
Precautions
- Cough
- difficulty breathing
- difficulty with swallowing
- hives or welts
- hoarseness
- large, hive-like swelling on the face, eyelids, lips, tongue, throat, hands, legs, feet, or sex organs
- noisy breathing
- redness of the skin
- shortness of breath
- skin rash
What are the adverse effects of albuterol?
When corticosteroids are prescribed for asthma at higher levels than what your body naturally produces, it suppresses inflammation. It can also suppress your immune system. However, this is usually more likely when on higher doses of oral corticosteroids, such as prednisone.
Is albuterol an immunosuppressive medication?
Albuterol is not a steroid. Many websites that sell anabolic steroids typically lump Albuterol as a steroid, which is wrong. Albuterol is not a steroid but is classified as a symphatomimetic drug. Sympathomimetic drugs, like Albuterol, are used to treat cardiac arrest, low blood pressure, and other conditions.
Is albuterol considered a steroid?
It is possible to overdose on albuterol. Too much of this drug, which treats lung conditions such as asthma by opening up airways, can be life threatening. Instead of opening airways, too much albuterol can cause them to suddenly constrict, making it even harder to breathe. Other signs of an albuterol overdose can include: trouble falling asleep or staying asleep.
Is it possible to overdose on albuterol?

What kind of agonist is albuterol?
Albuterol is a beta agonist for bronchospasm that is refractory to epinephrine. This agent relaxes bronchial smooth muscle through its action on beta2 receptors; it has little effect on cardiac muscle contractility.
Is albuterol an agonist or antagonist?
Albuterol is beta-agonist for bronchospasm refractory to epinephrine. It relaxes bronchial smooth muscle by action on beta2-receptors, with little effect on cardiac muscle contractility.
Is albuterol beta adrenergic?
There are two types of β2 adrenergic agonist: short-acting β2 agonists (SABAs) and the long-acting β2 agonists (LABAs). The short-acting type has bronchodilatory effects for 4 to 6 hours, exemplified by albuterol.
Is albuterol cholinergic or adrenergic?
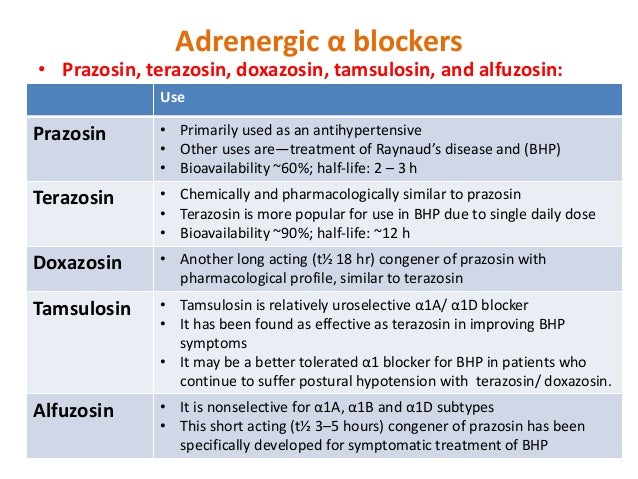
Lastly, beta-2 selective drugs are bronchodilators, such as albuterol and salmeterol. Adrenergic drugs can also be non-selective and hence bind to a combination of adrenergic receptors. Norepinephrine binds to the alpha-1, alpha-2, and beta-1 receptors.
What is the classification of albuterol?
Albuterol belongs to the family of medicines known as adrenergic bronchodilators. Adrenergic bronchodilators are medicines that are breathed in through the mouth to open up the bronchial tubes (air passages) in the lungs.
Is albuterol a beta-2 antagonist?
Some FDA-approved short-acting B2 agonists (SABAs) are albuterol, levalbuterol, metaproterenol, and terbutaline, and they are prescribed for bronchospasm caused by COPD, bronchial asthma, or emphysema.
Is albuterol a selective beta agonist?
