Is fibrocartilage the same as articular cartilage?
Fibrocartilage is a tough, dense, and fibrous material that helps fill in the torn part of the cartilage; however, it is not an ideal replacement for the smooth, glassy articular cartilage that normally covers the surface of joints.
Is articular cartilage hyaline or fibrocartilage?
hyaline cartilageArticular cartilage is hyaline cartilage and is 2 to 4 mm thick. Unlike most tissues, articular cartilage does not have blood vessels, nerves, or lymphatics. It is composed of a dense extracellular matrix (ECM) with a sparse distribution of highly specialized cells called chondrocytes.
What is the articular cartilage also known as?
Hyaline. Hyaline cartilage is the most common type in the body. This cartilage type is found in the larynx, nose, ribs, and trachea. A very thin layer of cartilage is also present on bony surfaces, such as over joints, to cushion them. This hyaline cartilage is known as articular cartilage.
What type of cartilage is found in fibrocartilage?
Fibrocartilage is a transition tissue that should be viewed as a blend between hyaline cartilage and dense fibrous connective tissue. It is a white, densely arranged, opaque, tufted tissue with a mixture of both chondrocytes and fibroblasts.
What is the difference between hyaline cartilage and fibrocartilage?
Hyaline cartilage contains fibers made primarily of type II collagen only. Fibrocartilage contains type II collagen but also contains abundant type I collagen. Elastic cartilage contains type II collagen and elastic fibers.
What is a fibrocartilage?
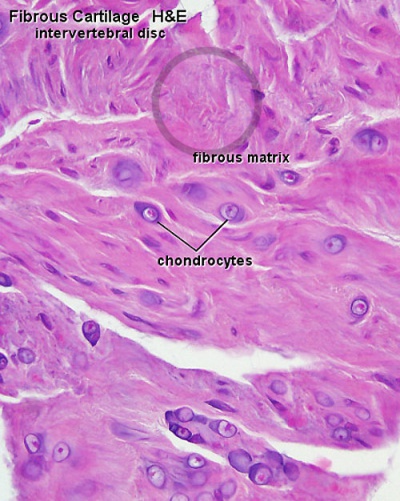
Fibrocartilage is a dense, whitish tissue with a distinct fibrous texture. It forms the intervertebral discs of the spine and menisci of the knee,as well as smaller structures such as the glenoid and acetabular labra, and the lining of bony grooves for tendons.
What are the 3 types of cartilage?
There are three types of cartilage in your body: Hyaline cartilage. Elastic cartilage. Fibrocartilage....Hyaline cartilageAt the ends of bones that form joints.Between your ribs.In your nasal passages.
Which statement about articular cartilage is correct?
The correct answer is d) It cushions and absorbs shock. The cartilage is one of the specialized connective tissues that lacks blood vessels, thus, it...
Where is articular cartilage found?
In a joint, hyaline cartilage is referred to as articular cartilage. This is because the cartilage covers bones' surfaces where they articulate, or meet to form the joint. For example, at the knee joint, the top of the tibia, the bottom of the femur, and the back of the kneecap are covered with articular cartilage.
Where is hyaline elastic and fibrocartilage found?
Hyaline - most common, found in the ribs, nose, larynx, trachea. Is a precursor of bone. Fibro- is found in invertebral discs, joint capsules, ligaments. Elastic - is found in the external ear, epiglottis and larynx.
Which of the following best describes the characteristics of fibrocartilage?
Which of the following is the best description of fibrocartilage? It is located at pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs. Which characteristics best describe the type of the connective tissue called osseous tissue? Its matrix consists of inorganic calcium salts plus an abundance of collagen fibers.
What is the structural difference between fibrocartilage and elastic cartilage?
Fibrocartilage – is the strongest cartilage, and is found in the in intervertebral discs, joint capsules and ligaments. Elastic Cartilage – provides strength and shape maintenance, and can be found in the external ear, epiglottis and the larynx.
What are examples of hyaline cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage is found around the bones of free-moving joints. This is known as articular cartilage. Another example of hyaline cartilage is the tissue found in the walls of the respiratory tract. This includes the bronchi, the nose, the rings of the trachea, and the tips of the ribs.
