Precautions
Azilect is a selective inhibitor of MAO-B at the recommended doses of 0.5 or 1 mg daily. Selectivity for inhibiting MAO-B diminishes in a dose-related manner as the dose is progressively increased above the recommended daily doses.
Is Azilect a selective inhibitor of MAO-B?
Azilect (rasagiline) is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) used to treat Parkinson's disease. Azilect’s exact mechanism of action is not known; however, by inhibiting MAO-B Azilect reduces the breakdown of dopamine resulting in increased levels of dopamine in the brain. Increased dopamine levels alleviate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
How does Azilect treat Parkinson's disease?
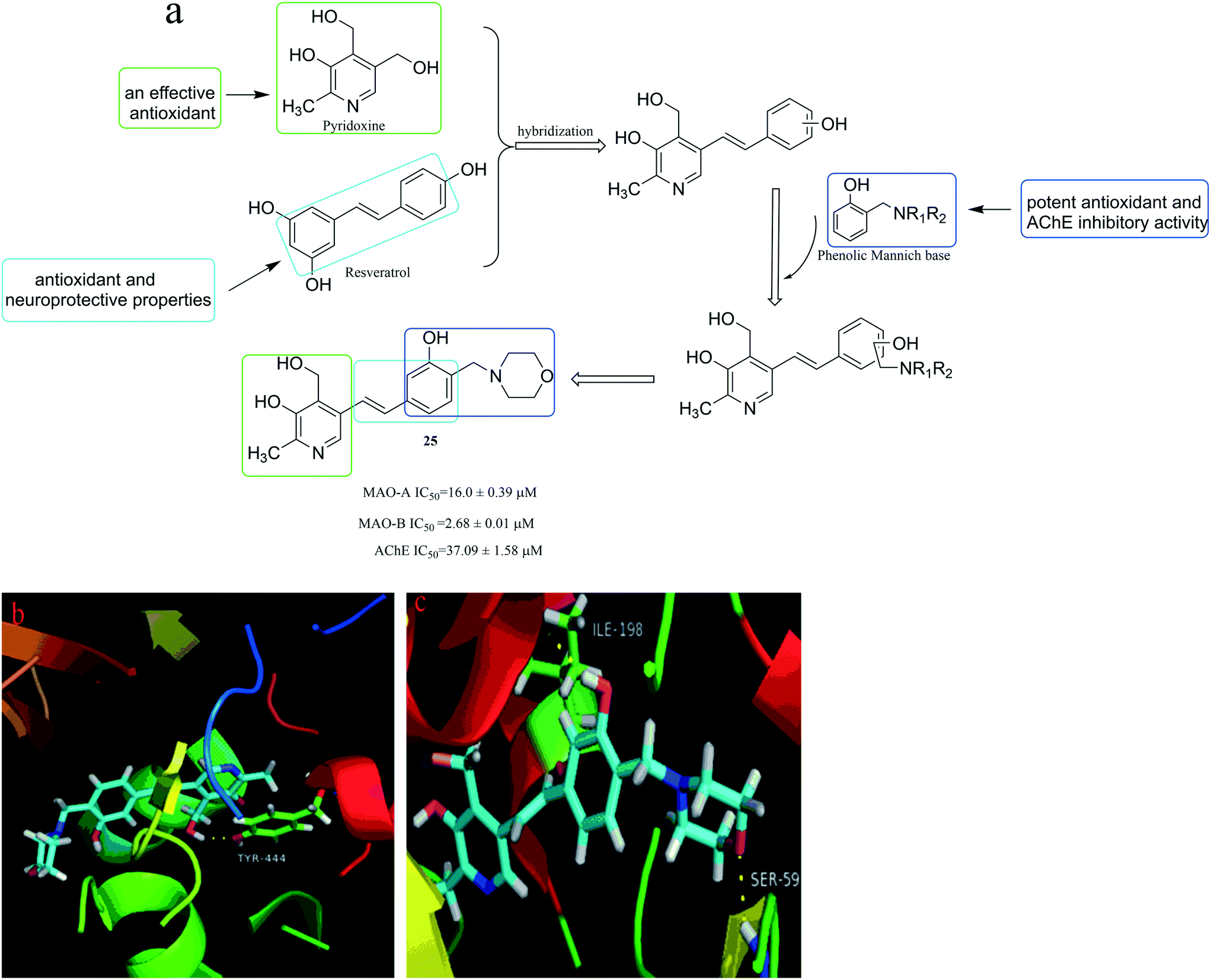
AZILECT is a selective, irreversible MAO-B inhibitor indicated for the treatment of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease.
