What are the 4 key powers of Congress?
What are the 4 key powers of Congress? – Make laws. – Declare war. – Raise and provide public money and oversee its proper expenditure. – Impeach and try federal officers. – Approve presidential appointments. – Approve treaties negotiated by the executive branch.
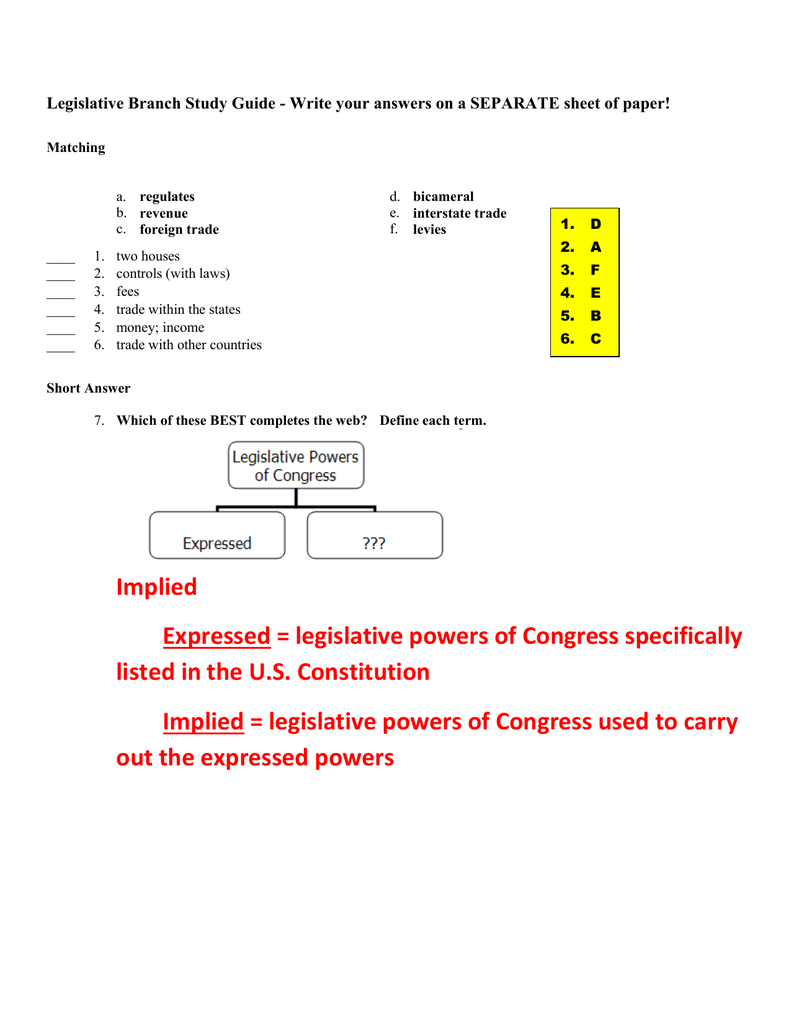
What are examples of expressed powers?
Examples of expressed powers are the powers of Congress to declare war, coin money, regulate interstate commerce, raise an army and navy, and collect taxes.
What are expressed powers and implied powers?
Expressed powers are the powers explicitly granted to the President in the Constitution. Implied powers are powers not expressly stated in the Constitution, but have been interpreted by presidents as necessary to faithfully execute laws and defend the Constitution.
What are the powers granted to Congress?
What are the 18 powers granted to Congress?
- Taxes. lay and collect taxes, duties, imposts and excises.
- Borrowing. borrowing money for the U.S.
- Commerce. regulate trade with foreign countries.
- Naturalization; bankruptcy. …
- Coins; weights; measures. …
- Counterfeiting. …
- Post Offices. …
- copy rights patents.

What are some examples of implied powers?
Congress has used its implied powers to do the following: 1940: Establishment of mandatory army conscription for men. 1947: Creation of the Air Force. 1965: Establishment of Medicare and Medicaid.
What is implied power?
The phrase implied powers refers to the abilities and powers that a government branch has that are not explicitly stated in the U.S. Constitution but are suggested to be applicable in some or all cases. This implied powers definition is contrasted with the idea of expressed powers, which are the powers that are described in detail in the Constitution or other documents. For instance, the U.S. Congress has the expressed power to collect taxes. As a result of this expressed power, it also has the implied power to punish tax evasion and to determine which items are taxed more heavily than others.
Why are implied powers clear?
