What is the difference between public charity and private foundation?
What’s the difference between a public charity and a private nonprofit?
- Purpose. PC: Public charities typically carry out a direct charitable program. ...
- Public Support Test. PC: Public charities commonly need to pass one of two public support tests (unless they can prove they are within a few special categories like churches, hospitals ...
- Requirements. ...
How to start a private charitable foundation?
- Make grants worth at least 5 percent of your foundation’s investment assets each year
- Must provide grants only to other nonprofits or for educational scholarships
- Must pay up top a 2 percent excise tax on your foundation’s investment assets
What are the different types of private foundation grants?
Here are a few examples of foundations that support this grant:
- Kresge Foundation Challenge grant – They support 6 specific causes: health, arts and culture, the environment, human services, education, and community development.
- Smith Family Foundation – They support one-time capital expenses for nonprofits in Greater Boston
- Kroger Co. ...
What is the difference between a foundation and a nonprofit?
Main Differences Between Nonprofit and Foundation
- Non-profit organizations need not make charitable contributions to certain other organizations. ...
- Volunteers are most likely employed by non-profit organizations. ...
- Both in cases, the taxation process is quite different. ...
- Non-profit organizations release a few basic financial data to demonstrate and confirm the public’s significant support. ...

Is a private foundation considered a charitable organization?
A private foundation is a type of charitable organization that is typically established by an individual, family or corporation to support charitable activities.
What is the difference between a private foundation and public charity?
Private foundations and public charities are distinguished primarily by the level of public involvement in their activities. Public charities generally receive a greater portion of their financial support from the general public or governmental units, and have greater interaction with the public.
Are donations to a private foundation tax deductible?
Also, contributions to private operating foundations described in Internal Revenue Code section 4942(j)(3) are deductible by the donors to the extent of 50 percent of the donor's adjusted gross income (AGI), whereas contributions to all other private foundations (except those discussed under Private Pass-through ...
What qualifies as a charitable organization?
A charitable organization is a nonprofit organization that seeks to advance some public benefit. Public benefit includes a broad range of areas such as education, poverty alleviation, scientific research, environment, diversity, religion, and health.
How are private foundations taxed?
There is an excise tax on the net investment income of most domestic private foundations. This tax must be reported on Form 990-PF, Return of Private FoundationPDF, and must be paid annually at the time for filing that return or in quarterly estimated tax payments if the total tax for the year is $500 or more.
What tax form does a private foundation file?
Form 990-PFForm 990-PF must be filed by the 15th day of the 5th month following the close of the organization's accounting period. If the foundation is on a calendar year, or if it has no established accounting period, the return will be due May 15 each year.
What is the difference between a foundation and a 501c3?
A 501(c)(3) is a public charity, meaning that at least one third of its income must come from public donations. A private foundation is usually funded by a single individual or a small pool of individuals.
What is the difference between a nonprofit and a foundation?
Foundations are organizations that did not qualify as public charities. They are very similar to nonprofits, except money for a foundation usually comes from a family or a corporate entity, whereas nonprofit money often comes from their revenues.
How do private foundations make money?
They are usually funded by endowments from a single source such as an individual or group of individuals. Family foundations are usually funded by an endowment from a family. With family foundations, the family members of the donor(s) have a substantial role in the foundation's governance.
What is another name for charitable organization?
What is another word for charitable organization?benefitcharitycharitable institutionnon-profit organizationfundaid organizationnoble causemovementcharitable foundationendowment8 more rows
What are the 3 types of nonprofits?
There Are Three Main Types of Charitable Organizations Most organizations are eligible to become one of the three main categories, including public charities, private foundations and private operating foundations.
What are the 4 types of non profit organizations?
Association, Trust, or Corporation A nonprofit organization can organize itself in four ways: an unincorporated association, a trust, a corporation, or a limited liability company.
Can a public charity be called a foundation?
Public charities include a wide variety of charitable organizations, including hospitals, schools, churches, and organizations that make grants to others. Charities that primarily make grants are commonly referred to as public foundations.
Can a public charity call itself a foundation?
Every U.S. and foreign charity that qualifies under Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Service Code as tax-exempt is considered a private foundation unless it demonstrates to the IRS that it falls into another category.
What defines a public charity?
Generally, organizations that are classified as public charities are those that (i) are churches, hospitals, qualified medical research organizations affiliated with hospitals, schools, colleges and universities, (ii) have an active program of fundraising and receive contributions from many sources, including the ...
What is the difference between a nonprofit a charity and a foundation?
Charities typically have set spending requirements, whereas nonprofits are free of restrictions. Foundations are also free of spending requirements but often spend the majority of their funds on grant purposes and the remaining on charitable activities.
Who can help with a private foundation?
The task of establishing a private foundation may require the assistance of a CPA, lawyer or other advisors. Your advisors will initiate the process, which includes establishing the entity. This involves filing for tax-exempt status and other related administrative documents.
