
Ar is the reason the standard atomic weight of terrestrial argon is greater than that of the next element, potassium, a fact that was puzzling when argon was discovered. Mendeleev positioned the elements on his periodic table in order of atomic weight, but the inertness of argon suggested a placement before the reactive alkali metal.
Why does argon have a higher mass than potassium?
(Continue reading) The mass given on the periodic table is the weighted average of the abundance of isotopes. Because heavier isotopes (more neutrons) of argon are more abundant than potassium's, by pure statistics, argon will appear with a greater mass on the periodic table.
Why is the atomic mass of potassium 19 and Argon 18?
Because the Periodic Table is based on atomic number, Z, and not on atomic mass. For potassium metal, Z = 19; its mass is 39.10 ⋅ g ⋅ mol−1. For argon gas, Z = 18; its mass is 39.95 ⋅ g ⋅ mol−1.
What is the mass of an argon atom?
For argon gas, Z = 18; its mass is 39.95 ⋅ g ⋅ mol−1. So even though most argon atoms are more massive than most potassium atoms, all potassium atoms have one more positively charged, massive nuclear particle than does argon.
Is argon an element or a compound?
view. talk. edit. | references. Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv ).
See more

Why mass of potassium is less than argon?
For potassium metal, Z=19 ; its mass is 39.10⋅g⋅mol−1 . For argon gas, Z=18 ; its mass is 39.95⋅g⋅mol−1 . So even though most argon atoms are more massive than most potassium atoms, all potassium atoms have one more positively charged, massive nuclear particle than does argon.
What is the difference between potassium and argon?
Potassium is highly reactive metal, while argon is an inert gas.
Why is relative atomic mass of argon greater than potassium?
Explain why the relative atomic mass of argon is greater than the relative atomic mass of potassium, even though the atomic number of potassium is greater than the atomic number of argon. Argon has a greater proportion of heavier isotopes with more neutrons than potassium.
Which atom is larger potassium or argon?
With respect to the parent atoms, potassium would be larger than argon, the which would be smaller than chlorine.
Which is more reactive argon or potassium?
Potassium is a highly reactive metal while argon is an inert | Quizlet.
How does potassium turn into argon?
One out of every 10,000 Potassium atoms is radioactive Potassium-40 (K-40). These each have 19 protons and 21 neutrons in their nucleus. If one of these protons is hit by a beta particle, it can be converted into a neutron. With 18 protons and 22 neutrons, the atom has become Argon-40 (Ar-40), an inert gas.
Why did scientists choose argon before potassium?
This is because modern periodic table is according to icnreasing atomic numbers. Since Ar has the atomic number 18 and potassium 19 so Argron is placed before K in the Modern periodic table.
Does potassium have more electrons than argon?
Potassium has nineteen electrons, one more than the noble gas argon, so its configuration could be written as [Ar]4s1.
What is the atomic weight of argon?
39.948 uArgon / Atomic massArgon is an inert gas in group VIII A of the periodic table with atomic number 18, an atomic weight of 39.948, and a density of 1.40 Mg/m3.
How can you tell which atom is larger?
0:093:34Atomic Radius: which atom is smaller? (Examples) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNow if you recall what we talked about the lower anatomy is on the periodic table the larger it willMoreNow if you recall what we talked about the lower anatomy is on the periodic table the larger it will be but as you move further to the right the smaller the atoms get within each row.
How do you rank atoms from smallest to largest?
In the periodic table, atomic radii decrease from left to right across a row and increase from top to bottom down a column. Because of these two trends, the largest atoms are found in the lower left corner of the periodic table, and the smallest are found in the upper right corner (Figure 2.8. 4).
Which atom has the largest size?
Atomic radii vary in a predictable way across the periodic table. As can be seen in the figures below, the atomic radius increases from top to bottom in a group, and decreases from left to right across a period. Thus, helium is the smallest element, and francium is the largest.
What are the properties of argon?
Argon has several desirable properties: 1 Argon is a chemically inert gas. 2 Argon is the cheapest alternative when nitrogen is not sufficiently inert. 3 Argon has low thermal conductivity. 4 Argon has electronic properties (ionization and/or the emission spectrum) desirable for some applications.
How abundant is argon?
Argon is the third-most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv ). It is more than twice as abundant as water vapor (which averages about 4000 ppmv, but varies greatly), 23 times as abundant as carbon dioxide (400 ppmv), and more than 500 times as abundant as neon (18 ppmv). Argon is the most abundant noble gas in Earth's ...
