The second generation H1-antihistamines such as fexofenadine (Allegra), loratidine (Claritin), cetirizine (Zyrtec) have less of a sedating effect. Cimetidine, a H2-antihistamine, blocks androgenic testosterone at high doses which has the side effect of gynecomastia, which is the enlargement of breasts in a male.
What are the similarities between H1 and H2 blockers?
What are the Similarities Between H1 and H2 Blockers? 1 Both are types of antihistamines. 2 They block the histamines receptors. 3 They are used for the treatment of human diseases. 4 Both exist as neutral receptor antagonists or inverse agonists. More ...
How do H1 blockers work?
H 1 histamine receptors exhibit constitutive activity. Therefore, H 1 blockers can be either neutral receptor antagonists or inverse agonists. Neutral receptor antagonists work by binding to the H1 receptor and blocking the activation of the receptor by histamine.
Is Zyrtec an H1 or H2 blocker?
Zyrtec and Benadryl are antihistamines, or H1 receptor blockers. They work by blocking histamine. Histamine is a substance your body makes during an allergic reaction, causing those pesky symptoms. By blocking histamine, Zyrtec and Benadryl help relieve allergy symptoms. Is Claritin an H1 or H2?
What is the difference between second and third generation H1-receptor blockers?
Second- and Third-generation Histamine H1-receptor Blockers. The second-generation of H1-receptor antagonists were developed in order to avoid the drowsy effects of the first class. These antihistamines have the same actions as the first-generation but are known for less daytime drowsiness, dry mouth, and confusion.
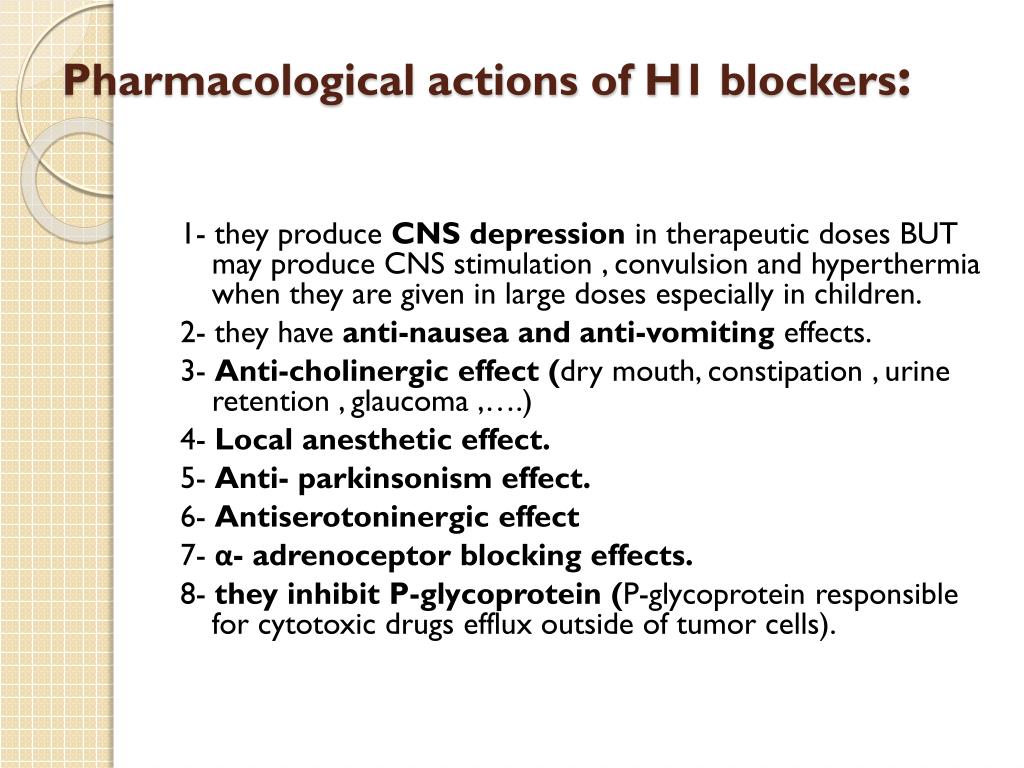
What meds are H1 and H2 blockers?
