the presence of phosphate groups in nucleotides. The phosphate backbone of DNA is negatively charged, which is due to the presence of bonds created between the phosphorus and oxygen atoms.
Is neutron positive or negative?
electrically neutralMiller, a UW physics professor, has found that the neutron has a negative charge both in its inner core and its outer edge, with a positive charge sandwiched in between to make the particle electrically neutral.
How do you know the charge of a nucleus?
0:081:46Calculating the Charge of an Atom - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBy comparing the number of protons to the number of electrons. We can determine whether the chargeMoreBy comparing the number of protons to the number of electrons. We can determine whether the charge of an atom is positive or negative and also can calculate the total charge of the atom.
Can neutrons have charge?
Atoms of all elements—except for most atoms of hydrogen—have neutrons in their nucleus. Unlike protons and electrons, which are electrically charged, neutrons have no charge—they are electrically neutral.
Do neutrons have no charge?
neutron, neutral subatomic particle that is a constituent of every atomic nucleus except ordinary hydrogen. It has no electric charge and a rest mass equal to 1.67492749804 × 10−27 kg—marginally greater than that of the proton but 1,838.68 times greater than that of the electron.
How do you know if an atom is positive or negative?
If the atom has more electrons than protons, it is a negative ion, or ANION. If it has more protons than electrons,it is a positive ion.
What type of atom has a positive charge?
ProtonsProtons and Electrons A proton carries a positive charge (+) and an electron carries a negative charge (-), so the atoms of elements are neutral, all the positive charges canceling out all the negative charges.
What part of the atom has no charge?
neutronsIn the middle of every atom is the nucleus. The nucleus contains two types of subatomic particles, protons and neutrons. The protons have a positive electrical charge and the neutrons have no electrical charge.
Is proton positive or negative?
positive chargeA proton carries a positive charge (+) and an electron carries a negative charge (-), so the atoms of elements are neutral, all the positive charges canceling out all the negative charges. Atoms differ from one another in the number of protons, neutrons and electrons they contain.
What is the particle with no charge in the nucleus?
In the middle of every atom is the nucleus. The nucleus contains two types of subatomic particles, protons and neutrons. The protons have a positive electrical charge and the neutrons have no electrical charge.
Does the nucleus of a neutral atom have a charge?
Neutrons, also found in the nucleus, have no charge or a neutral charge. And electrons, found in the electron cloud outside the nucleus, have a negative charge.
Can a nucleus gain or lose energy?
As the electrons circle the nucleus they travel at certain energy levels but can "jump" between different energy levels if they gain or lose energy.
What is the difference between the mass of a nucleus and the mass of a protons and neutron?
I have found from this link http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/nucene/nucbin.html that: Nuclei are made up of protons and neutron, but the mass of a nucleus is always less than the sum of the individual masses of the protons and neutrons which constitute it. The difference is a measure of the nuclear binding energy which holds the nucleus together. This binding energy can be calculated from the Einstein relationship: Nuclear binding energy = Δ m c 2.
Why does a deuteron weigh more than a proton?
It's tempting to think of the binding energy as something that has to be added to a proton and neutron to glue them together into a deuteron, and therefore that the deuteron must weigh more than the proton and neutron because it has had something extra added to it. However this is the exact opposite of what actually happens.
Is the nucleus intrinsically negative?
The binding energy of the nucleus is intrinsically negative, in the same way that my total energy within the gravitational field is negative, so I am bound to that field. I am trapped.
Does binding energy compensate for the difference between the mass of the nucleons and that of the nucleus?
The binding energy doesn't compensate for the difference between the mass of the nucleons and that of the nucleus, it is that difference.
When is a positive ANA clinically significant?
Now that we understand what an ANA actually is, we can now start to approach the subject of clinical significance AND when you should be tested.
What does a speckled ANA mean?
So what does that mean? When the lab tech was looking at the fluoresceinated antibodies, it basically literally looked speckled. There are many other kinds of patterns: homogenous, centromere, nucleolar, speckled, rim etc. Each of these patterns possibly indicate the presence of specific nuclear antibodies. For example, the presence of a speckled positive ANA indicates the presence of these specific autoantibodies, SSA, SSB, RNP, Smith, and Ku antibodies. These specific nuclear antibodies are themselves associated with specific autoimmune diseases. It’s important to take ANA patterns with a grain of salt because interpretation highly depends on experience.
What happens if you have a negative ANA?
If the ANA is negative, the person likely will NOT develop an autoimmune disease. If the ANA is positive, then the person has a high risk of developing an autoimmune disease like lupus, scleroderma or Sjogren’s syndrome.
How much dilution is enough to consider an ANA as positive?
Every lab has different cut off values, but in general, an ANA of 1:80 is typically considered positive. Whether it’s clinically significant, is a whole different question. This is where the art of medicine comes into play. But before that, let’s talk about patterns because those are important too.
Why is ANA test low clinical significance?
In this scenario, I would say that this test is of low clinical significance because that person did not have any symptoms. Because so many people who are completely healthy have an ANA, the test should only be run if a person has a symptom or better yet, multiple symptoms that potentially indicate the presence of an autoimmune disease like lupus, Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, mixed connective tissue disease, etc. In that situation, it is helping rule in or rule out certain diagnoses.
Can a positive ANA test show lupus?
As a physician I care about symptoms and signs way more than lab tests. Don’t get me wrong, these tests are important. For example, over 99% of people suffering from systemic lupus erythematosus have a positive ANA. It’s pretty much safe to say that if someone tests negative for ANA, they likely don’t have lupus. FYI that other less than 1% usually have a positive SSA, they have a problem with their complement system, or they have a lot of protein in their urine (nephrotic syndrome).