Can Barrett’s esophagus cause chest pain?
Chest Pain Though rarer than heartburn or dysphagia, some people with Barrett’s esophagus experience chest pain. Your gastroenterologist may decide to evaluate you for Barrett’s esophagus based on your risk factors and health history. Chronic heartburn.
How is Barrett's esophagus diagnosed?
Barrett's esophagus is often diagnosed in people who have long-term gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) — a chronic regurgitation of acid from the stomach into the lower esophagus. Only a small percentage of people with GERD will develop Barrett's esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is associated with an increased risk...
How can I prevent Barrett’s esophagus?
The best way to keep the lining of your esophagus healthy is to address heartburn or GERD symptoms. People with ongoing, untreated heartburn are much more likely to develop Barrett’s esophagus. Untreated heartburn raises the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma by 64 times. Other ways to decrease your risk factors include:
What is the rate of incidence for Barrett’s esophagus?
About 10 to 15 percent of people with acid reflux develop Barrett’s esophagus. The risk of getting cancer due to Barrett’s esophagus is even lower. Only 0.5 percent of people with Barrett’s are diagnosed with esophageal cancer per year.
What does Barrett's esophagus pain feel like?
The development of Barrett's esophagus is most often attributed to long-standing GERD , which may include these signs and symptoms: Frequent heartburn and regurgitation of stomach contents. Difficulty swallowing food. Less commonly, chest pain.
Where do you feel pain from Barrett's esophagus?
The main symptom of Barrett's Oesophagus is reflux, which can cause heartburn, regurgitation of food (bringing food back up), nausea and pain in the upper abdomen.
What aggravates Barrett's esophagus?
In people with Barrett's esophagus who are affected by reflux symptoms, the symptoms may be triggered by certain foods, especially spicy, citric or hot foods, as well as other stimuli, such as alcohol and coffee.
What are the symptoms of Barrett's esophagus getting worse?
What are the symptoms of Barrett's esophagus?Heartburn that worsens or wakes you from sleep.Painful or difficult swallowing.Sensation of food stuck in your esophagus.Constant sore throat, sour taste in your mouth or bad breath.Unintentional weight loss.Blood in stool.Vomiting.
How long does it take for Barrett's esophagus to become cancerous?
This cohort study showed that the incubation period from Barrett esophagus to invasive cancer is likely more than 30 years.
How fast does Barrett's progress?
Barrett esophagus (BE) is a precancerous condition that progresses to high-grade dysplasia (HGD) at an estimated rate of 0.5% to 0.9% per year.
What is the best medication for Barrett's esophagus?
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are drugs that block the three major pathways for acid production. PPIs suppress acid production much more effectively than H2 blockers. PPIs are the most effective medication for healing erosive esophagitis and providing long-term control of GERD symptoms.
What are the stages of Barrett's esophagus?
The stages of Barrett's esophagus are:non-dysplastic (no cancerous tissue present)low-grade dysplasia (minor cell changes found)high-grade dysplasia (extensive cell changes found, but not yet cancer)noninvasive cancer.invasive cancer.
Can you live a long life with Barrett's esophagus?
Furthermore, patients with Barrett's esophagus appear to live approximately as long as people who are free of this condition. Patients often die of other causes before Barrett's esophagus progresses to cancer. Monitoring for precancerous changes is recommended for most patients with Barrett's esophagus.
How many years can you live with Barrett's esophagus?
RESULTS: The mean age at diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus was 61.6 years in males and 67.3 years in females. The mean life expectancy at diagnosis was 23.1 years in males, 20.7 years in females and 22.2 years overall.
Should I be worried about Barrett's esophagus?
Barrett's esophagus is considered a precancerous condition and increases esophageal cancer risk. While only a small percentage of patients with Barrett's esophagus end up developing esophageal cancer, it is important to monitor the condition in case it begins to progress.
How do you keep your Barrett's esophagus from progressing?
Getting plenty of fiber in your daily diet is good for your overall health. Medical research shows that it may also help prevent Barrett's esophagus from worsening and lower your risk of cancer in the esophagus. Add these and other fiber-rich foods to your daily diet: fresh, frozen, and dried fruit.
Can esophagus pain be felt in the back?
Because of the intensity of heartburn associated with GERD, pain may radiate from the referred area of the esophagus to your lower back.
Where is hiatal hernia pain located?
A hiatal hernia occurs when the upper part of your stomach pushes up through your diaphragm and into your chest region. Hiatal hernias don't always cause symptoms. Hiatal hernia symptoms may include heartburn, acid reflux, and chest pain.
