
What does adipose tissue feel like?
What does adipose tissue feel like? Fat necrosis feels like a firm, round lump (or lumps) and is usually painless, but in some people it may feel tender or even painful. The skin around the lump may look red, bruised or occasionally dimpled.
What is the function of the adipose tissue?
Major Teaching Points
- Adipose tissue is required for the development of the breast throughout a life span of a women (embryonic development, puberty, pregnancy and lactation).
- Adipose tissue plasticity plays a major role in pregnancy and lactation by converting to PAT and epithelial cells.
- Correct involution requires proper adipose tissue functioning.
What are the different types of adipose tissue?
Types
- White adipose tissue: White adipose tissue (WAT) provides your body with energy, insulation, and protection, and is generally found around the hips, thighs, belly, or buttocks.
- Brown adipose tissue. A small amount of fat in your body is brown adipose tissue (BAT). ...
- Beige adipose tissue. ...
What does an adipose tissue look like?
Adipose tissue in the adult human appears white or yellowish in colour. In foetal life and in the newborn there is another variety of fat that is brownish in colour. The brown colour is in fact due to blood vessels. Brown fat is also present in adult animals of species which hibernate. We consider the commoner variety, white fat, first.

Is adipose in the dermis or epidermis?
In mammals, white adipose tissue (WAT) forms at specific bodily sites or depots. Major sites of adipocyte development include the visceral depot in the abdomen, subcutaneous adipocytes below the skin, and dermal adipocytes within the dermis of the skin (Gesta et al. 2007).
What layer of the skin is adipose tissue in?
hypodermisThe hypodermis, deep to the dermis of skin, is the connective tissue that connects the dermis to underlying structures; it also harbors adipose tissue for fat storage and protection.
Where are the adipose tissues found?
Where is my adipose tissue? Adipose tissue is commonly known as body fat. It is found all over the body. It can be found under the skin (subcutaneous fat), packed around internal organs (visceral fat), between muscles, within bone marrow and in breast tissue.
Which type of tissue is found in the dermis?
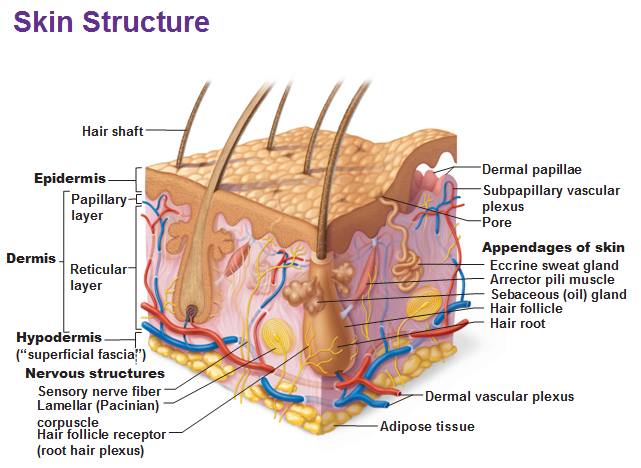
The dermis has connective tissue, blood vessels, oil and sweat glands, nerves, hair follicles, and other structures. It is made up of a thin upper layer called the papillary dermis, and a thick lower layer called the reticular dermis.
Where is the adipose tissue found quizlet?
Adipose tissue is found beneath the skin and around the heart and other organs. Adipose tissue is used for insulation, energy, and organ protection. Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat.
What is the location and function of adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue is found directly beneath the skin, between muscles, around the kidneys and heart, behind the eyeballs, and abdominal membranes. It serves as a layer of protection, absorbing shock potentially sustained by the tissue.
What type of tissue is adipose tissue?
connective tissueadipose tissue, or fatty tissue, connective tissue consisting mainly of fat cells (adipose cells, or adipocytes), specialized to synthesize and contain large globules of fat, within a structural network of fibres.
What two types of tissue make up the dermis?
What types of tissues make up the dermis? The papillary layer is areolar connective tissue, and the reticular layer is dense irregular connective tissue.
What types of tissues cells are found in the dermis quizlet?
What types of tissues/cells are found in the dermis? capillaries, nerves, glands, and hair follicles.
What types of tissues make up the epidermis and dermis?
1 – Layers of Skin: The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures.
