What should the cell potential be for a spontaneous reaction?
For a spontaneous reaction in an electrolytic cell, the cell potential (E°cell) should be positive. What kind of chemical reactions spontaneously takes place in electrochemical cells?
What is an electrochemical cell?
An electrochemical cell is a device which is capable of producing electrical energy from chemical reactions or making chemical reactions easy through the introduction of electrical energy.
What is the difference between cell reaction and non spontaneous reaction?
In this condition, the electric current begins to flow in the opposite direction; similarly, as in an electrolytic cell, the non-spontaneous reaction takes place. A cell reaction describes the overall chemical change in an electrochemical cell.
What is an electrolytic cell?
An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that drives a non-spontaneous redox reaction through the application of electrical energy.
Is an electrochemical cell spontaneous or Nonspontaneous?
In the electrolytic cell, the redox reaction is not spontaneous and electrical energy has to be supplied to initiate the reaction.
How do you know if an electrochemical cell is spontaneous?
For standard electrochemical cells 1: A redox reaction is spontaneous if the standard electrode potential for the redox reaction, Eo(redox reaction), is positive. If Eo(redox reaction) is positive, the reaction will proceed in the forward direction (spontaneous).
Why is electrochemical cell spontaneous?
An electrochemical cell in which the chemistry is spontaneous is called a voltaic cell. This means that the oxidation will occur spontaneously at the anode and the reduction spontaneously at the cathode.
Are electrochemical reactions spontaneous?
Any electrochemical process is spontaneous if the cell voltage is less (i.e., less positive or more negative) than the electromotive force of the cell.
How do you know if its spontaneous or Nonspontaneous?
A reaction with a negative value for ΔG releases free energy and is thus spontaneous. A reaction with a positive ΔG is nonspontaneous and will not favor the products. Some reactions may be spontaneous at some temperatures and nonspontaneous at other temperatures.
What is non spontaneous reaction in electrochemistry?
Electrochemical reactions are either spontaneous, or nonspontaneous. A spontaneous redox reaction generates a voltage itself. A nonspontaneous redox reaction occurs when an external voltage is applied. The reactions that occur in an electric battery are electrochemical reactions.
What reactions are spontaneous?
A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that favors the formation of products at the conditions under which the reaction is occurring. A roaring bonfire is an example of a spontaneous reaction, since it is exothermic (there is a decrease in the energy of the system as energy is released to the surroundings as heat).
How do you know if a reaction is spontaneous?
If ΔH is negative, and –TΔS positive, the reaction will be spontaneous at low temperatures (decreasing the magnitude of the entropy term). If ΔH is positive, and –TΔS negative, the reaction will be spontaneous at high temperatures (increasing the magnitude of the entropy term).
Are galvanic cells always spontaneous?
Yes. Galvanic cells are also called voltaic cells. The reaction that produces a voltage, and a current flow in an external circuit, is a spontaneous reaction, that is, it occurs with no outside intervention.
Which process is Nonspontaneous?
A nonspontaneous process is one that occurs only when work is done by external force or external energy. (a) A bike going up the hill is a nonspontaneous \textbf{nonspontaneous} nonspontaneous process because external force is required for the bike to uphill.
Is E cell positive for spontaneous reactions?
A spontaneous redox reaction is characterized by a negative value of ΔG°, which corresponds to a positive value of E°cell.
Is negative e cell spontaneous?
In order for delta G to be negative, which indicates that the reaction is a spontaneous one, E cell must be positive. For electrolytic cells, which are reactions that occur only with the input of an external energy source, E cell is negative because they are nonspontaneous.
Is oxidation or reduction spontaneous?
The oxidation of Zn(s) into Zn2+ and the reduction of Cu2+ to Cu(s) occur spontaneously. In other words, the redox reaction between Zn and Cu2+ is spontaneous. This is due to the difference in potential energy between the two substances.
What is always true for a spontaneous reaction run under standard conditions?
Correct answer: In order for a reaction to be spontaneous, Gibb's free energy must have a negative value. Based on the equation, we can see that a positive enthalpy in combination with a negative entropy will always result in a positive value for Gibb's free energy.
What are the standard conditions for an electrochemical cell?
Standard conditions are those that take place at 298.15 Kelvin (temperature), 1 atmosphere (pressure), and have a Molarity of 1.0 M for both the anode and cathode solutions.
What does a dead battery mean chemically?
The redox reaction is spontaneously approaching equilibrium, and as the reaction proceeds, electrons flow within the cell. At equilibrium, the voltage drops to zero and the current stops. (A battery at equilibrium is a dead battery.)
What is the Function of a Salt Bridge in an Electrochemical Cell?
The salt bridge completes the circuit of an electrochemical cell, thereby allowing the flow of current through it. It also helps maintain the overa...
What is Standard Electrode Potential?