Which joints have hyaline cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage is found in the synovial joints and assists the motion of joints. It is composed of chondrocytes and extracellular matrix.
Where is hyaline elastic and fibrocartilage found?
Hyaline - most common, found in the ribs, nose, larynx, trachea. Is a precursor of bone. Fibro- is found in invertebral discs, joint capsules, ligaments. Elastic - is found in the external ear, epiglottis and larynx.
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread and is the type that makes up the embryonic skeleton. It persists in human adults at the ends of bones in free-moving joints as articular cartilage, at the ends of the ribs, and in the nose, larynx, trachea, and…
What percentage of articular cartilage is made up of collagen?
If a portion of ‘wet’ articular cartilage with all of its layers was separated into the most important individual elements, water would provide 65–80% of its weight, type II collagen fibrils would account for 10–20% (along with very small percentages of other collagen types), and 10–15% would be made up primarily of Aggrecan, but also other proteoglycans. Chondrocytes only provide approximately 5% of the wet weight of articular cartilage, and lubricating glycoproteins (such as the aptly named lubricin) and noncollagenous proteins are represented in even lower amounts.
What are the layers of cartilage?
Articular cartilage does not have a perichondrium, and is composed of four different layers: superficial, transitional (mid), deep (radial), and calcified layers, or zones. A ‘tidemark’ distinguishes between the non-calcified and calcified layers. The extracellular matrix of these four layers are further split into three regions called the pericellular region (immediately surrounding the chondrocyte), the territorial region (protective, collagen-rich area), and the interterritorial region (largest region with high amounts of collagen and proteoglycans, and structurally important).
Why is articular cartilage important?
Articular cartilage’s role is often better understood in patients in which it has degenerated (usually due to the ageing process or intensive sports). Inflammation and friction where the surfaces of two bones rub against each other cause pain and limited mobility. In the lower limbs, the weight-bearing properties of articular cartilage are unable ...
What does low oxygen levels mean for chondrocytes?
Low levels of oxygen mean chondrocytes primarily depend upon anaerobic metabolism. Nutrients are provided directly from the synovial fluid and not from the perichondrium, which is absent in articular cartilage.
What is the function of articular cartilage?
Articular cartilage function is based upon its composition of hyaline cartilage, which is practically frictionless due to the glass-like surface and ability to self-lubricate via lubricating glycoproteins within the extracellular matrix. When articulation is smooth, less stress is exercised on the cartilage surface and the tissue is more resistant ...
How thick is cartilage?
Articular cartilage is usually found in layers of between 2 and 4 mm thick. As with all types of cartilage, the absence of blood vessels and lymph vessels creates a very slow metabolic environment. Chondrocyte proliferation and apoptosis (death) exists at much lower rates than in noncartilagenous connective tissue.
Which layer of cartilage is flat?
In the superficial layer – the top layer of articular cartilage – chondrocytes are quite flat in shape. At this level there are fewer proteoglycans and higher numbers of organized collagen fibrils. This layer protects the deeper layers from sheer stresses, but is very thin.
How does cartilage heal?
A full-thickness lesion, however, may begin to heal from the blood supply inside the bone. Your body will form a scar in the area using a special type of cartilage called fibrocartilage. Fibrocartilage is a dense, tough, fibrous material that helps fill in the lesion. However, it lacks the smooth, glassy surface of the articular cartilage that normally covers the surface of the knee joint.
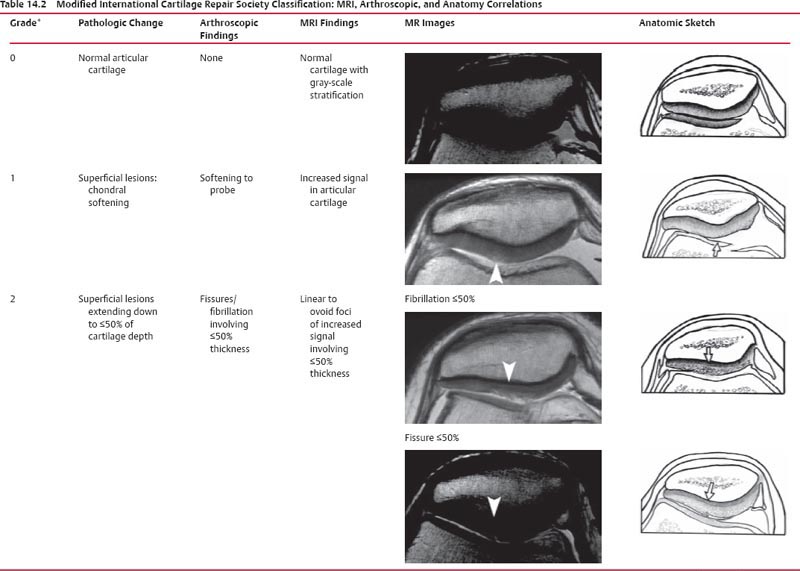
What is grade IV knee cartilage?