What type of drug is Azilect?
AZILECT is contraindicated for use with meperidine, tramadol, methadone, propoxyphene, and MAO inhibitors (MAOIs), including other selective MAO-B inhibitors, because of risk of serotonin syndrome [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ]. At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of AZILECT and initiation of treatment with these medications.
What medications are contraindicated with Azilect?
Is rasagiline a MAOI?
RASAGILINE (ra SA ji leen) is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). It is used to treat Parkinson's disease. This medicine may be used for other purposes; ask your health care provider or pharmacist if you have questions.
Is Azilect an MAOI?
Azilect and certain pain medications Azilect is a type of drug called a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI).
What class of drug is Azilect?
Azilect belongs to a class of drugs called Antiparkinson Agents, MAO Type B Inhibitors.
Are MAO inhibitors used for Parkinson's?
MAO-B (monoamine oxidase-B) inhibitors are a class of drugs used to treat the symptoms of Parkinson's disease (PD).
Which drugs are MAOI?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved these MAOIs to treat depression:Isocarboxazid (Marplan)Phenelzine (Nardil)Selegiline (Emsam)Tranylcypromine (Parnate)
What foods should be avoided when taking Azilect?
Those taking monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitors such as Azilect (rasagiline) or Eldepryl (selegeline) should avoid foods containing tyramine (including cured, fermented or air-dried meats or fish, aged cheeses, fermented cabbage, soybean products, and red wine and tap beer) because they could lead to high blood ...
Can you stop Azilect abruptly?
Do not stop taking rasagiline without talking to your doctor. Your doctor will probably decrease your dose gradually. If you suddenly stop taking rasagiline, you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as a fever; muscle stiffness; unsteadiness, wobbliness, or lack of coordination; or changes in consciousness.
Does rasagiline cause dementia?
Digit Span, verbal fluency, and Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) showed non-significant directional favoring of rasagiline; no effects were observed in Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Subscale (ADAS-cog) or activities of daily living.
Does Azilect Slow Progression Parkinson's?
In early Parkinson's disease, Azilect can be used as single drug therapy to slow progression of symptoms. In more advanced Parkinson's disease, it can be used as an adjunct with levodopa to improve performance with motor skills and activities of daily living.
What does rasagiline do for Parkinson's?
Rasagiline inhibits striatal dopamine metabolism, thereby providing relief from motor symptoms of PD. It may be dosed once daily and, unlike selegiline, it is metabolized to non-amphetamine compounds. In a large clinical trial, rasagiline has proved effective, safe, and well tolerated in early PD as monotherapy.
Does rasagiline increase serotonin?
Rasagiline should not be administered with antidepressants that increase serotonin levels. Combining rasagiline with such antidepressants may lead to excessive levels of serotonin and a fatal condition called the serotonin syndrome.
Why are MAOIs rarely prescribed?
Since then, our understanding of the pharmacology of MAOIs has advanced considerably but unfortunately, the use of these agents has waned in recent decades often due to lack of education about the importance of these agents and their unique effectiveness properties.
What class of drug is rasagiline?
Rasagiline is in a class of medications called monoamine oxidase (MAO) type B inhibitors. It works by increasing the amounts of certain natural substances in the brain.
What does Azilect do for Parkinson's?