Mechanism of Action: Albuterol is a selective Beta-2 agonist primarily used to cause bronchodilation in the lungs. However, Beta-2 receptors in the heart can also be stimulated, causing cardiovascular side effects. Indications: Albuterol is commonly used to treat asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
What are beta-2 agonists examples?
Examples of these short-acting medications include: albuterol (AccuNeb, Proventil HFA, ProAir HFA, Ventolin HFA) and levalbuterol (Xopenex, Xopenex HFA). Long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs) are taken on a daily basis to relax the muscles lining the airways that carry air to the lungs.
What is a beta 2 agonist inhaler?
Beta2 (ß2)-agonist medications are a type of inhaled bronchodilator used to treat asthma. In the pathophysiology of asthma, tightened airways cause wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and chronic cough. 1 ß2-agonists relax the smooth muscles of the airways to relieve these symptoms.
What are adrenergic agonist drugs?
Adrenergic agonists are drugs that work by mimicking the functioning of the sympathetic nervous system—the part of the nervous system that increases heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and eye pupil size.
Is albuterol an anticholinergic?
What are the two main types of bronchodilator medicines? There are beta 2-agonists (short- and long-acting forms) and anticholinergics. In inhaled forms, these medications include: Albuterol (Proventil® HFA, Ventolin® HFA, ProAir®HFA, Accuneb®).
Which drug is classified as an adrenergic antagonist?
Two examples of competitive adrenergic antagonists are propranolol and phentolamine. Phentolamine is a competitive and nonselective α-adrenoreceptor antagonist. Propranolol is a β-adrenoreceptor antagonist.
What is albuterol used for?
Albuterol is used for the treatment and prevention of bronchospasm (acute or severe) in patients with reversible obstructive airway disease. It also has an indication for the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm . This activity reviews the indications, contraindications, mechanism of action, adverse events, ...
What are the side effects of albuterol?
The primary adverse effects of albuterol therapy are tremors and nervousness, mostly seen in children who are 2 to 6 years of age, though can be seen at any age. Tremors are the result of activation of the beta-2 receptors found on the motor nerve terminals which increases intracellular cAMP.
How much albuterol should I take for bronchospasm?
Several forms of albuterol are accepted for the treatment of bronchospasm. A nebulized solution of 2.5 mg two or three times a day as needed is acceptable for quick relief of symptoms. Dosing of 1.25 to 5 mg every four to eight hours as needed of the nebulized solution is also effective for quick relief of symptoms.
How much albuterol is in an inhaler?
Albuterol comes in a variety of dosing forms and strengths. An aerosol metered-dose inhaler gives 90 mcg (base)/actuation, which is equivalent to 108 mcg of albuterol sulfate. The powder metered-dose inhaler form gives the same values as the aerosol metered-dose inhaler.
What role does a nurse play in albuterol?
While the clinician will initiate albuterol therapy, the nurse and pharmacist will play significant roles in contributing to the interprofessional team management of treatment . Nursing can provide education on administration and dosing, and monitor therapy at subsequent visits while also assessing patient adherence.
How often should I use a nebulizer for bronchospasm?
For the treatment of acute or severe bronchospasm, it is advisable to use a nebulizer solution with a concentration of 2.5 to 5 mg every 20 minutes for three cycles, followed by repeat nebulizer treatments of 2.5 to 10 mg every 1 to 4 hours as needed.
How often should I take 90 mcg inhaler?
If treating with a metered-dose inhaler, 4 to 8 puffs of 90 mcg every 20 minutes for up to 4 hours is a standard practice followed by 4 to 8 puffs every 1 to 4 hours as needed. For exercise-induced bronchospasm, the recommendation is to treat with aerosol or powder metered-dose inhaler before exercise.
2. Chemical Defense therapeutic area (s)
Albuterol has been investigated as a potential medical mitigation agent against both upper and lower chemical-induced pulmonary injury by the agents such as chlorine gas, mustard gas, phosgene and nerve agents sarin and soman.
4. Pharmacokinetic and toxicokinetics data
AIM: To study the pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability of salbutamol metered-dose inhaler (MDI) in healthy volunteers. METHODS: An HPLC method for the determination of salbutarnol in human plasma was improved. Ten healthy male Chinese volunteers were enrolled in a randomized crossover study.