Lesions can appear in the surface, damaging the articular cartilage. A grade IV, or full-thickness, lesion is a tear that goes all the way through the cartilage. Grade IV lesions usually require surgical repair.
What is in the extracellular matrix?
The extracellular matrix is an amalgamation of multiple substances that gives cartilage its biomechanical properties. Its composition varies with each subtype of cartilage. Generally, it consists of varying amounts of:
What is the transition between hyaline cartilage and dense fibrous connective tissue?
elastic. fibrocartilage. Fibrocartilage is a transition tissue that should be viewed as a blend between hyaline cartilage and dense fibrous connective tissue. It is a white, densely arranged, opaque, tufted tissue with a mixture of both chondrocytes and fibroblasts.
What is circumferential fibrocartilage?
circumferential fibrocartilage (e.g., glenoid and acetabular labrum) present in the form of a ring without a centre to protect the joint margins and improve the bony fit.
How many types of fibrocartilage are there?
On the basis of their presence and functional significance, fibrocartilage can be categorized into four different types:
Where is the triangular fibrocartilage complex located?
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) in an amalgam of several fibrocartilaginous and ligamentous structures located at the distal radioulnocarpal interface. The articular disc which forms the triangular fibrocartilage proper is supported on the volar and dorsal surfaces by radioulnar ligaments. The ulnocarpal meniscus and tendon sheath of the extensor carpi ulnaris also contribute to the complex.
Where is fibrocartilage found?
While it is difficult to differentiate fibrocartilage from hyaline or elastic cartilage at times, it should be known that fibrocartilage is more commonly observed at enthesis organs and wrap-around regions. The wrap-around regions represent areas where tendons of limb muscles course around pulley systems within the joint and change directions (e.g. the action of the quadriceps femoris across the knee joint ). On the other hand, the enthesis organs represent points of increased stress within a fibrocartilaginous joint (e.g. the insertion of the Achilles tendon into the calcaneus).
What is the role of intervertebral disks in joints?
connecting fibrocartilage (e.g., intervertebral disks) present in the limited-motion joints, acting as a cushion to distribute stresses;
What is the ground substance of fibrocartilage?
The ground substance of the fibrocartilage contains equal amounts of dermatan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. The fibrocartilage is shown in figure 1. The fibrocartilage occurs in the pubic symphysis, menisci of the stifle joint, and the annulus fibrosis of the intervertebral discs.
What is the difference between hyaline and fibrocartilage?
They also absorb shocks. The main difference between fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage is the density of collagen fibers in each type of cartilage.
What are the two types of connective tissue?
Fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage are two types of connective tissues.
What is the matrix of hyaline cartilage?
The matrix of the hyaline cartilage contains collagen fibrils of type II collagen and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). Since the GAGs trap a lot of water, the hyaline cartilage consists of a high diffusion rate. The hydrated nature of the hyaline cartilage allows shock absorbance.
What are the three types of cartilage?
Fibrocartilage, hyaline cartilage, and elastic cartilage are the three types of cartilage that are found in the human body. Cartilages are a type of connective tissue that is made up of chondrocytes and an extracellular matrix. In the fetus, the skeleton is completely made up of cartilage. Then the cartilages are replaced with bones.
Why is fibrocartilage flexible?
The flexibility of both fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage is due to chondroitin.
What is the most abundant type of cartilage in adults?
In the fetus, the skeleton is first laid down as the hyaline cartilage. In the adolescence, the calcification of the hyaline cartilage is replaced by the bones. However, the most abundant type of cartilage in adults is the hyaline cartilage .