It acts by slowing down the breakdown of dopamine in the brain. Dopamine is a chemical that sends information to the parts of the brain that control movement and coordination. In early Parkinson's disease, Azilect can be used as single drug therapy to slow progression of symptoms.
What's the difference between selegiline and rasagiline?
Rasagiline is about 10 times more potent in the inhibition of MAO-B than selegiline in ex vivo studies. This higher potency of rasagiline is corrected in the clinic with dose adjustments (approved daily dose 1 and 5–10 mg for rasagiline and selegiline, respectively).
What does rasagiline do for Parkinson's?
Rasagiline inhibits striatal dopamine metabolism, thereby providing relief from motor symptoms of PD. It may be dosed once daily and, unlike selegiline, it is metabolized to non-amphetamine compounds. In a large clinical trial, rasagiline has proved effective, safe, and well tolerated in early PD as monotherapy.
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not take Azilect if you are allergic to rasagiline.Do not use Azilect if you have used any other MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days. A da...
How Should I Take Azilect?
Take Azilect exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all directions on your prescription label. Your doctor may occasionally change your dose....
Azilect Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose for Parkinson's Disease:Monotherapy:Recommended dose: 1 mg orally once a dayAdjunct therapy:Initial dose (in patients on concomita...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Azilect?
Taking Azilect with other drugs that make you sleepy can worsen this effect. Ask your doctor before taking a sleeping pill, narcotic medication, mu...
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to...
What Happens If I Overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.Overdose symptoms may include drowsiness, dizziness, severe headach...
What Should I Avoid While Taking Azilect?
Rasagiline may impair your thinking or reactions. Avoid driving or operating machinery until you know how this medicine will affect you. Avoid gett...
Can you take azilect if you have liver disease?
involuntary movements (dyskenesias), hallucinations or lowered blood pressure to occur. Avoid taking Azilect if you have liver disease or a tumor of the adrenal gland. Inform your physician if you are taking or planning to take any prescriptions or over-the-counter drugs, especially ciprofloxacin or antidepressants.
Can azilect be taken with food?
When Azilect is taken with certain foods and medication, adverse reactions can occur. Consider the following precautions if you take Azilect:
Can azilect cause indigestion?
The most common side effects which may occur on Azilect alone are headache, joint pain and indigestion. Inform your physician if these do not go away. involuntary movements (dyskenesias), hallucinations or lowered blood pressure to occur. Avoid taking Azilect if you have liver disease or a tumor of the adrenal gland.
What is the drug name for AZILECT?
AZILECT® tablets contain rasagiline (as the mesylate), a propargylamine-based drug indicated for the treatment of idiopathic Parkinson's disease. It is designated chemically as: 1H-Inden-1amine, 2, 3-dihydro-N-2-propynyl-, (1R)-, methanesulfonate. The empirical formula of rasagiline mesylate is (C 12 H 13 N)CH 4 SO 3 and its molecular weight is 267.34.
What is azilect used for?
Azilect is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of Parkinson Disease. Azilect may be used alone or with other medications. Azilect belongs to a class of drugs called Antiparkinson Agents, MAO Type B Inhibitors. It is not known if Azilect is safe and effective in children younger than 18 years of age.
What antidepressants are used for serotonin syndrome?
Serotonin syndrome has been reported with concomitant use of an antidepressant (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors-SSRIs, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors-SNRIs, tricyclic antidepressants, tetracyclic antidepressants, triazolopyridine antidepressants) and a nonselective MAOI (e.g., phenelzine, tranylcypromine) or selective MAO-B inhibitors, such as selegiline (Eldepryl) and rasagiline (AZILECT). Serotonin syndrome has also been reported with concomitant use of AZILECT with meperidine, tramadol, methadone, or propoxyphene. AZILECT is contraindicated for use with meperidine, tramadol, methadone, propoxyphene, and MAO inhibitors (MAOIs), including other selective MAO-B inhibitors [see CONTRAINDICATIONS and DRUG INTERACTIONS ].
