Is acute tubular necrosis of the kidney reversible?
In most people, ATN is reversible. The goal of treatment is to prevent life-threatening complications of acute kidney failure. Treatment focuses on preventing the buildup of fluids and wastes, while allowing the kidneys to heal.
How long does acute tubular necrosis last?
Acute tubular necrosis can last for a few days or as long as several weeks. For relatively healthy people, the condition can be reversible. For those with other health conditions, recovery may take longer and may not be complete. Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/11/2020.
What is the pattern of injury that defines acute tubular necrosis?
The pattern of injury that defines acute tubular necrosis includes renal tubular cell damage and death. Intrarenal vasoconstriction or a direct effect of drug toxicity is caused by an ischemic event, nephrotoxic mechanism, or a mixture of both 2).
What are the treatment options for acute tubular necrosis?
Acute tubular necrosis - Treatment may include any of the following 1 Identifying and treating the underlying cause of the problem. 2 Restricting fluid intake. 3 Taking medicines to help control potassium level in the blood. 4 Medicines taken by mouth or through an IV to help remove fluid from the body.

How long does it take to recover from acute tubular necrosis?
Prognosis and Patient Counseling. The majority of patients recover from ATN with the renal failure phase typically lasting 7-21 days. However, depending on the severity of the initial insult, time to renal recovery can often be prolonged and patients may require dialysis for months.
How long does it take ATN to resolve?
Outlook (Prognosis) ATN can last for a few days to 6 weeks or more. This may be followed by 1 or 2 days of making an unusually large amount of urine as the kidneys recover. Kidney function often returns to normal, but there may be other serious problems and complications.
Is acute tubular necrosis fatal?
The most common causes of this cell damage are heart attacks, strokes, and clots that cut off blood flow to your kidneys. Kidneys can also be directly damaged by poisons and other harmful substances. Acute tubular necrosis can be fatal.
What are the long-term effects of acute tubular necrosis?
Concurrently, the long-term effects of AKI are increasingly appreciated, namely, increased risk of subsequent chronic kidney disease, end stage kidney disease requiring renal replacement therapies and a higher rate of cardiovascular events.
Can you fully recover from acute kidney failure?
Most people with AKI make a full recovery, but some people go on to develop chronic kidney disease or long-term kidney failure as a result. In severe cases, dialysis, where a machine filters the blood to rid the body of harmful waste, extra salt and water, may be needed.
How do you treat acute tubular necrosis?
Generally, the treatment of choice for nephrotoxic ATN is to stop all nephrotoxic agents to prevent further damage to the kidney. Of note, calcium channel blockers may have some use in cyclosporine toxicity, as they may reduce the vasoconstrictive action of cyclosporine.
Can kidneys repair themselves?
While a damaged kidney typically can't repair itself, the condition can be treated if caught early. Acute kidney failure can be reversed with prompt hospitalization, although the recovery process can take weeks to months and requires regular monitoring, diet modifications, and medications.