Which layer of skin is abundant in adipose tissue quizlet?
Also called a subcutaneous layer, this is a layer of adipose tissue located under the dermis of the skin; helps to insulate the body and protects underlying muscles and blood vessels, stores nutrients.
Which tissue layer is generally supplied with adipose or fat cells?
HypodermisHypodermis is largely composed of adipose tissue (fat tissue), which is made up of adipocytes, or fat cells.
What is adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue, also known as fat tissue or fatty tissue, is a connective tissue that is mainly composed of fat cells called adipocytes. Adipocytes...
How is adipose tissue classified?
Adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that arises from the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes during fet...
Where is adipose tissue found?
Adipose tissue can be found in a number of different places throughout the body. White adipose tissue is the most abundant type of fat in humans. I...
What is the function of adipose tissue?
The main function of white adipocytes is to store excess energy in the form of fatty molecules, mainly triglycerides. Fat storage is regulated by s...
What are the most important facts to know about adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue is a specialized connective tissue mainly composed of fat cells known as adipocytes. Adipocytes can be subdivided into three cell ty...
Where is adipose tissue found?
Adipose tissue can be found in a number of different places throughout the body. White adipose tissue is the most abundant type of fat in humans. It is distributed within subcutaneous fat, visceral fat, and bone marrow fat. Subcutaneous fat is found throughout the whole body, in the spaces between the skin and underlying muscles. Visceral fat is predominantly found around the organs in the abdominal cavity, such as the liver, intestines and kidneys, as well as in the peritoneum (a serous membrane that lines the outside of the abdominal organs). White adipose tissue is also present in the bone marrow (a sponge-like tissue present in the central cavity of bones). In addition, white adipose tissue can be found in the pericardium surrounding the heart, or cushioning other parts of the body, like the soles of the feet, eyeballs, and certain blood vessels.
What is adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue, also known as fat tissue or fatty tissue, is a connective tissue that is mainly composed of fat cells called adipocytes. Adipocytes are energy storing cells that contain large globules of fat known as lipid droplets surrounded by a structural network of fibers.
What is the function of adipose tissue?
The main function of white adipocytes is to store excess energy in the form of fatty molecules, mainly triglycerides. Fat storage is regulated by several hormones, including insulin, glucagon, catecholamines ( adrenaline and noradrenaline), and cortisol. Depending on the body ’s immediate energy requirements, these hormones can either stimulate adipose tissue formation and storage (i.e. lipogenesis) or initiate the release of fat from adipose tissue (i.e. lipolysis ). Under the influence of insulin, for instance, adipocytes can increase the uptake of blood glucose and transform it into fatty molecules, thereby increasing fat storage.
What are the most important facts to know about adipose tissue?
Accordingly, adipose tissue can be classified as white adipose tissue, composed primarily of white and beige adipocytes, and brown adipose tissue, composed of brown adipocytes. White adipose tissue is the predominant type of fat in the human body. It can be found beneath the skin ( subcutaneous fat ), around internal organs (visceral fat), and in the central cavity of bones (bone marrow fat), as well as cushioning various parts of the body. Its main role is to serve as an energy storing reservoir, but it also insulates the body from extreme temperatures, cushions vital organs, and secretes hormones and biological factors. On the other hand, brown adipose tissue is mostly present during fetal life and in infants. It is mainly located in the upper back, above the clavicles, around the vertebrae, and in the mediastinum. The main role of brown adipose tissue is to generate heat through non-shivering thermogenesis; a process that’s especially important to prevent hypothermia in newborns.
What is the most common type of fat in the human body?
Accordingly, adipose tissue can be classified as white adipose tissue, composed primarily of white and beige adipocytes, and brown adipose tissue, composed of brown adipocytes. White adipose tissue is the predominant type of fat in the human body.
What is the difference between brown and white adipose tissue?
Based on the type of adipocytes, adipose tissue can be classified into two functionally different tissues: white adipose tissue, composed primarily of white and beige adipocytes, and brown adipose tissue, composed of brown adipocytes. The increased concentration of iron-containing mitochondria in brown adipocytes gives brown adipose tissue its ...
What is the name of the adipocytes that generate heat?