What are the stages of Barrett's esophagus?
The stages of Barrett's esophagus are:non-dysplastic (no cancerous tissue present)low-grade dysplasia (minor cell changes found)high-grade dysplasia (extensive cell changes found, but not yet cancer)noninvasive cancer.invasive cancer.
Which side is the esophagus on?
leftEsophagus is located at left of midline at level of 1st dorsal vertebra, right of midline at level of 6th dorsal vertebra, and left of midline again at level of 10th dorsal vertebra. Thus, esophagus makes a reverse “S” all the way in front of vertebral column.
Who gets Barrett's esophagus?
It is the most common chronic gastrointestinal disease. About 5 percent of patients with chronic GERD or inflammation of the esophagus will develop Barrett's esophagus. This condition is more common in men than in women and more common in Caucasian Americans than in African Americans. The average age at diagnosis is 55 years.
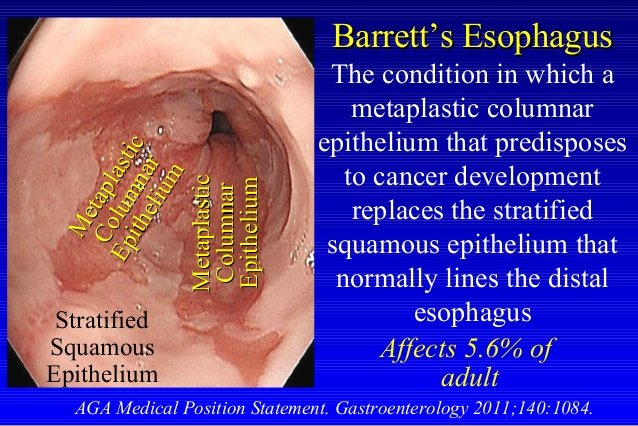
What does Barrett's esophagus look like?
Barrett's esophagus occurs when the lining of the esophagus heals abnormally and changes from cells that look like skin to cells that look like intestinal cells. Hence, Barrett’s esophagus is suspected by the appearance of the esophageal lining (salmon pink color compared to normal white color) and is confirmed by the microscopic examination ...
What is the procedure to diagnose Barrett's esophagus?
Upper Endoscopy . A gastroenterologist will most likely perform an upper endoscopy with biopsy to help diagnose Barrett's esophagus. During this procedure, the lining of the esophagus is checked for abnormalities. The endomicroscope is often used to analyze the tissue during an endoscopy, avoiding the need for a more invasive biopsy.
What is the difference between gastrointestinal and upper endoscopy?
An upper endoscopy allows your doctor to examine the lining of your esophagus, stomach and the first part of your small intestine, called the duodenum. A gastrointestinal endoscopy examines the mucous lining of your upper gastrointestinal tract. The endoscopy and biopsy are two parts of the same procedure:
What is the liquid used to remove stains from the esophagus?
During the endoscopy, we apply stains to the esophagus with a liquid called Lugol's solution. The dye stains only the normal cells; unstained areas may be malignant. The unstained areas are easily seen and tissue is removed from that area and sent for biopsy.
Is it safe to have endoscopic treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
There is a risk of Barrett's esophagus becoming cancerous, so your condition may need to be monitored frequently. If there are precancerous cells (dysplasia) diagnosed in the Barrett’s esophagus, endoscopic treatment is recommended and proven safe and effective for preventing progression to cancer.
Does Barrett's esophagus cause GERD?
Barrett's esophagus does not cause symptoms. It may be associated with complications of associated GERD. See a gastroenterologist if you experience any of the following symptoms for more than two weeks: Heartburn. Indigestion. Blood in vomit or stool. Difficulty swallowing solid foods.
Why does Barrett's esophagus irritate?
This chronic (ongoing) condition occurs when stomach contents flow backward into the esophagus. Experts believe the acidic liquid irritates the lining of the esophagus, leading to changes in the tissue. But you can also have Barrett’s esophagus without having GERD.
What is Barrett's esophagus?
Barrett’s esophagus is a change in the tissue lining your esophagus, the tube in your throat that carries food to your stomach. For reasons no one understands completely, cells in the esophageal lining sometimes become more like intestinal cells. Researchers suspect that having acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) ...
How to keep esophagus healthy?
The best way to keep the lining of your esophagus healthy is to address heartburn or GERD symptoms. People with ongoing, untreated heartburn are much more likely to develop Barrett’s esophagus. Untreated heartburn raises the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma by 64 times.