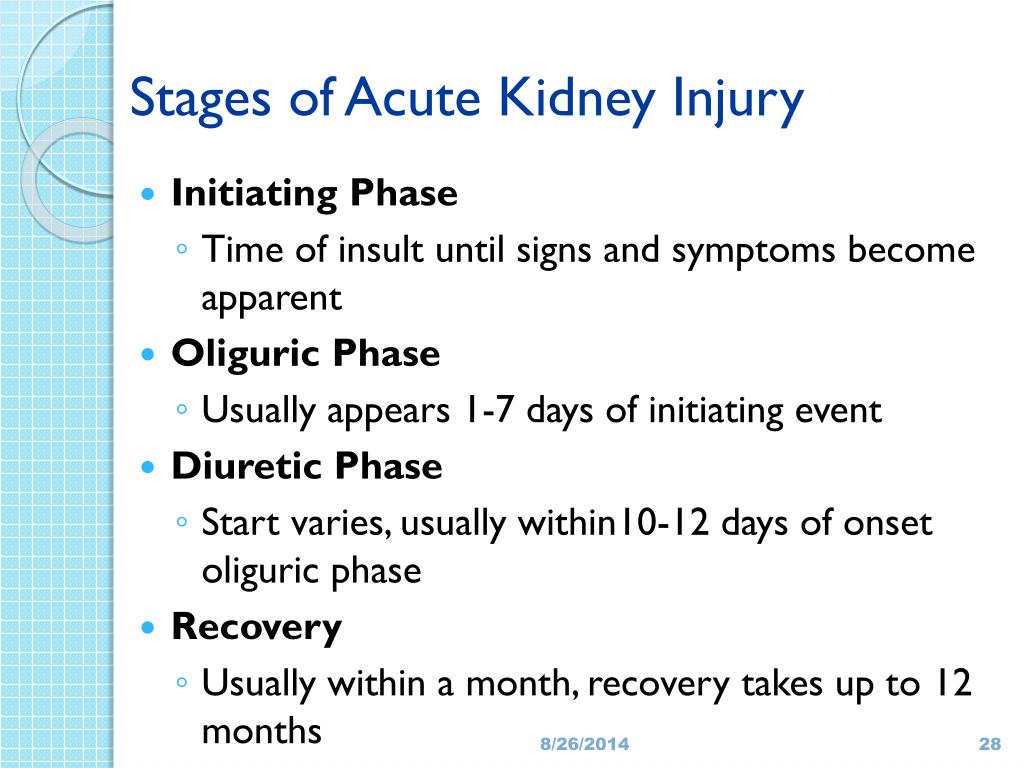
What are the 3 phases of ATN?
The course of ATN can be divided into three phases:Onset or initiating phase. Lasting hours or days, this is the time from onset of the precipitating event (for example, toxin exposure) until tubular injury occurs.Maintenance phase. ... Recovery phase.
How do you heal your kidneys?
What can I do to keep my kidneys healthy?Make healthy food choices. ... Make physical activity part of your routine. ... Aim for a healthy weight. ... Get enough sleep. ... Stop smoking. ... Limit alcohol intake link. ... Explore stress-reducing activities. ... Manage diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease.More items...
Does AKI cause permanent damage?
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is an increasingly common complication of hospitalization and acute illness. Experimental data indicate that AKI may cause permanent kidney damage through tubulointerstitial fibrosis and progressive nephron loss, while also lowering the threshold for subsequent injury.
How can acute tubular necrosis be prevented?
Preventing acute tubular necrosis To avoid ATN, treat conditions that decrease oxygen and blood flow to the kidneys. Control existing disorders such as diabetes, heart conditions, and liver disease. Drink plenty of water after using any contrast dyes.
What happens when there is tubular necrosis?
Acute tubular necrosis is kidney injury caused by damage to the kidney tubule cells (kidney cells that reabsorb fluid and minerals from urine as it forms). Common causes are low blood flow to the kidneys (such as caused by low blood pressure), drugs that damage the kidneys, and severe bodywide infections.
Why is it difficult to identify toxic causes of acute tubular necrosis?
It is difficult to identify toxic causes of acute tubular necrosis, because they often develop in the context of therapy for other illnesses or may result from difficult-to-identify exogenous agents. The isometric vacuolization of intravenous IgG must be distinguished from that of other osmotic agents.
What causes tubular necrosis?
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) can be caused by transient ischemia, since the high metabolic rate of proximal tubules makes them unusually susceptible to interruptions in energy or oxygen delivery. Clinically, ATN most often occurs following transient hypotension. If the whole kidney is involved by ATN, acute renal failure develops that is usually corrected over the course of days as precursor cells proliferate and reepithelialize tubules. Recovery is typically preceded by a marked diuresis and is usually complete if the patient survives because the extracellular matrix and tubular basement membranes are not damaged.
Is ATN a predictor of death?
ATN once was considered to be merely a marker of illness severity, rather than an independent predictor of mortality, because patients could be supported if necessary by means of dialysis. It is now clear, however, that ATN, as the most common presentation of AKI, is an independent predictor of death in hospitalized patients. 4,19–21 In patients with ATN and no other significant comorbid illness, mortality rates range between 5% and 25%. Various risk factors associated with increased mortality rates in patients with ATN include male gender, oliguria, sepsis, presence of malignancy, mechanical ventilation, older age, multiple organ dysfunction, and increased severity-of-illness scores. 22,23
Is autolysis a renal necrosis?