Beige adipocytes, also known as Brite adipocytes, are generally found scattered amongst pockets of white adipocytes and have the potential to generate heat under certain conditions, such as cold exposure and during stimulation of specific nervous adrenergic receptors . Based on the type of adipocytes, adipose tissue can be classified ...
Where is adipose tissue located?
Adipose Tissue Location. Adipose tissue is found in various places in the body. Some of these locations include the subcutaneous layer under the skin; around the heart, kidneys, and nerve tissue; in yellow bone marrow and breast tissue; and within the buttocks, thighs, and abdominal cavity.
What are the different types of adipose tissue?
There are three types of adipose tissue: white, brown, and beige adipose. White adipose stores energy and helps to insulate the body. Brown and beige adipose tissue burn energy and generate heat. Their color is derived from the abundance of blood vessels and mitochondria in the tissue.
Why is adipose tissue important?
In addition to storing fat, adipose tissue also produces endocrine hormones which regulate adipocyte activity and are necessary for the regulation of other vital bodily processes. Adipose tissue helps to cushion and protect organs, as well as insulate the body from heat loss.
What is the function of adipocytes?
Adipose, or fat, tissue is loose connective tissue composed of fat cells known as adipocytes. Adipocytes contain lipid droplets of stored triglycerides. These cells swell as they store fat and shrink when the fat is used for energy. Adipose tissue helps to store energy in the form of fat, cushion internal organs, ...
Which cells are derived from precursor cells that develop into one of three types of adipose tissue?
Other types of cells that comprise adipose tissue include fibroblasts, white blood cells, nerves, and endothelial cells . Adipocytes are derived from precursor cells that develop into one of three types of adipose tissue: white adipose tissue, brown adipose tissue, ...
Where is brown fat found?
In adults, small deposits of brown fat are found on the upper back, the side of the neck, the shoulder area, and along the spine. Infants have a greater percentage of brown fat than do adults. This fat can be found on most of the back region and is important for generating heat.
Where is adipose tissue located?
In humans, adipose tissue is located: beneath the skin ( subcutaneous fat ), around internal organs ( visceral fat ), in bone marrow ( yellow bone marrow ), intermuscular ( Muscular system) and in the breast ( breast tissue ). Adipose tissue is found in specific locations, which are referred to as adipose depots. Apart from adipocytes, which comprise the highest percentage of cells within adipose tissue, other cell types are present, collectively termed stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells. SVF includes preadipocytes, fibroblasts, adipose tissue macrophages, and endothelial cells.
Which layer of the body is the adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue contains many small blood vessels. In the integumentary system, which includes the skin, it accumulates in the deepest level, the subcutaneous layer, providing insulation from heat and cold. Around organs, it provides protective padding.
What is the stromal vascular fraction of adipose tissue?
In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes , fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Adipose tissue is derived from preadipocytes.
What is the layer of brown adipose tissue in the inguinal depot?
The inguinal depots enclose the inguinal group of lymph nodes.
How to find the relationship between subcutaneous adipose layer and total body fat?
The relationship between the subcutaneous adipose layer and total body fat in a person is often modelled by using regression equations. The most popular of these equations was formed by Durnin and Wormersley, who rigorously tested many types of skinfold, and, as a result, created two formulae to calculate the body density of both men and women. These equations present an inverse correlation between skinfolds and body density—as the sum of skinfolds increases, the body density decreases.
What is the role of adipose tissue?
Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and insulates the body. Far from being hormonally inert, adipose tissue has, in recent years, been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNFα ).
Where are the adipose depots in mice?
Mice have eight major adipose depots, four of which are within the abdominal cavity. The paired gonadal depots are attached to the uterus and ovaries in females and the epididymis and testes in males; the paired retroperitoneal depots are found along the dorsal wall of the abdomen, surrounding the kidney, and, when massive, extend into the pelvis. The mesenteric depot forms a glue-like web that supports the intestines and the omental depot (which originates near the stomach and spleen) and - when massive - extends into the ventral abdomen. Both the mesenteric and omental depots incorporate much lymphoid tissue as lymph nodes and milky spots, respectively.
Where is adipose tissue located?
Adipose tissue is distributed within two compartments of the human body: Parietal or subcutaneous fat, which is embedded in the connective tissue under the skin. Visceral fat, which surrounds the internal organs, such as eyeballs (periorbital fat) or kidneys (perirenal fat capsule).