The standard electrode potential of an electrode can be defined as the potential difference that arises between the electrode and the electrolyte u...
What are the Key Differences between Cathode and Anode?
The cathode of an electrochemical cell is the site at which reduction occurs. It is generally represented by a positive (+) sign. The electrons flo...
Is it Possible for an Electrochemical Cell to have a Positively Charged Anode or a Negatively Charged Cathode?
Yes, the anode of an electrolytic cell is positively charged (and the cathode is negatively charged). However, oxidation still occurs at the anode...
What are electrolytic cells?
Electrolytic cells are a class of electrochemical cells that use electric currents to facilitate the cell reaction. The chemical reaction that occu...
What is an electrochemical cell, and how does it work?
An electrochemical cell is an apparatus or device that produces electric current from chemical change and energy released by this spontaneous redox...
What are the two types of electrochemical cells?
Based on the reactions going inside, electrochemical cells are divided into two types: Galvanic cell or voltaic cell and Electrolytic cell. Galvani...
What is the principle of an electrochemical cell?
The basic principle of working of an electrochemical cell is the transfer of electrons generated from redox reaction occurring in it that results i...
What is the function of an electrochemical cell?
The function of an electrochemical cell is to convert chemical energy to electrical energy from the chemical reactions going in it or to convert el...
What is an electrochemical cell? Explain with an example?
The device that brings about electrical energy from the chemical reactions going in it or uses chemical energy to produce electricity is known as a...
What are some of the applications of electrochemical cells?
Electrochemical cells find applications in torches, military applications, corrosion protection, digital watches, etc.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of electrochemical cells?
The advantages of electrical cells are innumerable. They are used in electrolytic refining of metals, electroplating, and batteries. Batteries of d...
What are the four components of an electrochemical cell?
The four components of an electrochemical cell are Anode – The cell compartment where oxidation takes place. Cathode - The cell compartment where r...
How does an electrochemical cell work?
An electrochemical cell is an apparatus or device that produces electric current from chemical change and energy released by this spontaneous redox reaction. Electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another; thus, electric current is produced. An electrochemical cell is comprised of two half-cells. Each of them consists of an electrode and an electrolyte that can be the same or different in the two half cells. The main components of an electrochemical cell are:
What are the two types of electrochemical cells?
Electrochemical cells are primarily of two types: 1 Galvanic cell or voltaic cell 2 Electrolytic cell
What is the basic principle of working of an electrochemical cell?
The basic principle of working of an electrochemical cell is the transfer of electrons generated from redox reaction occurring in it that results in the production of electric current. 2. Electrons are released from metals used as electrodes. 3.
What is the relationship between electrochemical and electrical energy?
Thus we can conclude that Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry that establishes the relation between chemical energy and electrical energy . The key feature of an electrochemical cell is the redox reaction which takes place in an electrolytic solution at the interface of the conductors. Based on the types of redox reactions going inside, electrochemical cells are divided into two types: Galvanic cell or voltaic cell and Electrolytic cell. A voltaic cell or galvanic cell comprises two half cells composed of metal electrodes like copper and zinc.
What are electrolytic cells used for?
Applications of Electrochemical cell. In metallurgy, electrolytic cells are used in electrorefining, producing highly pure metals such as lead, zinc, aluminium, and copper. It is used to extract pure sodium metal from molten sodium chloride by keeping it in an electrolytic cell.
How do electrolytic cells convert electrical energy into chemical energy?
In comparison, electrolytic cells convert electrical energy into chemical energy by electrolysis. An electrochemical cell can behave like an electrolytic cell when a potential difference that is greater than the potential difference of an electrochemical cell is applied. In this condition, the electric current begins to flow in ...
How many cells are in an electrochemical cell?
An electrochemical cell is comprised of two half-cells. Each of them consists of an electrode and an electrolyte that can be the same or different in the two half cells. The main components of an electrochemical cell are:
What is an electrochemical cell?
An electrochemical cell is a device capable of either generating electrical energy from chemical reactions or using electrical energy to cause chemical reactions. The electrochemical cells which generate an electric current are called voltaic or galvanic cells and those that generate chemical reactions, via electrolysis for example, are called electrolytic cells. A common example of a galvanic cell is a standard 1.5 volt cell meant for consumer use. A battery consists of one or more cells, connected in parallel, series or series-and-parallel pattern.
How many cells are in an electrochemical cell?