Antihistamine agentsOverview of antihistamine agentsGroupGenerationDrugH1 antihistaminesSecond-generation antihistaminesLoratadine Desloratadine Cetirizine Fexofenadine Levocetirizine AzelastineH2 antihistaminesCimetidine Famotidine Nizatidine Ranitidine (no longer available in the US)1 more row•Mar 17, 2022
Is Allegra an H2 blocker?
Fexofenadine, sold under the brand name Allegra among others, is an antihistamine pharmaceutical drug used in the treatment of allergy symptoms, such as hay fever and urticaria. Therapeutically, fexofenadine is a selective peripheral H1 blocker.
Is fexofenadine a H1 or H2?
Fexofenadine (Allegra) Fexofenadine competes with histamine for H1 receptors in the GI tract, blood vessels, and respiratory tract, reducing hypersensitivity reactions. It does not sedate. Fexofenadine is available as a 30-, 60-, or 180-mg tablet.
Is Allegra an H1?
Allegra and Zyrtec are two medications indicated for the treatment of allergies. Both drugs are available in brand and generic and can be purchased over-the-counter (OTC). They are classified in a group of medications called H1 antagonists, or H1 blockers, and they are also known as non-sedating antihistamines.
Which antihistamines are H2 blockers?
Description and Brand NamesAxid.Axid AR.Axid Pulvules.Heartburn Relief.Pepcid.Pepcid AC.Tagamet.Tagamet HB.More items...•
Who should not take Allegra?
Ask a doctor before using this medicine if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Older adults may be more sensitive to the effects of this medicine. If you are 65 or older, ask a doctor before taking fexofenadine. This medicine may contain phenylalanine.
Is Allegra good for histamine intolerance?
You might be familiar with histamine in relation to your immune system. If you have seasonal or food allergies, you may notice that antihistamine medications including ZYRTEC®, Allegra®, or Benadryl® provide quick relief for your symptoms. Histamine's role in the body is to cause an immediate inflammatory response.
What can you not take with fexofenadine?
You should always take this medicine with water. Do not take it with juice such as grapefruit, orange, or apple juice . You should NOT take antacids that contain aluminum or magnesium hydroxide within 15 minutes of taking this medicine. If you are uncertain about this, ask your doctor or pharmacist .
Which antihistamine is best for mast cell activation syndrome?
Drugs that modulate the symptoms of mast cell activation Antihistamines are the first line of treatment in MCAD. Non-sedating H1 antihistamines, eg cetirizine, loratadine, fexofenadine, are often preferred.
Is fexofenadine an H1 blocker?
Fexofenadine HCl is a new, nonsedating H1-receptor antagonist approved for treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR).
What type of antihistamine is Allegra?
Generic Name: fexofenadine Fexofenadine is an antihistamine used to relieve allergy symptoms such as watery eyes, runny nose, itching eyes/nose, sneezing, hives, and itching. It works by blocking a certain natural substance (histamine) that your body makes during an allergic reaction.
Should I take Allegra in the morning or at night?
Should I take Allegra (fexofenadine) at night or in the morning? If you are taking a 12 hour form of Allegra (fexofenadine), it can be taken once in the morning and once in the evening. If you are taking an Allegra (fexofenadine) once-a-day 24 hour tablet, it can be taken at any time of the day.
What are some OTC H2 blockers?
Common OTC H2-blockers include: Tagamet HB (cimetidine) Pepcid Complete or Pepcid AC (famotidine) Axid AR (nizatidine)
What is the best H2 blocker?
Famotidine is the most potent, selective H2-receptor antagonist yet available for ulcer therapy. On a weight basis, famotidine is approximately eight times more potent than ranitidine and 40 times more potent than cimetidine.
Why do you have to take Allegra on an empty stomach?
Allegra was designed to target tiny receptors on cells in your small intestines. These receptors absorb the Allegra and help it work where it needs to. Unfortunately, certain fruit juices, especially orange and grapefruit juice, interfere with this absorption.
What's the difference between Allegra and Benadryl?
