Aortic false aneurysm is a rare complication after cardiac surgery. Aortic dissection, infection, arterial wall degeneration, and poor surgical technique are recognized as risk factors for the occurrence of postsurgical false aneurysm.
What is the prognosis of aortic dissection?
The 10‐year actuarial survival rate of patients with an aortic dissection who leave the hospital alive ranges from 30% to 60%. 20,21,22,23,26,27 The long‐term approach is based on understanding that dissection of the aorta is the epitome of systemic aortic media degeneration or defective wall structure, with the entire aorta and its branches being predisposed to dissection, aneurysm formation, and/or aortic rupture. Subsequently, management in these patients includes life time medical ...
What causes an aortic dissection?
These include:
- Chronic high blood pressure (hypertension) - It is thought that ongoing high blood pressure may stress the aortic tissue, making it more likely to tear
- Coronary artery disease (atherosclerosis) - Hardened arteries increase the pressure on the aorta
- Smoking
- Aortic valve defect (heart valve disease)
- Aortic aneurysm
What are the signs of aortic aneurysm?
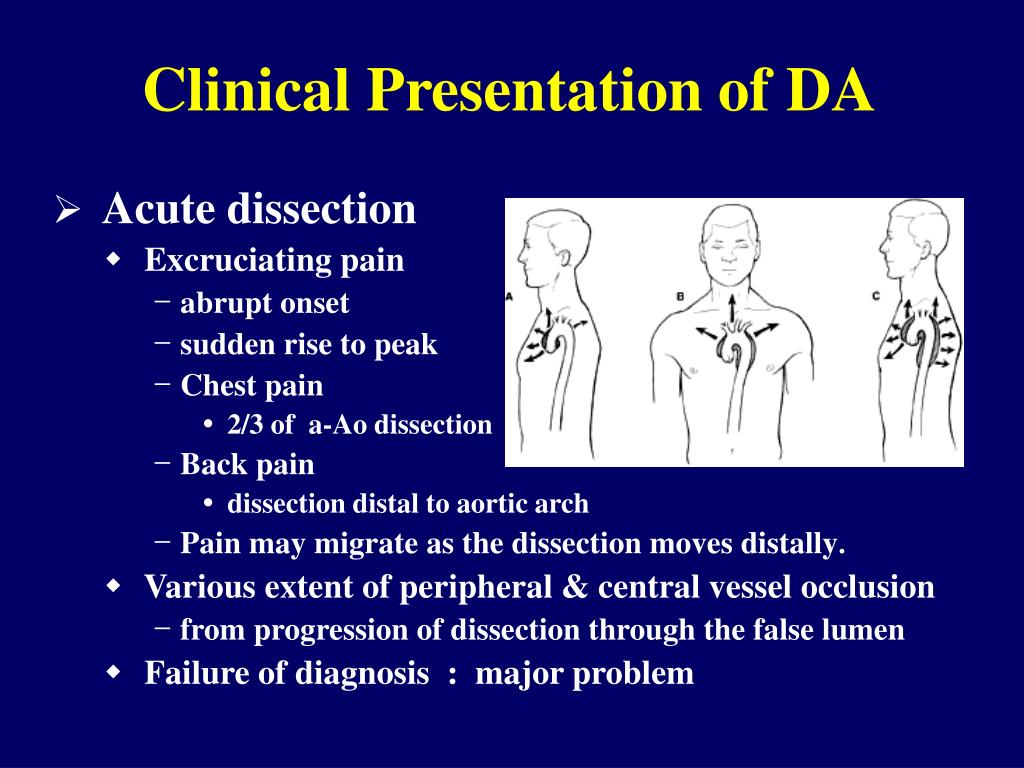
- Pain in the chest, neck, and/or back
- Swelling of the head, neck, and arms
- Coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood
How serious is a torn aorta?
The condition is generally fatal in most of the cases because of the excessive internal bleeding as a result of the rupture. The aorta is the main blood vessel which carries blood out of your heart.

Is an aortic dissection the same as an aortic aneurysm?
An aortic aneurysm occurs when a weak spot in the wall of the aorta begins to bulge, as shown in the image on the left. An aneurysm can occur anywhere in the aorta. Having an aortic aneurysm increases the risk of a tear in the aortic lining (aortic dissection), as shown in the image on the right.
Is a dissecting aneurysm a false aneurysm?
Dissecting aneurysms are not true aneurysms but rather hematomas within the arterial media that occur almost exclusively in the aorta. An intimal tear allows access of blood to the media, and luminal blood pressure causes propagation of the thrombus through the arterial media over the course of hours to days (Fig.
What is the difference between false aneurysm and dissection?
Unlike a false aneurysm, in which blood bursts through all three layers of the vessel, in a dissection, the outer layers of the vessel are still intact, and blood forms a channel within the vessel wall itself.
What is false and true aneurysm?
A pseudoaneurysm, or pseudoaneurysm of the vessels, occurs when a blood vessel wall is injured and the leaking blood collects in the surrounding tissue. It is sometimes called a false aneurysm. In a true aneurysm, the artery or vessel weakens and bulges, sometimes forming a blood-filled sac.
What is a false aortic aneurysm?
False aneurysms, also known as pseudoaneurysms, are abnormal outpouchings or dilatation of arteries which are bounded only by the tunica adventitia, the outermost layer of the arterial wall. These are distinguished from true aneurysms, which are bounded by all three layers of the arterial wall.