What is the purpose of argon in packaging?
Argon is used to displace oxygen- and moisture-containing air in packaging material to extend the shelf-lives of the contents (argon has the European food additive code E938) . Aerial oxidation, hydrolysis, and other chemical reactions that degrade the products are retarded or prevented entirely. High-purity chemicals and pharmaceuticals are sometimes packed and sealed in argon.
Why do incandescent lights have argon?
Incandescent lights are filled with argon, to preserve the filaments at high temperature from oxidation. It is used for the specific way it ionizes and emits light, such as in plasma globes and calorimetry in experimental particle physics. Gas-discharge lamps filled with pure argon provide lilac/violet light; with argon and some mercury, blue light. Argon is also used for blue and green argon-ion lasers .
How is argon extracted?
Argon is extracted industrially by the fractional distillation of liquid air in a cryogenic air separation unit; a process that separates liquid nitrogen, which boils at 77.3 K, from argon, which boils at 87.3 K, and liquid oxygen, which boils at 90.2 K. About 700,000 tonnes of argon are produced worldwide every year.
What is the most abundant isotope of argon?
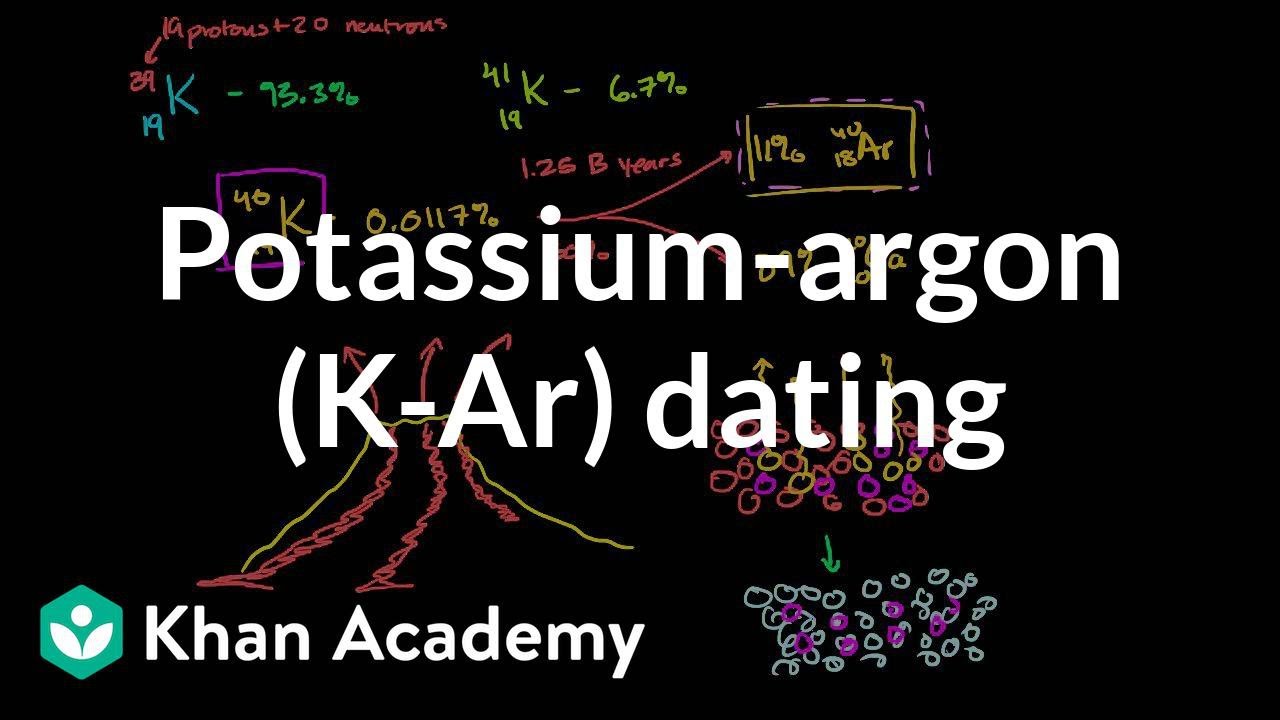
In radioactive decays. 40 Ar, the most abundant isotope of argon, is produced by the decay of 40 K with a half-life of 1.25 × 10 9 years by electron capture or positron emission. Because of this, it is used in potassium–argon dating to determine the age of rocks.