Benadryl is also used to treat insomnia, motion sickness, and mild cases of Parkinsonism. A main difference between Benadryl and Allegra is that Allegra tends to cause less drowsiness and sedation than Benadryl. Benadryl and Allegra are available in generic form and over-the-counter (OTC).
What is the Difference Between H1 and H2 Blockers?
H 1 blockers refer to compounds that inhibit the activity of the H 1 histamine receptors that occur throughout the vascular endothelial cells in the heart and central nervous system . On the other hand, H 2 blockers refer to compounds that inhibit the activity of the H 2 histamine receptors that mainly occur in the parietal cells of the gastric mucosa. Thus, this is the key difference between H1 and H2 blockers. Furthermore, H 1 blockers were discovered in 1933, while H2 blockers were found much later in 1964.
What is H1 blocker?
H 1 blockers refer to compounds that inhibit the activity of the H 1 histamine receptors. They occur throughout the vascular endothelial cells in the heart and central nervous system. They are also called H1 antagonists or H1 antihistamines. They help to relieve the symptoms of allergic reactions. H 1 histamine receptors exhibit constitutive ...
What antihistamines are used for allergies?
Currently, most people use antihistamines to treat allergies. The first generation of antihistamines was available from the 1930s. H1 and H2 blockers are two antihistamines. H1 blockers affect the nose, while H2 blockers affect the stomach. Furthermore, H 1 blockers refer to compounds that inhibit the activity of the H 1 histamine receptors, while H 2 blockers refer to compounds that inhibit the activity of the H 2 histamine receptors. Thus, this is the summary of the difference between H1 and H2 blockers.
What is the H2 receptor?
Usually, histamine acts upon H2 receptors to induce acid secretion. Thus, H2 blockers inhibit H2 signalling and reduce the secretion of gastric acid. H2 blockers are the first-line treatment for gastrointestinal conditions, including peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Further, they are also used for the treatment of dyspepsia.
What are the two types of antihistamines?
But they are usually for short-term treatment. There are several types of antihistamines. H1 and H2 blockers are two main types of antihistamines used to treat allergic reactions.
Where do H2 antihistamines work?
These H2 antihistamines act upon H2 histamine receptors, mainly in the parietal cells of the gastric mucosa. Parietal cells of the gastric mucosa are a part of the endogenous signalling pathway for gastric acid secretion.
What is the H1 receptor antagonist?
H 1 histamine receptors exhibit constitutive activity. Therefore, H 1 blockers can be either neutral receptor antagonists or inverse agonists. Neutral receptor antagonists work by binding to the H1 receptor and blocking the activation of the receptor by histamine. On the other hand, inverse agonists work by binding to the H1 receptor ...
What is H2 blocker?
The selective histamine type 2 receptor antagonists/blockers (H2 blockers) are widely used in the treatment of acid-peptic disease, including duodenal and gastric ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease and common heartburn. The four H2 blockers in current use are available by prescription as well as over-the-counter, and are some of the most widely used drugs in medicine. The H2 blockers are very well tolerated, but have been linked to rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury.
How do H2 receptor blockers work?
The H2 receptor blockers act by binding to histamine type 2 receptors on the basolateral (antiluminal) surface of gastric parietal cells , interfering with pathways of gastric acid production and secretion. The selectivity of H2 blockers is of key importance, as they have little or no effect on the histamine type 1 receptors, which are blocked by typical antihistamines that are used to treat allergic reactions and have little effect on gastric acid production. The selective H2 blockers are less potent in inhibiting acid production than the proton pump inhibitors (which block the common, final step in acid secretion) but, nevertheless, suppress 24 hour gastric acid secretion by about 70%. The effect of H2 blockers is largely on basal and nocturnal acid secretion, which is important in peptic ulcer healing. The selective H2 blockers were first developed in the early 1990s by Sir James Black, who subsequently received the Nobel Prize for his work developing selective receptor antagonists for clinical use (including the beta blockers as well as the H2 blockers). The initial H2 blocker approved for use in the United States was cimetidine (1977), which was followed by ranitidine (1983), famotidine (1986), and nizatidine (1988). All four of these agents are available by prescription and as over-the-counter oral formulations. Intravenous and intramuscular forms are available for cimetidine, ranitidine and famotidine.