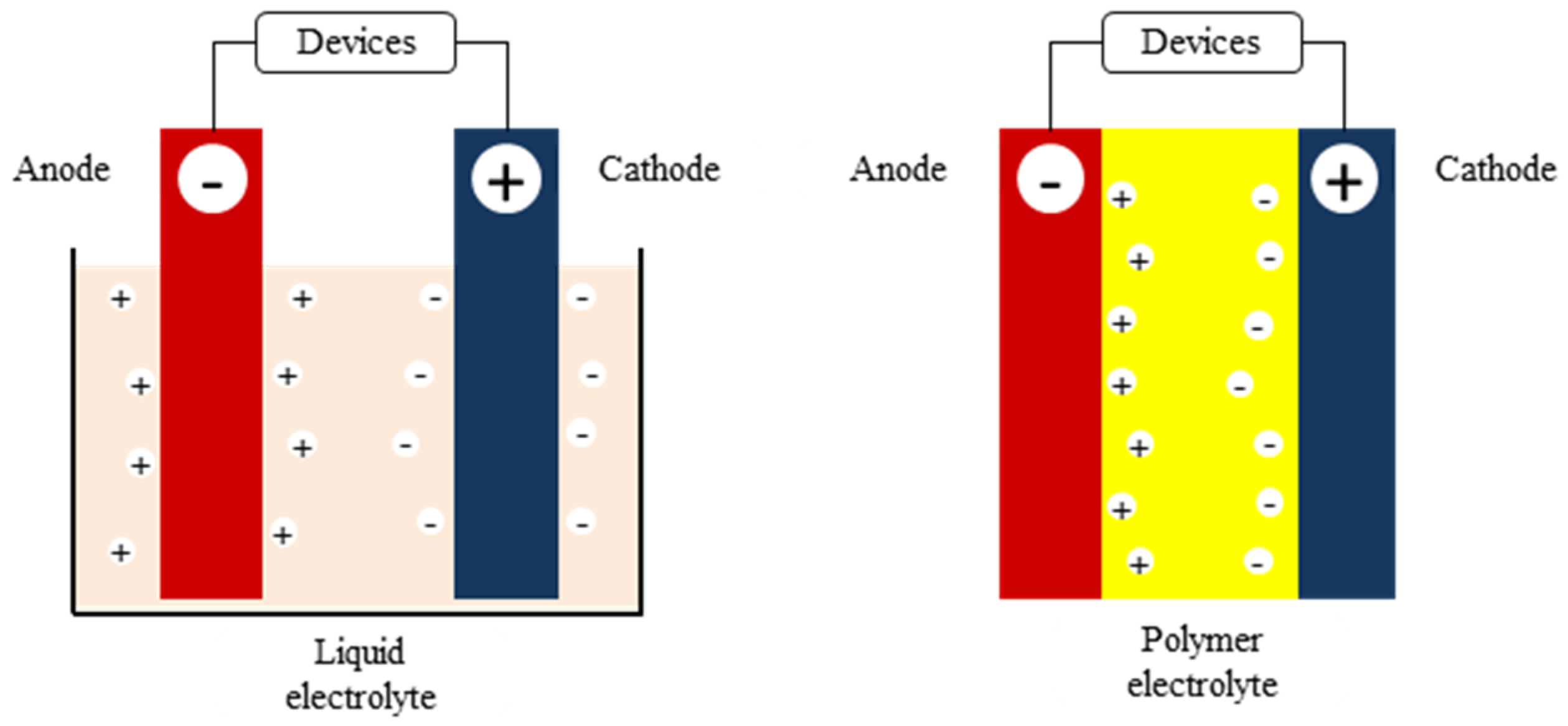
An electrochemical cell consists of two half-cells. Each half-cell consists of an electrode and an electrolyte. The two half-cells may use the same electrolyte, or they may use different electrolytes. The chemical reactions in the cell may involve the electrolyte, the electrodes, or an external substance (as in fuel cells that may use hydrogen gas as a reactant). In a full electrochemical cell, species from one half-cell lose electrons ( oxidation) to their electrode while species from the other half-cell gain electrons ( reduction) from their electrode.
What are the components of an electrolytic cell?
An electrolytic cell has three component parts: an electrolyte and two electrodes (a cathode and an anode ). The electrolyte is usually a solution of water or other solvents in which ions are dissolved. Molten salts such as sodium chloride are also electrolytes. When driven by an external voltage applied to the electrodes, the ions in the electrolyte are attracted to an electrode with the opposite charge, where charge-transferring (also called faradaic or redox) reactions can take place. Only with an external electrical potential (i.e. voltage) of correct polarity and sufficient magnitude can an electrolytic cell decompose a normally stable, or inert chemical compound in the solution. The electrical energy provided can produce a chemical reaction which would not occur spontaneously otherwise.
What is a galvanic cell?
A galvanic cell, or voltaic cell, named after Luigi Galvani, or Alessandro Volta respectively, is an electrochemical cell that derives electrical energy from spontaneous redox reactions taking place within the cell. It generally consists of two different metals connected by a salt bridge, or individual half-cells separated by a porous membrane.
What is a primary cell?