Some implied powers are clear because they naturally follow expressed powers. For instance, the expressed power of Congress to raise an army implies the power to establish a military draft if needed. However, many examples of implied power actually come from a very specific expressed power as listed in the Constitution.
What are the powers of Congress?
In addition to these expressed powers, the United States Congress has established its implied power to do the following: 1 Create a national bank 2 Establish a federal minimum wage 3 Establish a military draft 4 Create gun control laws in some cases
What are the two types of congressional powers?
There are two types of congressional power in the United States: expressed power, which is detailed in Article I, Section 8 of the Constitution, and implied power, which includes the Necessary and Proper Clause (which allows Congress to create any law needed to serve the country) and extensions of other expressed powers.
What was the Maryland case?
Maryland was an 1819 court case in which the state of Maryland attempted to impose a tax on the national bank and also questioned the validity of a national bank as an extension of the Necessary and Proper Clause.
Where does the Congress sit?
Congress sits in the Capitol Building and has done since 1800. What are the implied powers of Congress? The Constitution gives Congress a number of expressed powers in Article I, Section 8 of the Constitution. There are a large number of expressed powers of Congress.
Why did the government use the implied powers clause?
Using the expressed powers as a guide, the government would be able to use the “necessary and proper” clause to meet the ever-expanding needs of the American people.
What is the implied power clause?
Constitution. This clause is called the “necessary and proper” clause or “elastic clause.” It states:
What is the difference between implied and inherent powers?
The difference between implied and inherent powers is where you will find them. You will not find inherent powers established in the Constitution. That is because inherent powers are those that the government needs to be able to get their job done right. This can include acquiring land or regulating immigration.
How many powers are implied?
You can’t look at inherent and implied powers without defining “expressed powers” too. These are the 17 powers that are clearly stated in the Constitution.
Why does the fact that this clause expands the others creates issues?
Additionally, the fact that this clause expands the others creates issues, because questions arise as to where that power stops. This generates controversy from the limitations of the articles and the power they create.
What is the government's power to regulate commerce?
Using their power to regulate commerce, collect taxes, raise an army and establish post offices, to name a few, the government has enacted the following: The U.S. government created the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) using their power to collect taxes.
Which amendment was the ADA based on?
The creation of the American Disabilities Act (ADA) under the commerce clause was later justified by the 14th Amendment. The government can punish tax evaders using the power to collect taxes clause. Prohibition of mail fraud is based on the clause to establish post offices.
What is implied power?
Implied powers are powers of U.S. government which have not been explicitly granted by the Constitution but that is implied by the necessary and proper clause to be delegated for the purpose of carrying out the enumerated powers.
Why are implied powers necessary?
They're implied to be granted because similar powers have set a precedent. These implied powers are necessary for the function of any given governing body.
Is it an implied power of Congress to pass tax law?
Income Tax: While Article I gives Congress the broad specific power to “lay and collect Taxes,” Congress cited its implied powers under the Elastic Clause in passing the Revenue Act of 1861 creating the nation’s first income tax law.
What are the implied powers granted to Congress?
Implied powers are not directly stated in the Constitution. These powers derive from Congress’s power to make all laws “necessary” and appropriate to fulfill its enumerated rights. This clause is found at the end of Article I Section 8. It is often called the elastic Clause because it extends Congress’ authority.
Which of these is an example of implied power?
An example of an implied authority is: the national government creates a military air force division.
What are 3 of the implied powers of Congress?
Maryland’s Supreme Court under Chief Justice John Marshall held that Congress has the implied power of establishing a national banking institution because of the powers to tax, borrow and coin money.
What are the implied and explicit powers of Congress?
Overview: Congress has certain powers that are explicitly outlined in the Constitution. Other powers, known as implied powers, are available to Congress that are not explicitly stated but that Congress can assume to carry out its express powers. This does not grant Congress full control.
What are implied powers?
Implied powers are political power granted to the United States government by law that isn’t explicitly stated in its Constitution. Because similar powers have been granted, they are impliedly granted. These powers are necessary to perform the functions of any given governing body.
What are the two implied powers of Congress?
Implied powers. Congress has implied power derived from clauses such as the Commerce Clause, Necessary and Proper Clause, and the General Welfare Clause.
Answer
Implied powers of the congress would mean creating taxes and raising and supporting an army
New questions in History
PLZ!!! HELP ILL GIVE BRAINLIEST AND 100 PNTS!! What does the story Asoka Follows the Buddha reveal about the central Buddhist attitude toward human be …