What is the H1 antagonist?
H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H 1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic reactions. Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of histamine receptors are termed antihistamines; other agents may have antihistaminergic action ...
Which antihistamines are more selective?
The newer, second-generation H 1 -antihistamines are far more selective for peripheral histamine H 1 -receptors and have a better tolerability profile compared to the first-generation agents. The most common adverse effects noted for second-generation agents include drowsiness, fatigue, headache, nausea and dry mouth.
What is the best cough medicine for a cold?
The authors of the American College of Chest Physicians Updates on Cough Guidelines (2006) recommend that, for cough associated with the common cold, first-generation antihistamine-decongestants are more effective than newer, non-sedating antihistamines. First-generation antihistamines include diphenhydramine (Benadryl), carbinoxamine (Clistin), clemastine (Tavist), chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton), and brompheniramine (Dimetane). However, a 1955 study of "antihistaminic drugs for colds," carried out by the U.S. Army Medical Corps, reported that "there was no significant difference in the proportion of cures reported by patients receiving oral antihistaminic drugs and those receiving oral placebos. Furthermore, essentially the same proportion of patients reported no benefit from either type of treatment."
What is the term for agents that have negative modulation of histamine receptors?
Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of histamine receptors are termed antihistamines; other agents may have antihistaminergic action but are not true antihistamines. In common use, the term "antihistamine" refers only to H 1 -antihistamines.
What does histamine do to the body?
Once released, the histamine can react with local or widespread tissues through histamine receptors. Histamine, acting on H 1 -receptors, produces pruritus, vasodilation, hypotension, flushing, headache, bradycardia, bronchoconstriction, increase in vascular permeability and potentiation of pain.
Why are antihistamines bad?
This is due to their relative lack of selectivity for the H 1 -receptor and their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier .
What happens when an allergen crosses the mast cell?
Once the allergen cross-links Immunoglobulin E, tyrosine kinases rapidly signal into the cell, leading to cell degranulation and the release of histamine (and other chemical mediators) from the mast cell or basophil. Once released, the histamine can react with local or widespread tissues through histamine receptors.
What is the H1 blocker?
A combination of H1 (like Benadryl, Atarax, Claritin, Allegra, Zyrtec) and H2 blocking antihistamines ( like Zantac and Pecid AC)
What are the inactive ingredients in antihistamines?
Antihistamines and Mast Cell Stabilizing medications often have artificial colors, potassium sorbate, sodium benzoate, or titanium dioxide (Worm, 2011) (Swiss Interest Group Histamine Intolerance, 2016). These are major Mast Cell and Histamine Triggers! Why would they even use these ingredients?? I truly don’t know.
What is a Functional Root Cause Approach to Mast Cell Activation Syndrome and Histamine Intolerance?
A Functional Root Cause Approach is about looking at: What is triggering the Mast Cell Activation Syndrome or Histamine Intolerance? What is actually causing these symptoms.
What is the biggest problem with antihistamines?
The Biggest Problem with Antihistamines in Mast Cell Activation Syndrome and Histamine Intolerance – You May Be Making It Worse!
Why was Seldane removed from the market?
Seldane was later removed from the market due to dangerous side effects. This is a lot of medication for an adult! And it was certainly a lot of medication for a child.
Can you recover from histamine intolerance?
But there is good news! By working with a Functional Mast Cell Activation Syndrome and Histamine Intolerance specialist, you can recover your health and your life!
Can antihistamines cause masking?
People who aren’t willing to put work into their health do need to go the traditional medical route of medications like antihistamines. But you also have to know that these are just masking symptoms. And Mast Cell Activation Syndrome and Histamine Intolerance will still be progressive if you just use pharmaceuticals.
The new case report
Study co-author Natalie Lambert, an associate research professor of biostatistics and health data sciences at the Indiana University School of Medicine, originally identified the two patients featured in the case report.
More support for antihistamines
The small case report should not be generalized across all people with long COVID, Pinto emphasized. "This is not to be extrapolated as, 'This will help everyone,'" she said.