How much does AZILECT decrease blood pressure?
In Study 3, the incidence of orthostatic hypotension consisting of a systolic blood pressure decrease (≥ 30 mm Hg) or a diastolic blood pressure decrease (≥ 20 mm Hg) after standing was 13% with AZILECT (1 mg/day) compared to 9% with placebo [see ADVERSE REACTIONS ].
What are the side effects of azilect?
The most common side effects of Azilect include: depressed mood, sleep problems (insomnia), strange dreams, involuntary muscle movements, loss of appetite, weight loss, indigestion,
What is MAO in the gastrointestinal tract?
MAO in the gastrointestinal tract and liver (primarily type A) provides protection from exogenous amines (e.g., tyramine) that have the capacity, if absorbed intact, to cause a tyramine reaction with hypertension including clinical syndromes referred to as hypertensive urgency, crisis, or emergency. Foods and medications containing large amounts of exogenous amines (e.g., from fermented cheese, herring, over-the-counter cough/cold medications) may cause release of norepinephrine resulting in a rise in systemic blood pressure.
Is AzilECT a levodopa?
AZILECT was studied as an adjunct therapy without levodopa (Study 2), or as an adjunct therapy to levodopa, with some patients also taking dopamine agonists, COMT inhibitors, anticholinergics, or amantadine (Study 3 and Study 4).
What is azilect used for?
Azilect (rasagiline tablets) is indicated for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD).
How much rasagiline is in Azilect?
Each Azilect tablet for oral administration contains 0.5 mg or 1 mg of rasagiline (equivalent to 0.78 mg or 1.56 mg of rasagiline mesylate). Each Azilect tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: mannitol, starch, pregelatinized starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, stearic acid, and talc.
How long does rasagiline last?
Rasagiline mean steady-state half life is 3 hours but there is no correlation of pharmacokinetics with its pharmacological effect because of its irreversible inhibition of MAO-B.
Where does rasagiline undergo biotransformation?
Rasagiline undergoes almost complete biotransformation in the liver prior to excretion. The metabolism of rasagiline proceeds through two main pathways: N-dealkylation and/or hydroxylation to yield 1-aminoindan (AI), 3-hydroxy-N-propargyl-1 aminoindan (3-OH-PAI) and 3-hydroxy-1-aminoindan (3-OH-AI). In vitro experiments indicate that both routes of rasagiline metabolism are dependent on the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system, with CYP1A2 being the major isoenzyme involved in rasagiline metabolism. Glucuronide conjugation of rasagiline and its metabolites, with subsequent urinary excretion, is the major elimination pathway.
What is the volume of rasagiline?
The mean volume of distribution at steady-state is 87 L , indicating that the tissue binding of rasagiline is in excess of plasma protein binding. Plasma protein binding ranges from 88-94% with mean extent of binding of 61-63% to human albumin over the concentration range of 1-100 ng/mL.
Does rasagiline inhibit MAO-B?
Studies in healthy subjects and in Parkinson’s disease patients have shown that rasagiline inhibits platelet MAO-B irreversibly. The inhibition lasts at least 1 week after last dose. Almost 25-35% MAO-B inhibition was achieved after a single rasagiline dose of 1 mg/day and more than 55% of MAO-B inhibition was achieved after a single rasagiline dose of 2 mg/day. Over 90% inhibition was achieved 3 days after rasagiline daily dosing at 2 mg/day and this inhibition level was maintained 3 days postdose. Multiple doses of rasagiline of 0.5, 1, and 2 mg per day resulted in complete MAO-B inhibition.
Can Rasagiline be used for hepatic impairment?
Patients with mild hepatic impairment should not exceed a dose of 0.5 mg/day. Azilect should not be used in patients with moderat e or severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.3 ), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5) and Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )].
What is azilect used for?
Azilect is a brand-name prescription medication. It’s approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat Parkinson’s disease. This is a condition that affects the nervous system and causes muscle movements that you can’t control.