What is the difference between an aneurysm and a pseudo aneurysm?
A pseudoaneurysm happens as a result of injury to a blood vessel. The artery leaks blood, which then pools near the damaged spot. It's different from a true aneurysm, which happens when the wall of a blood vessel stretches and forms a bulge. Most pseudoaneurysms are complications from medical procedures.
Is dissection and aneurysm the same?
Aneurysms can occur in any vessel, most notably in the brain, heart, thoracic aorta, and abdominal aorta. A dissection is a tear of the inside layer of a blood vessel wall that allows blood to flow between the layers that make up the vessel wall and separate these layers.
What are the 3 types of aneurysms?
The three types of cerebral aneurysms are: berry (saccular), fusiform and mycotic. The most common, "berry aneurysm," occurs more often in adults. It can range in size from a few millimeters to more than two centimeters. A family history of aneurysms may increase your risk.
What are the four types of aneurysms?
Four Main Types of AneurysmsA saccular (berry) aneurysm bulges from one side of an artery.A giant aneurysm can involve more than one artery and can be over 2.5 centimeters wide.A fusiform aneurysm bulges from all sides of an artery.A mycotic aneurysm is caused by an infected artery wall.
Which of the following types of aneurysm is considered a false aneurysm?
A saccular-shaped aneurysm bulges or balloons out only on one side. A pseudoaneurysm, or false aneurysm, is not an enlargement of any of the layers of the blood vessel wall. A false aneurysm may be the result of a prior surgery or trauma. Sometimes, a tear can occur on the inside layer of the vessel.
What is a true aneurysm?
True aneurysms. are an abnormal dilation of an artery due to a weakened vessel wall.
What can be mistaken for an aneurysm?
Pain from a bleeding brain aneurysm sometimes can be confused with a migraine headache. Wrongly perceiving a severe headache as a migraine that will eventually resolve on its own can delay treatment and can have disastrous consequences.
What should the second arrow point up or down in an aortic dissection?
To really show what’s happening in an aortic dissection, the wall of the aorta should be more clearly depicted, and the second arrow should point up or down within the wall itself, showing the path of blood as forms a tunnel within the vessel wall.
What happens in a dissection?
In a dissection, only the inner portion of the vessel wall is damaged. Blood enters into that damaged area, and tunnels up or down within the wall of the vessel. Unlike a false aneurysm, in which blood bursts through all three layers of the vessel, in a dissection, the outer layers of the vessel are still intact, ...
Does blood go down or up in a dissection?
It doesn’t tunnel down or up into the wall of the vessel at all. After some time, the blood organizes and becomes firm – kind of like a blood clot – and it prevents further blood from escaping the damaged vessel. In a dissection, only the inner portion of the vessel wall is damaged.
What causes an aortic aneurysm?
Causes. The most common cause of aortic aneurysms is. Atherosclerosis , which weakens the wall of the aorta. Less common causes include. Injuries to the aorta, most often due to a motor vehicle crash. Inflammatory diseases of the aorta ( aortitis ) Hereditary connective tissue disorders, such as Marfan syndrome.
What happens when you dissect your aorta?
Aortic dissection occurs when the inner lining of the aorta separates (tears) from the middle layer of the aorta, allowing blood to push between these layers, separating (dissecting) the middle layer of the wall from the still-intact outer layer. As a result, a new, false channel forms in the wall of the aorta. Virtually everyone who has an aortic dissection experiences pain—typically sudden, excruciating pain, often described as tearing or ripping. As the dissection advances further along the aorta, it can close off the points at which one or more arteries branch off from the aorta, blocking blood flow. The consequences vary depending on which arteries are blocked.
What arteries can cause aneurysms?
The arteries supplying the head (carotid arteries), the arteries supplying the brain (cerebral arteries), and the arteries supplying the heart muscle (coronary arteries) may also develop aneurysms. A ruptured aneurysm in the brain may cause subarachnoid hemorrhage.
What is the diameter of the aorta?
Overview of Aortic Aneurysms and Aortic Dissection. The aorta, which is about 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) in diameter, is the largest artery of the body. It receives oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle and distributes it to all of the body except the lungs (which receive blood from the right ventricle). Just after the aorta leaves the heart, ...
What is the largest artery in the body?
The aorta, which is about 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) in diameter, is the largest artery of the body. It receives oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle and distributes it to all of the body except the lungs (which receive blood from the right ventricle). Just after the aorta leaves the heart, smaller arteries that carry blood to ...
Where do aneurysms develop?
Aneurysms can develop anywhere along the aorta. Three fourths of aortic aneurysms develop in the part that passes through the abdomen ( abdominal aorta ), and the rest develop in the part that passes through the chest ( thoracic aorta ).
Why does a thrombus develop in an aneurysm?
A blood clot (thrombus) often develops in the aneurysm because blood flow inside the aneurysm is sluggish. The clot may extend along the entire wall of the aneurysm. A blood clot may break loose (becoming an embolus), travel through the bloodstream, and block arteries.
What is a false aneurysm?
False aneurysms , also known as pseudoaneurysms, are abnormal outpouchings or dilatation of arteries which are bounded only by the tunica adventitia, the outermost layer of the arterial wall. These are distinguished from true aneurysms, which are bounded by all three layers of the arterial wall.
Why is the risk of rupture higher than that of a true aneurysm of comparable size?
The risk of rupture is higher than that of a true aneurysm of comparable size due to poor support of the aneurysm wall and thus false aneurysms generally require treatment.