What is adipose tissue?
Definition. A type of specialized connective tissue whose main functions are to store the energy, protect the organs and contribute to the endocrine profile of the body. Types.
Why do brown adipocytes have sponges?
In contrast to white adipocytes, brown adipocytes have the appearance of a sponge due to the multiple droplets in the cytoplasm. Groups of adipocytes are divided into lobules by connective septa, which contain a substantial amount of blood vessels and unmyelinated nerve fibers. The extracellular matrix between individual cells within the lobules is sparse.
Why do adipocytes appear empty?
This is described as "signet ring" appearance of the unilocular tissue. This is because the intracellular fat droplet gets dissolved when dyed with standard histology staining methods (H&E staining).
What are the two types of fat tissue?
Based on its location, fat tissue is divided into parietal (under the skin) and visceral (surrounding organs ). Depending on adipocyte morphology, there are two types of adipose tissue: White adipose tissue - mainly found in adults. Brown adipose tissue - mainly found in newborns.
What is the function of adipose tissue?
As it comprises about 20-25% of total body weight in healthy individuals, the main function of adipose tissue is to store energy in the form of lipids (fat). Based on its location, fat tissue is divided into parietal (under the skin) ...
Why are adipocytes important?
The strong external membrane of adipocytes is of key importance for resilience to mechanical stress and disruption.
What are the shapes of tissue?
A tissue has many layers and the cells have all kinds of shapes. They are columnar at the bottom, cuboidal in the middle, and squamous at the top. What would we call this tissue?
Where is the squamous epithelium found?
Simple squamous epithelium can be found in the kidney.
What is the thyroid made of?
The thyroid gland would be made of epithelial tissue.
What is the papilla of a hair follicle?
The papilla of a hair follicle is where blood vessels enter to nourish the hair matrix.
Which is thicker, the lip or the cheek?
The epithelium of the lips is thicker than that of the cheeks.
Is sweat a unicellular exocrine gland?
A sweat gland would be an example of a unicellular exocrine gland.
Which layer of the dermis is composed of loose connective tissue?
The papillary dermis is the superficial layer, lying deep to the epidermis. The papillary dermis is composed of loose connective tissue that is highly vascular. The reticular layer is the deep layer, forming a thick layer of dense connective tissue that constitutes the bulk of the dermis. Collagen is the principal component of the dermis.
What are the primary cells of the dermis?
Fibroblasts are the primary cells within the dermis, but histiocytes, mast cells, and adipocytes also play important roles in maintaining the normal structure and function of the dermis. The dermis is a connective tissue layer sandwiched between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissue. The dermis is a fibrous structure composed of collagen, ...
How does UV damage affect the dermis?
Aging and chronic sun exposure can weaken the dermis. Solar elastosis is due to chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure, resulting in damage to elastic fibers. Histology reveals basophilic degeneration of elastic fibers in the dermis.[29] The reduction of connective tissue in aging, usually with concomitant UV damage, causes actinic purpura (i.e., senile purpura) where the dermis cannot support its vasculature. As a result, minor trauma can lead to extravasation of blood.[30] Similar manifestations may be seen in chronic glucocorticoid users. Glomus tumors can also occur within the dermis and deeper tissues, especially within the digits and palms where glomus bodies are concentrated. [31]
What are the components of the dermis?
Collagen is the principal component of the dermis. Specifically, type I and type III collagen are found in abundance. Elastic fibers also play an important structural role within the dermis. Elastic fibers are composed of elastin and fibrillin microfibrils. In contrast to collagen , the biochemical configuration of elastin allows for gliding, stretching, and recoiling of fibers.[2] The reticular dermis comprises thick elastic fibers. Two subtypes of elastic fibers are worth further discussion: elaunin and oxytalan fibers[3]. Elaunin fibers are horizontally arranged elastic fibers found near the junction of the papillary and reticular dermis. Oxytalan fibers are perpendicular elastic fibers found in the papillary dermis. [4]
How is dermis examined?
The dermis is examined using a standard skin biopsy. The tissue sample should first be fixated with formalin to preserve tissue structure. After fixation, the specimen is dehydrated with an alcohol (e.g., ethanol) to remove water. The alcohol agent is then cleared using xylol.