7. Current off label utilization and dosing
The following dosing is from the National Asthma Education and Prevention guidelines.
10. Contraindication (s)
Albuterol tablets are contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to albuterol, or any of its components.
11. Clinical studies in progress
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) and a lesser condition that occurs prior to ARDS, Acute Lung Injury (ALI), are medical conditions that occur when there is severe inflammation and increased fluids (edema) in both lungs, making it hard for the lungs to function properly.
16. Global regulatory status
AccuNeb is indicated for the relief of bronchospasm in patients 2 to 12 years of age with asthma (reversible obstructive airway disease).
17. Other potentially useful information
Albuterol sulfate has been investigated as a potential medical mitigation agent against both upper and lower chemical-induced pulmonary injury.
Does albuterol cause heart problems?
Therefore, a person using albuterol may experience cardiovascular effects too. These include increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, tremors, and changes on their EKG. Lesson Summary. Albuterol is a medication that works to open up the airways affected by bronchoconstriction, known as bronchodialation.
Is albuterol a good asthma medicine?
Albuterol is an effective medication often used for asthma and COPD. In this lesson, we will learn about the pharmacokinetics of albuterol as well as its mechanism of action. Create an account.
Is albuterol a fast acting medication?
Albuterol can be used as a fast-acting rescue medication that provides relief quickly. Now that you have a basic understanding of what albuterol is for, let's look closer into the pharmacokinetics of albuterol. 3:29. You must c C reate an account to continue watching. Register to view this lesson.
What are the three categories of inhaled drugs?
The majority of inhaled drugs fall in the three categories employed in the treatment and prevention of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, namely β 2-adrenergic agonists (short- and long-acting), anticholinergics (short- and long-acting) and glucocorticosteroids . Drugs in these categories have been reviewed extensively elsewhere [19 ]. Drug candidates are selected to facilitate the study of solution and suspension MDI formulations. Drugs used in marketed pMDI products can be cited to cover the range of physico-chemical properties observed. Example drugs and their properties are shown in Table 4.1.
What drugs target GPCRs?
Some of the drugs targeting GPCRs are receptor agonists and include mu-opiate agonists for treatment of pain, β 2-adrenergic agonists used to treat asthma, and α2 -adrenergic agonists to treat glaucoma.
What is an adrenergic agonist?
Adrenergic agonists are autonomic nervous system drugs that stimulate the adrenergic receptors of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), either directly (by reacting with receptor sites) or indirectly (by increasing norepinephrine levels). An adrenergic agonist is also called a sympathomimetic because it stimulates the effects of SNS.
What is the effect of alpha adrenergic agonists on the pupil?
Alpha adrenergic agonists help dilate the pupils, decrease the secretion of aqueous humor, and increase the uveoscleral outflow. This mechanisms relieve the eyes of too much pressure. Shock is a complication most commonly caused by acute blood loss that can significantly alter the functions of the organs and tissues.
What are the effects of dobutamine on the heart?
They can increase the heart rate and cause bronchodilation as well as increasing the rate and depth of respirations. They can put patients with peripheral CV disease into exacerbation because of their vasoconstrictive effects. Lastly, dopamine is the sympathomimetic of choice for shock.
What are the therapeutic actions of alpha and beta agonists?
The desired and beneficial actions of alpha- and beta-agonists are as follows: Acting on the adrenergic receptors of the target organs, (i.e., increased heart rate and myocardial contractility with the heart, bronchodilation with lungs, decrease intraocular pressure with eyes).
What are the two classes of agonists?
Alpha- and Beta-Adrenergic Agonists. Alpha- and beta- agonists are drugs that are generally sympathomimetic. These agonists stimulate all of the adrenergic receptors so they affect both alpha- and beta-receptors. Popular examples of drugs under this class include dopamine, dobutamine, and epinephrine.
What are the interactions between alpha and beta agonists?