What is a public charity?
Public charities comprise the majority of charitable organizations (such as hospitals, schools and homeless shelters), community foundations and charities that sponsor donor-advised fund programs, an alternative to a private foundation. A donor-advised fund is a dedicated account for charitable giving that can be established under ...
What is a 501c3?
The IRS classifies every section 501 (c) (3) organization as either a private foundation or a public charity. A private foundation is typically controlled and funded by an individual or family: The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation is a well-known example. A private foundation is also subject to more-stringent tax laws and regulations than public charities. There are two types of private foundations: 1 Operating foundations are directly involved in operating a charitable project or enterprise such as a museum. 2 Non-operating foundations serve their charitable purpose primarily by making grants to charities. Although they can operate programs, that isn’t their primary purpose.
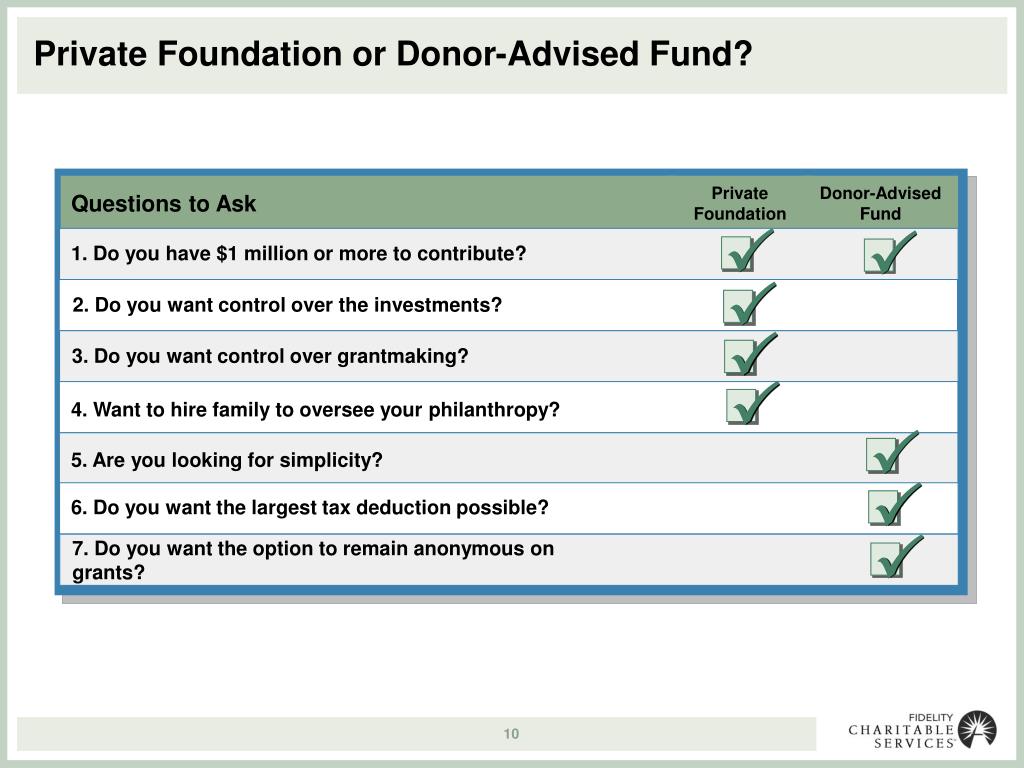
Why do you need a donor advised fund?
Donor-advised funds also offer streamlined recordkeeping because the sponsoring organization handles administrative reporting and other functions. Additionally, you can establish a donor-advised fund for significantly less than a private foundation. Some charities, like Fidelity Charitable, offer support and services for donors who make a generous philanthropic contribution to establish a donor-advised fund. In some cases, you may also consider using a donor-advised fund and a private foundation together for greater flexibility.
What is an operating foundation?
Operating foundations are directly involved in operating a charitable project or enterprise such as a museum.
What is a board of directors?
A board of directors or trustees oversees a private foundation and is responsible for receiving charitable contributions, managing and investing charitable assets, and making grants to other charitable organizations. It is also responsible for filing tax returns and other administrative reporting requirements.
What to consider before setting up a private foundation?
There are several administrative and tax considerations to keep in mind before setting up a private foundation. In many cases, the tax treatment and costs of a donor-advised fund may be more favorable.
What is a private foundation?
By definition, a private foundation is a 501 (c) (3) organization, usually established for the purpose of granting money to charitable causes. It is the default category the IRS assigns a nonprofit seeking 501 (c) (3) status, unless the applicant has requested and demonstrated suitability for public charity status.
What differentiates private foundations from public charities?
Another area that differentiates private foundations from their public charity counterparts is their ability to be funded by a small group of donors, even as few as one. The IRS requires public charities to have a diverse base of public support, but not so for private foundations. In fact, it is somewhat the exception to see a private foundation seeking outside donor support. Thus, more funding flexibility is experienced with a foundation.