The renal weight is not increased in autolysis as it is in acute tubular necrosis, in which renal weights of 200 g and more are typical.
How long does ATN last?
ATN can last for a few days to 6 weeks or more. This may be followed by 1 or 2 days of making an unusually large amount of urine as the kidneys recover. Kidney function often returns to normal, but there may be other serious problems and complications. When to Contact a Medical Professional.
What are the risks of ATN?
Risks for ATN include: Blood transfusion reaction. Injury or trauma that damages the muscles.
Is ATN reversible?
In most people, ATN is reversible. The goal of treatment is to prevent life-threatening complications of acute kidney failure. Treatment focuses on preventing the buildup of fluids and wastes, while allowing the kidneys to heal. Temporary dialysis can remove excess waste and fluids.
How long does tubular necrosis last?
Acute tubular necrosis can last for a few days to 6 weeks or more . This may be followed by 1 or 2 days of making an unusually large amount of urine as the kidneys recover. Kidney function often returns to normal, but there may be other serious problems and complications.
What causes tubular necrosis?
Acute tubular necrosis is often caused by a lack of blood flow and oxygen to the kidney tissues (ischemia of the kidneys). Acute tubular necrosis may also occur if the kidney cells are damaged by a poison or harmful substance.
Can prerenal azotemia cause ischemic tubular necrosis?
In fact, any factor that leads to prerenal azotemia can lead to ischemic acute tubular necrosis. Some common causes include hypovolemic states such as diarrhea, vomiting, bleeding, dehydration, burns, renal losses via diuretics or osmotic diuresis, and third fluid sequestration. Edematous states such as heart failure and cirrhosis cause reduced kidney perfusion. Sepsis or anaphylaxis leads to systemic vasodilation. Coagulopathy, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), can also cause acute tubular necrosis.
What is the medical term for the death of tubular epithelial cells?
Acute tubular necrosis. Acute tubular necrosis ( ATN) is a medical condition involving the death of tubular epithelial cells that form the renal tubules of the kidneys. ATN presents with acute kidney injury (AKI) and is one of the most common causes of AKI. Common causes of ATN include low blood pressure and use of nephrotoxic drugs.
How long does it take to recover from ATN?
Because the tubular cells continually replace themselves, the overall prognosis for ATN is quite good if the underlying cause is corrected, and recovery is likely within 7 to 21 days.
Is tubular necrosis a renal injury?
Acute tubular necrosis is classified as a "renal" (i. e. not pre- renal or post-renal) cause of acute kidney injury. Diagnosis is made by a FENa ( fractional excretion of sodium) > 3% and presence of muddy casts (a type of granular cast) in urinalysis. On histopathology, there is usually tubulorrhexis, that is, localized necrosis of the epithelial lining in renal tubules, with focal rupture or loss of basement membrane. Proximal tubule cells can shed with variable viability and not be purely "necrotic".
Is ATN toxic or ischemic?
ATN may be classified as either toxic or ischemic. Toxic ATN occurs when the tubular cells are exposed to a toxic substance ( nephrotoxic ATN). Ischemic ATN occurs when the tubular cells do not get enough oxygen, a condition that they are highly sensitive and susceptible to, due to their very high metabolism.
How long does it take for ATN to resolve?
ATN-induced AKI usually requires more than 72 hours to resolve. It is advisable to query or escalate this to your physician advisor. References: UpToDate: Etiology and diagnosis of prerenal disease and acute tubular necrosis in acute kidney injury in adults, May 2020.
What causes 65-75% of AKI?
In the hospital setting, 65-75% of AKI is caused by one of two etiologies: prerenal causes and acute tubular necrosis (ATN). What is a “prerenal” condition?
What does ATN do to kidneys?
These cells are involved in helping regulate reabsorption of water and sodium (Na) out of the urine back into the bloodstream; in ATN, kidneys tend to lose water and sodium, making urine Na content higher and urine osmolality lower than that seen in prerenal AKI alone.