The following are drug-drug interactions involved in the use of alpha- and beta-agonists: Tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors ( MAOI ). Increased effects of these drugs related to increased norepinephrine levels or increased receptor stimulation that occurs with both drugs.
Why are older adults more likely to have toxic levels of the drug?
They are more likely to have toxic levels of the drug because of renal or hepatic impairments. Both adults and older adults must be cautioned against using OTC drugs and complementary therapies.
Albuterol Description
Albuterol (also known as salbutamol) is used to treat wheezing and shortness of breath caused by breathing problems (such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
May Treat: Acute asthma attack · Bronchospasm · Bronchospastic pulmonary disease · Exercise-induced bronchospasm
Brand Names: Vospire ER · Ventolin HFA · ProAir HFA · Proventil HFA · ProAir RespiClick and more
Drug Class: Asthma/COPD Therapy - Beta 2-Adrenergic Agents, Inhaled, Short Acting · Asthma/COPD Therapy - Beta Adrenergic Agents
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
May Treat: Acute asthma attack · Bronchospasm · Bronchospastic pulmonary disease · Exercise-induced bronchospasm
Brand Names: Vospire ER · Ventolin HFA · ProAir HFA · Proventil HFA · ProAir RespiClick and more
Drug Class: Asthma/COPD Therapy - Beta 2-Adrenergic Agents, Inhaled, Short Acting · Asthma/COPD Therapy - Beta Adrenergic Agents
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Lactation: Consult a doctor before using
Driving: May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Use caution
Albuterol - Clinical Pharmacology
Indications and Usage For Albuterol
Contraindications
Precautions
Adverse Reactions
- In vitro studies and in vivo pharmacologic studies have demonstrated that Albuterol has a preferential effect on beta 2-adrenergic receptors compared with isoproterenol. While it is recognized that beta 2-adrenergic receptors are the predominant receptors in bronchial smooth muscle, data indicate that there is a population of beta 2-receptors in the human heart existing i…
Overdosage
- Albuterol tablets are indicated for the relief of bronchospasm in adults and children 6 years of age and older with reversible obstructive airway disease.
How Is Albuterol Supplied
- Albuterol tablets are contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to Albuterol, or any of its components.
Frequently Asked Questions
- General
Albuterol, as with all sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, especially coronary insufficiency, cardiac arrhythmias, and hypertension; in patients with convulsive disorders, hyperthyroidism, or diabetes mellitus; and in patients who … - Information for Patients
The action of Albuterol tablets may last up to 8 hours or longer. Albuterol tablets should not be taken more frequently than recommended. Do not increase the dose or frequency of Albuterol tablets without consulting your physician. If you find that treatment with Albuterol tablets becom…
Chemical Defense Therapeutic Area
- In clinical trials, the most frequent adverse reactions to Albuterol tablets were: Rare cases of urticaria, angioedema, rash, bronchospasm, and oropharyngeal edema have been reported after the use of Albuterol. In addition, Albuterol, like other sympathomimetic agents, can cause adverse reactions such as hypertension, angina, vomiting, vertigo, central nervous system stimulation, un…
Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetics Data
- The expected symptoms with overdosage are those of excessive beta-adrenergic stimulation and/or occurrence or exaggeration of any of the symptoms listed under ADVERSE REACTIONS, e.g., seizures, angina, hypertension or hypotension, tachycardia with rates up to 200 beats/min, arrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, dry mouth, palpitation, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, …
Current Fda/Eua Approved Indications and Dosing
- Albuterol Tablets, USP are available containing Albuterol sulfate, USP 2.4 mg equivalent to Albuterol 2 mg or Albuterol sulfate, USP 4.8 mg equivalent to Albuterol 4 mg. The 2 mg tablets are white to off white color round shaped flat beveled edge tablets scored on one side and debossed with ' D126' on other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 100 tablets NDC 75834-273-0…
Current Available Formulations/Shelf Life
Current Off Label Utilization and Dosing
Route of Administration/Monitoring
Adverse Effects
Contraindication
Clinical Studies in Progress
Needed Studies For Non Chemical Defense Clinical Indications