What is the dermis in histology?
Histology, Dermis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. The dermis is a connective tissue layer sandwiched between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissue. The dermis is a fibrous structure composed of collagen, elastic tissue, and other extracellular components that includes vasculature, nerve endings, hair follicles, and glands.
What is the dermis?
The dermis is a connective tissue layer of mesenchymal origin located deep to the epidermis and superficial to the subcutaneous fat layer .[1] . The composition of the dermis is mainly fibrous, consisting of both collagen and elastic fibers. Between the fibrous components lies an amorphous extracellular "ground substance" containing ...
Adipose Tissue Composition
Adipose Tissue Location
- Adipose tissue is found in various places in the body. Some of these locations include the subcutaneous layer under the skin; around the heart, kidneys, and nerve tissue; in yellow bone marrow and breast tissue; and within the buttocks, thighs, and abdominal cavity. While white fat accumulates in these areas, brown fat is located in more specific a...
Adipose Tissue Endocrine Function
- Adipose tissue acts as an endocrine system organ by generating hormones that influence metabolic activity in other organ systems. Some of the hormones produced by adipose cells influence sex hormone metabolism, blood pressure regulation, insulin sensitivity, fat storage and use, blood clotting, and cell signaling. A major function of adipose cells is to increase the body's …
Sources
- "Adipose Tissue." You and Your Hormones, Society for Endocrinology,
- Stephens, Jacqueline M. "The Fat Controller: Adipocyte Development." PLoS Biology, vol. 10, no. 11, 2012, doi:
Overview
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Adipose tissue is derived from preadipocytes. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and insulates the body. Far from bein…
Anatomical features
In humans, adipose tissue is located: beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat), around internal organs (visceral fat), in bone marrow (yellow bone marrow), intermuscular (Muscular system) and in the breast (breast tissue). Adipose tissue is found in specific locations, which are referred to as adipose depots. Apart from adipocytes, which comprise the highest percentage of cells within adipose tissue, other cell types are present, collectively termed stromal vascular fraction (SVF) o…
Physiology
Free fatty acids (FFAs) are liberated from lipoproteins by lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and enter the adipocyte, where they are reassembled into triglycerides by esterifying them onto glycerol. Human fat tissue contains about 87% lipids.
There is a constant flux of FFAs entering and leaving adipose tissue. The net direction of this flux is controlled by insulin and leptin—if insulin is elevated, then there is a net inward flux of FFA, an…
Body fat meter
A body fat meter is a tool used to measure the body fat to weight ratio in the human body. Different meters use various methods to determine the ratio. They tend to under-read body fat percentage.
In contrast with clinical tools, one relatively inexpensive type of body fat meter uses the principle of bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) in order to determine an individual's body fat percentage. To achieve this, the meter passes a small, harmless, electric current thro…
A body fat meter is a tool used to measure the body fat to weight ratio in the human body. Different meters use various methods to determine the ratio. They tend to under-read body fat percentage.
In contrast with clinical tools, one relatively inexpensive type of body fat meter uses the principle of bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) in order to determine an individual's body fat percentage. To achieve this, the meter passes a small, harmless, electric current through the body and measu…
Animal studies
Within the fat (adipose) tissue of CCR2 deficient mice, there is an increased number of eosinophils, greater alternative Macrophage activation, and a propensity towards type 2 cytokine expression. Furthermore, this effect was exaggerated when the mice became obese from a high fat diet.
Gallery
• Diagrammatic sectional view of the skin (magnified).
• White adipose tissue in paraffin section
• Electronic instrument of body fat meter
See also
• Adipose differentiation-related protein
• Adipocytes
• Apelin
• Bioelectrical impedance analysis – a method to measure body fat percentage.
Further reading
• Stock MJ, Cinti S (2003). "Adipose Tissue / Structure and Function of Brown Adipose Tissue". Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition. pp. 29–34. doi:10.1016/B0-12-227055-X/00008-0. ISBN 978-0-12-227055-0.
• Vernon RG, Flint DJ (2003). "Adipose Tissue / Structure and Function of White Adipose Tissue". Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition. pp. 23–29. doi:10.1016/B0-12-227055-X/00007-9. ISBN 978-0-12-227055-0.