A primary cell is a Galvanic battery that is designed to be used once and discarded, in contrast to a secondary cell ( rechargeable battery ), which can be recharged with electricity and reused. In general, the electrochemical reaction occurring in the cell is not reversible, rendering the cell unrechargeable. As a primary cell is used, chemical reactions in the battery use up the chemicals that generate the power; when they are gone, the battery stops producing electricity and is useless. In contrast, in a secondary cell, the reaction can be reversed by running a current into the cell with a battery charger to recharge it, regenerating the chemical reactants. Primary cells are made in a range of standard sizes to power small household appliances such as flashlights and portable radios.
How does a fuel cell work?
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through an electrochemical reaction of hydrogen fuel with oxygen or another oxidizing agent . Fuel cells are different from batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy comes from chemicals already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied.
What are some examples of electrolysis?
Important examples of electrolysis are the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen, and bauxite into aluminium and other chemicals . Electroplating (e.g. of copper, silver, nickel or chromium) is done using an electrolytic cell. Electrolysis is a technique that uses a direct electric current (DC).
How to tell if a reaction is spontaneous?
To predict whether a reaction occurs spontaneously you can look at the sign of the EMF value for the cell. If the EMF is positive then the reaction is spontaneous. If the EMF is negative then the reaction is not spontaneous.
What is the EMF of a cell?
It turns out that the sign of the EMF is equivalent to whether a cell reaction is spontaneous or not. Those reactions that are spontaneous have a positive EMF and those reactions that are non-spontaneous have a negative EMF.
How to calculate EMF of a cell?
Step 1: Determine the overall equation for this reaction. Step 2: Which reactant should be oxidised, and which should be reduced? Step 3: Predict whether the reaction will be spontaneous or non-spontaneous. Step 4: Calculate the EMF of the cell.
What are the two half reactions?
the two half-reactions are as follows: EMF = E° (reduction half-reaction) – E° (oxidation half-reaction) The sign of the EMF is negative, therefore this reaction will not take place spontaneously. Let’s look at the reasoning behind this in more detail.
Is EMF positive or negative?
The EMF is positive, therefore the reaction is spontaneous.
Is EMF a non-spontaneous reaction?
The EMF is negative, therefore the reaction is non-spontaneous.
Does EMF take place spontaneously?
The sign of the EMF is negative, therefore this reaction will not take place spontaneously. Let’s look at the reasoning behind this in more detail.
Overview
Electrolytic cell
An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that drives a non-spontaneous redox reaction through the application of electrical energy. They are often used to decompose chemical compounds, in a process called electrolysis—the Greek word lysis means to break up.
Important examples of electrolysis are the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen, and bauxite into aluminium and other chemicals. Electroplating (e.g. of copper, silver, nickel or chromiu…
Galvanic cell or voltaic cell
A galvanic cell, or voltaic cell, named after Luigi Galvani or Alessandro Volta respectively, is an electrochemical cell that derives electrical energy from spontaneous redox reactions taking place within the cell. It generally consists of two different metals connected by a salt bridge, or individual half-cells separated by a porous membrane.
Volta was the inventor of the voltaic pile, the first electrical battery. In common usage, the word "b…
Primary cell
A primary cell is a galvanic battery that is designed to be used once and discarded, in contrast to a secondary cell (rechargeable battery), which can be recharged with electricity and reused. In general, the electrochemical reaction occurring in the cell is not reversible, rendering the cell unrechargeable. As a primary cell is used, chemical reactions in the battery use up the chemicals that generate the power; when they are gone, the battery stops producing electricity and is usele…
Secondary cell
A secondary cell, commonly referred to as a rechargeable battery, is an electrochemical cell that can be run as both a galvanic cell and an electrolytic cell. This is used as a convenient way to store electricity: when current flows one way, the levels of one or more chemicals build up (charging); while it is discharging, they reduce and the resulting electromotive force can do work.
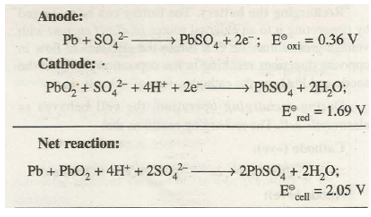
A common secondary cell is the lead-acid battery. This can be commonly found as car batteries. …
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through an electrochemical reaction of hydrogen fuel with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Fuel cells are different from batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy comes from chemicals already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as lo…
Half-cells
An electrochemical cell consists of two half-cells. Each half-cell consists of an electrode and an electrolyte. The two half-cells may use the same electrolyte, or they may use different electrolytes. The chemical reactions in the cell may involve the electrolyte, the electrodes, or an external substance (as in fuel cells that may use hydrogen gas as a reactant). In a full electrochemical cell, species from one half-cell lose electrons (oxidation) to their electrode while species from the othe…
See also
• Activity (chemistry)
• Cell notation
• Electrochemical potential
• Electrochemical engineering
• Battery (electricity)