Why is argon used in wine?
In winemaking, argon is used in a variety of activities to provide a barrier against oxygen at the liquid surface, which can spoil wine by fueling both microbial metabolism (as with acetic acid bacteria) and standard redox chemistry. Argon is sometimes used as the propellant in aerosol cans.
How much argon is in the atmosphere?
There are 50 trillion tonnes of argon swirling around in the Earth's atmosphere and this has slowly built-up over billions of years, almost all coming from the decay of the radioactive isotope potassium-40 which has a half-life of 12.7 billion years. Although argon makes up 0.93% of the atmosphere it evaded discovery until 1894 when the physicist Lord Rayleigh and the chemist William Ramsay identified it. In 1904 Rayleigh won the Nobel Prize for Physics and Ramsay won the Nobel Prize for Chemistry for their work.
When was argon first discovered?
Although argon is abundant in the Earth’s atmosphere, it evaded discovery until 1894 when Lord Rayleigh and William Ramsay first separated it from liquid air. In fact the gas had been isolated in 1785 by Henry Cavendish who had noted that about 1% of air would not react even under the most extreme conditions.
What is the use of argon in welding?
Uses and properties. The image reflects the use of the element in the welding industry. Argon provides an inert atmosphere in which welded metals will not oxidise. Argon is a colourless, odourless gas that is totally inert to other substances. Argon is often used when an inert atmosphere is needed.
Why is argon used in inert atmosphere?
Argon is often used when an inert atmosphere is needed. It is used in this way for the production of titanium and other reactive elements. It is also used by welders to protect the weld area and in incandescent light bulbs to stop oxygen from corroding the filament.
Is argon a biological element?
Argon has no known biological role. Natural abundance. Argon makes up 0.94% of the Earth’s atmosphere and is the third most abundant atmospheric gas. Levels have gradually increased since the Earth was formed because radioactive potassium-40 turns into argon as it decays.
Overview
Isotopes
The main isotopes of argon found on Earth are Ar (99.6%), Ar (0.34%), and Ar (0.06%). Naturally occurring K, with a half-life of 1.25×10 years, decays to stable Ar (11.2%) by electron capture or positron emission, and also to stable Ca (88.8%) by beta decay. These properties and ratios are used to determine the age of rocks by K–Ar dating.
In the Earth's atmosphere, Ar is made by cosmic ray activity, primarily by neutron capture of Ar fol…
Characteristics
Argon has approximately the same solubility in water as oxygen and is 2.5 times more soluble in water than nitrogen. Argon is colorless, odorless, nonflammable and nontoxic as a solid, liquid or gas. Argon is chemically inert under most conditions and forms no confirmed stable compounds at room temperature.
Although argon is a noble gas, it can form some compounds under various extr…
History
Argon (Greek ἀργόν, neuter singular form of ἀργός meaning "lazy" or "inactive") is named in reference to its chemical inactivity. This chemical property of this first noble gas to be discovered impressed the namers. An unreactive gas was suspected to be a component of air by Henry Cavendish in 1785.
Argon was first isolated from air in 1894 by Lord Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsay
Occurrence
Argon constitutes 0.934% by volume and 1.288% by mass of the Earth's atmosphere. Air is the primary industrial source of purified argon products. Argon is isolated from air by fractionation, most commonly by cryogenic fractional distillation, a process that also produces purified nitrogen, oxygen, neon, krypton and xenon. The Earth's crust and seawater contain 1.2 ppm and 0.45 ppm of argon, respectively.
Compounds
Argon's complete octet of electrons indicates full s and p subshells. This full valence shell makes argon very stable and extremely resistant to bonding with other elements. Before 1962, argon and the other noble gases were considered to be chemically inert and unable to form compounds; however, compounds of the heavier noble gases have since been synthesized. The first argon compou…
Production
Argon is extracted industrially by the fractional distillation of liquid air in a cryogenic air separation unit; a process that separates liquid nitrogen, which boils at 77.3 K, from argon, which boils at 87.3 K, and liquid oxygen, which boils at 90.2 K. About 700,000 tonnes of argon are produced worldwide every year.
Ar, the most abundant isotope of argon, is produced by the decay of K with a half-life of 1.25×10 y…
Applications
Argon has several desirable properties:
• Argon is a chemically inert gas.
• Argon is the cheapest alternative when nitrogen is not sufficiently inert.
• Argon has low thermal conductivity.