What are the compliance requirements for private foundations?
Private foundations are subject to specific compliance regulations that govern their operations and financial activity. Some rules are the same or similar to those that govern other nonprofits, and some are unique only to private foundations.
What is Foundation Group?
For over 20 years, Foundation Group has helped start and maintain private foundations. Our team members provide expert assistance and support, designed to meet all of your structure and compliance concerns. From incorporation and 501 (c) (3) foundation status, to bookkeeping and IRS Form 990-PF compliance, our professionals have you covered.
Why do people start private foundations?
For those families and others that choose that path, they are embarking on a journey of philanthropy that can impact communities for good and establish a charitable legacy for years to come.
What is nonprofit organization?
Introduction. When most people think of a nonprofit organization, it is usually a public charity that first comes to mind. Whether it is a large organization that serves the entire world, or a much smaller charity, like a food pantry, that serves a single community, charities are the most visible of nonprofits.
How much do foundations have to distribute?
A private foundation is required by the IRS to distribute a minimum of 5% of average net investments each year. This is true even in years where the foundation experiences no additional income or investment return. Distributions that satisfy the 5% criteria include gifts and grants to charities and administrative costs associated with such activity. Also, qualifying distributions in excess of 5% can roll forward to help offset the distribution requirement of the next year.
What is a private foundation?
A private family foundation is one way to create a framework for giving that can enable you to establish a philanthropic legacy. It can also provide income tax and estate tax benefits, though other types of charitable giving vehicles, such as donor-advised funds, may provide more.
How does a private family foundation work?
There are no legal requirements specific to private family foundations—they are simply a type of private foundation governed and funded by family members and must meet all the same IRS guidelines for private foundations.
What is a donor advised fund?
A donor-advised fund is like a charitable investment account used for the sole purpose of supporting charitable organizations you care about. It can bear your family name or any other name of your choosing. After making an irrevocable contribution, the donating family can make recommendations to the sponsor to make grants to any IRS-qualified public charity over time; there are no mandatory annual disbursements.
How much tax do private foundations pay?
Although private foundations are exempt from federal income tax, their investment income is subject to an excise tax of 1 to 2 percent. It is increasingly common for families to transition an existing private foundation into a donor-advised fund with assistance from legal and tax advisors.
What is a good alternative to a private foundation?
One popular alternative to a private family foundation is a donor-advised fund, such as a Giving Account at Fidelity Charitable, which can also provide a way for families to create a structure for giving, while offering greater tax benefits and lower administrative burden.
How many private foundations are family foundations?
About 50 percent of private foundations in the U.S. are family foundations, according to the Council on Foundations. Family members will often serve as members of the foundation’s board, and will decide how the assets of the foundation can be used to meet the foundation mission—by making grants to charities or individuals.
What is family governance?
A family governance system spells out who participates in philanthropic discussions, expectations for time commitments to the foundation, grant recommendation guidelines, instructions for adding goals and ways to educate family members about the mission as they become old enough to participate. Setting up a private family foundation: As ...
Why do people choose private foundations over public charities?
Chief among those is control. In exchange for somewhat disadvantaged deductibility limits to donors, mandatory Form 990-PF filings, and minimum annual asset distributions (5% each year), private foundations can be controlled by related parties and be funded by a relatively small group…even one individual or family. This is often more than enough tradeoff for those starting a foundation.
Why do organizations need private foundations?
Another significant reason may simply be operational. If the organization has as its primary purpose the financial support of public charities, as opposed to operating a particular program, a private foundation is likely more appropriate.
How many tax filing requirements do charities have?
Also, public charities have 3 possible tax filing requirements, depending upon annual revenue (listed in order of complexity):
How does a charity represent the public interest?
In addition, a public charity must represent the public interest by having a diversified board of directors. More than 50% of the board must be unrelated by blood, marriage or outside business co-ownership and not be compensated as employees of the organization. We are often asked where that is in the “code” and, frankly, it isn’t there…at least not verbatim. It is an extrapolation of the IRS’s requirement that governance of a public charity be at arms-length and without private benefit (inurement)to insiders. As such, the IRS requires that a quorum of board members be possible who have no personal stake, either directly or potentially through relationship.
What is the income test for a charity?
Revenue. Finally comes the income test, better known as the public support test. Public charities must be supported by the general public. For that to be true, a significant amount of revenue, at least 33%, must come from relatively small donors (those who give less than 2% of the organization’s income), from other public charities, and/or the government. While that is significant, that leaves 67% to potentially come from other, less diverse sources.
What is public charity?
Public Charities. Public charities represent the largest share of active, 501(c)(3) organizations. Those starting a new organization usually prefer public charity status, not just because it better describes the organization’s purpose. Public charities also enjoy some advantages over private foundations:
What is a private operating foundation?
This is best thought of as a hybrid of the other two. This is a private foundation with direct program serviceslike that operated by public charities.