What is the active drug class of azilect?
The active drug in Azilect is rasagiline. Azilect belongs to a drug class known as monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors, which are also known as MAOIs. A drug class is a group of medications that work in a similar way.
Are there any contraindications to using Azilect?
Yes. A contraindication is a condition or factor that would prevent you from taking a medication. There are some contraindications to using Azilect.
Will I be able to have surgery if I’m taking Azilect?
Yes, but it’s important to be aware that some medications used for surgery may interact with Azilect. These include:
Why is it important to dispose of Azilect?
If you no longer need to take Azilect and have leftover medication, it’s important to dispose of it safely. This helps prevent others, including children and pets, from taking the drug by accident. It also helps keep the drug from harming the environment.
How long does it take for Azilect to go away?
Most of these side effects may go away within a few days or a couple of weeks. But if they become more severe or don’t go away, talk with your doctor or pharmacist. * These are partial lists of mild side effects from Azilect. To learn about other mild side effects, talk with your doctor or pharmacist, or view Azilect’s prescribing information.
Does azilect cause Parkinson's disease?
Mild side effects of Azilect when taken with other drugs for Parkinson’s disease. If you take Azilect in addition to other drugs for Parkinson’s disease, mild side effects* can include: peripheral edema (swelling in your hands, legs, or feet) cough. insomnia (trouble falling asleep or staying asleep) weight loss.
How much does rasagiline cost?
The lowest GoodRx price for the most common version of rasagiline is around $45.00, 92% off the average retail price of $595.10. Prescription Settings. generic.
What foods should I avoid with tyramine?
It is very important that you restrict dietary tyramine by avoiding the following tyramine-rich foods and beverages: Aged cheese. Air dried, aged and fermented meats, sausages and salamis (eg, cacciatore, hard salami and mortadella) Animal livers that are spoiled or improperly stored.
Is rasagiline safe for children?
Appropriate studies have not been performed on the relationship of age to the effects of rasagiline in the pediatric population. Safety and efficacy have not been established.
Can you take Valbenazine and Ziprasidone together?
Valbenazine. Ziprasidone. Using this medicine with any of the following medicines may cause an increased risk of certain side effects, but using both drugs may be the best treatment for you. If both medicines are prescribed together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use one or both of the medicines.
Can Rasagiline be used with levodopa?
Overview TOP. Rasagiline is used alone or together with levodopa for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease is a condition of the brain that becomes worse over time and may cause movement problems, rigidity, tremors, and slowed physical movement.
What is azilect used for?
Azilect (rasagiline) is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) used to treat Parkinson's disease. Azilect’s exact mechanism of action is not known; however, by inhibiting MAO-B Azilect reduces the breakdown of dopamine resulting in increased levels of dopamine in the brain. Increased dopamine levels alleviate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Common side effects of Azilect include flu like symptoms, headache, nausea, joint pain, upset stomach, depression, falls, constipation, dizziness on standing, dry mouth, rash, hallucinations, vomiting, and difficulty moving. There are no adequate studies of Azilect in pregnant women. It is unknown if Azilect passes into breast milk.
Why is azilect contraindicated?
Azilect is contraindicated for use with other MAO inhibitors because of the increased risk of nonselective MAO inhibition that may lead to a hypertensive crisis.
What are the side effects of azilect?
rash, hallucinations, vomiting, and. difficulty moving. Serious side effects of Azilect include hypertensive crisis if foods high in tyr amine are consumed while taking Azilect. Drug interactions of Azilect include ciprofloxacin, which inhibits the enzymes in the liver that eliminate Azilect, increasing blood levels and possible side effects ...
Why did Azilect discontinue?
In Study 1, approximately 5% of the 149 patients treated with Azilect discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions compared to 2% of the 151 patients who received placebo.
What enzyme breaks down serotonin?
Monoamine oxidase is an enzyme that breaks down serotonin, norepinephrine, dopamine, tyramine and similar chemicals that serve as neurotransmitters, chemicals that nerves use to communicate with one another. There are two types of monoamine oxidase enzymes, MAO-A and MAO-B. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors inhibit one or both enzymes resulting in ...
What are the two types of monoamine oxidase inhibitors?
There are two types of monoamine oxidase enzymes, MAO-A and MAO-B. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors inhibit one or both enzymes resulting in increased levels of the chemicals normally broken down by MAO-A or MAO-B.
Can you take rasagiline with tyramine?
Results of a special tyramine challenge study indicate that rasagiline is selective for MAO-B at recommended doses and can be used without dietary tyramine restriction. However, certain foods may contain very high amounts (i.e., 150 mg or greater) of tyramine and could potentially cause a hypertensive reaction in individual patients taking Azilect due to increased sensitivity to tyramine.
What are MAO inhibitors?
This allows serotonin and other hormones to remain in the brain for longer, and helps to reduce symptoms of depression. These drugs are called “MAO inhibitors” and include phenelzine (Nardil®), tranylcypromine (Parnate®), and isocarboxazid (Marplan®). Because MAO is involved in the metabolism of multiple compounds in the human body and brain, MAO inhibitors have also been used to treat a variety of conditions including anxiety, dementia, and Parkinson’s disease. Since MAO inhibitors cause increases in serotonin and other natural chemicals, they can interact with other antidepressants or drugs that act in a similar way. Serotonin syndrome is a serious medical condition that is caused by the presence of excess serotonin in the human body. Serotonin syndrome can occur when an individual takes multiple medications or high doses of drugs that affect serotonin release or metabolism. Patients who develop serotonin syndrome often require specialized care or hospitalization. Because MAO inhibitors affect serotonin metabolism, people who take MAO inhibitors are at risk for developing serotonin syndrome.
What happens if you take a MAO inhibitor?
One of the other chemicals targeted and metabolized by MAO inhibitors is called tyramine. In the human body, the presence of excess tyramine causes high blood pressure along with other unpleasant symptoms such as nausea, skin flushing, and headache. This condition is often described as a “tyramine reaction”. Tyramine is present in the human digestive system and is normally metabolized there by MAO-A. The use of MAO inhibitor medications causes high levels of tyramine to build up in the body and can result in tyramine reactions. People who take higher doses of MAO inhibitors, as well as those who overdose on these medications, are at higher risk for developing tyramine reactions. Since tyramine is naturally present in some foods including aged cheeses and meats, draft beer, and sauerkraut, people who take standard prescribed doses of MAO inhibitors may develop tyramine reactions if they eat these foods. Because of this, individuals who take MAO inhibitors are often advised to follow a special low-tyramine diet.
Where is monoamine oxidase found?
Monoamine oxidase (or “MAO”) is an enzyme found in the human body. The MAO enzyme converts chemicals including dopamine, serotonin, and adrenaline into ammonia, hydrogen peroxide, and other products. There are two types of MAO found in the human body. MAO type A (or MAO-A) is found in the stomach and intestines, while most MAO type B (MAO-B) is located in other organs including the brain.
Can MAO be used for depression?
MAO inhibitors are commonly used for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and depression. Serious medical conditions can occur if MAO inhibitors are used in higher doses or taken in overdose. In addition, people who take MAO inhibitors should avoid eating certain foods, to reduce their risk of unwanted side effects.
Can you take MAO inhibitors with children?
Only take MAO inhibitors as always prescribed and always keep them out of reach of children.
Which MAO inhibitors are used for PD?
Of all the MAO inhibitors, only selegiline and rasagiline have been found to be useful in treating the progression of PD.
How many types of MAO are there?
There are actually 2 types of MAO in the body, and although similar, have different preferences for the monoamines they break down (deaminate). MAO-A, and MAO-B.
Is azilect a MAO inhibitor?
Azilect ( generic Rasagiline) on the other hand is a MAO irreversible inhibitor which is still studied very intensively to this day not only for PD but depression.
Is Azilect a natural drug?
Azilect (rasagiline) is an Interesting drug (which has passed several Phase III trials) as an alternative to deprenyl (selegiline) , but certainly not "natural". Azilect is about 4 times the cost of its generic equivalent, rasagiline. Both usually come in either .5 and 1 mg tablets. Selegiline generic is about 50% the cost of rasagiline.
Can you mix selegiline and rasagiline?
Do not combine Rasagiline with Selegiline. Serious reactions can and do occur.
Does selegiline kill TrkB?
More importantly from a PD perspective, selegiline (as with Rasagiline) may inhibit the negative action of the protein "Alpha Synuclein" which can interfere with the brain's neuroprotective pathway. This protein "kills" TrkB activities leading to the cell death of dopamine...leading to increased vunerability to PD in the long run.
Is Rasagiline an inhibitor?
Rasagiline is as an irreversible MAO-B inhibitor and the active agent of Azilect. It is frequently prescribed to manage symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.

Azilect Dosage and Administration
Rasagiline is used alone or with other medications (such as levodopa/carbidopa) to treat symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
May Treat: Idiopathic parkinsonism
Drug Class: Antiparkinson Therapy - Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor(MAO-B)
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Lactation: Consult a doctor before using
May Treat: Idiopathic parkinsonism
Drug Class: Antiparkinson Therapy - Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor(MAO-B)
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Lactation: Consult a doctor before using
Alcohol: Limit intake while taking this medication
Driving: May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Use caution
Manufacturer: TEVA NEUROSCIEN
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Contraindications
Warnings and Precautions
Adverse Reactions
- General Dosing Recommendations
When Azilect is prescribed as monotherapy or as adjunct therapy in patients not taking levodopa, patients may start Azilect at the recommended dose of 1 mg administered orally once daily. In patients taking levodopa, with or without other PD drugs (e.g., dopamine agonist, amantadine, a… - Patients Taking Ciprofloxacin or Other CYP1A2 Inhibitors
Patients taking concomitant ciprofloxacin or other CYP1A2 inhibitors should not exceed a dose of Azilect 0.5 mg once daily [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Drug Interactions (7.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Drug Interactions
- Azilect 0.5 mg Tablets: White to off-white, round, flat, beveled tablets, debossed with “GIL 0.5” on one side and plain on the other side. Azilect 1 mg Tablets: White to off-white, round, flat, beveled tablets, debossed with “GIL 1” on one side and plain on the other side.
Use in Specific Populations
- Azilect is contraindicated for use with meperidine, tramadol, methadone, propoxyphene, and MAO inhibitors (MAOIs), including other selective MAO-B inhibitors, because of risk of serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of Azilect and initiation of treatment with these medication...
Drug Abuse and Dependence
- Hypertension
Exacerbation of hypertension may occur during treatment with Azilect. Medication adjustment may be necessary if elevation of blood pressure is sustained. Monitor patients for new onset hypertension or hypertension that is not adequately controlled after starting Azilect. In Study 3, … - Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome has been reported with concomitant use of an antidepressant (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors-SSRIs, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors-SNRIs, tricyclic antidepressants, tetracyclic antidepressants, triazolopyridine antidepressants) and a nonselecti…
Overdosage
- The following adverse reactions are described in more detail in the Warnings and Precautionssection of the label: 1. Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] 2. Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] 3. Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] 4. Hypotension / Orthostatic Hypotensio…
Azilect Description
- Meperidine
Serious, sometimes fatal reactions have been precipitated with concomitant use of meperidine (e.g., Demerol and other tradenames) and MAO inhibitors including selective MAO-B inhibitors [see Contraindications (4)]. - Dextromethorphan
The concomitant use of Azilect and dextromethorphan was not allowed in clinical studies. The combination of MAO inhibitors and dextromethorphan has been reported to cause brief episodes of psychosis or bizarre behavior. Therefore, in view of Azilect’s MAO inhibitory activity, dextrome…