What is the procedure to remove a spot on the esophagus?
Surgery: If you have severe dysplasia or esophageal cancer, your provider may recommend an esophagectomy, a surgery to remove all or part of the esophagus.
How to diagnose Barrett's esophagus?
How is Barrett's esophagus diagnosed? The only way to confirm the diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus is with a test called an upper endoscopy. This involves inserting a small lighted tube (endoscope) through the throat and into the esophagus to look for a change in the lining of the esophagus.
What is the most common procedure for esophageal sloughing?
Radiofrequency ablation: This is the most common procedure. It burns off abnormal tissue using radio waves, which generate heat. Cryotherapy: Healthcare providers use liquid nitrogen to freeze diseased parts of the esophagus lining so it will slough off (shed).
How to treat GERD?
If you have GERD, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to treat GERD. These medicines decrease stomach acid, which can protect your esophagus from damage. Lifestyle changes, like sleeping slightly inclined and avoiding eating dinner late, often help, too.
How to treat Barrett's esophagus?
Your doctor may recommend minimally invasive procedures using laparoscopy to treat Barrett’s esophagus. In a laparoscopic procedure, your doctor makes a small incision to access the interior of your abdomen. The doctor then performs the treatment using a narrow, lighted tube and specialized surgical instruments.
Why is Barrett's esophagus a diagnostic challenge?
Barrett’s esophagus presents a diagnostic challenge because many people do not experience symptoms of the condition.
What is the procedure to remove precancerous cells from the esophagus?
Ablation for esophagus disorders: Our ablation techniques include several procedures using hot or cold energy to safely remove precancerous cells from your esophagus.
What is the procedure called when the doctor tightens the esophagus?
During a Nissen procedure, the doctor tightens your esophagus thorough several small abdominal incisions. Gastric bypass: For some people, reducing the size of the stomach can help lower the amount of stomach acid the esophagus is exposed to, preventing further damage.
What does early treatment mean for Barrett's esophagus?
For people with Barrett’s esophagus, early treatment can mean the difference between good health and a decreased quality of life.
Can antacids help with Barrett's esophagus?
Certain medications are sometimes enough to stop symptoms of Barrett’s esophagus that result from acid reflux. Your doctor can help you determine if medication is a good treatment choice for you. You may need one or more of these medications: Antacids to help neutralize stomach acid.
What is the treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
Gastroenterologists at Johns Hopkins developed the use of cryoablation therapy, an effective treatment for Barrett's esophagus. Ablation therapy may cause Barrett's esophagus to regress. Medications will be given to suppress your stomach acid. Then, during an endoscopy, thermal injury is administered to the abnormal mucous lining.
What is the name of the doctor who treats Barrett's esophagus?
Doctors at Johns Hopkins are at the forefront of diagnosing and treating Barrett's esophagus. In fact, gastroenterologists at Hopkins pioneered the use of cryoablation, a revolutionary new therapy, to treat Barrett's esophagus.
Why do people with high grade dysplasia need an esophagectomy?
Patients with high-grade dysplasia may need to undergo an esophagectomy (removal of the esophagus) because of the increased risk of cancer.
What foods affect peristalsis?
Avoiding foods that affect peristalsis (the muscle movements in your digestive tract), such as coffee, alcohol and acidic liquids
Can antacids cause reflux?
Over-the-counter antacids are best for intermittent and relatively infrequent symptoms of reflux. When taken frequently, antacids may worsen the problem. They leave the stomach quickly, and your stomach actually increases acid production as a result.
What is Barrett’s Esophagus?
Barrett’s esophagus is a change in the lining of the esophagus. This is caused by chronic acid reflux.
How rare is Barrett's esophagus cancer?
Developing cancer from Barrett’s esophagus is rare. Studies found that less than one percent of patients develop esophageal cancer each year. The studies also found that patients with Barrett’s esophagus live as long as people without the condition, and patients often die from unrelated causes before Barrett’s esophagus becomes cancer.
What is the condition that causes difficulty swallowing?
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, is a common side effect of gastrointestinal disorders. Dysphagia in those with Barrett’s esophagus happens when acid reflux creates scar tissue, which narrows the esophagus, and often occurs when other symptoms peak. 3. Chest Pain. Though rarer than heartburn or dysphagia, some people with Barrett’s esophagus ...
What does it mean when you have a burning sensation after eating?
Frequent Heartburn . A burning sensation after eating is heartburn. If heartburn occurs two or more times a week, it’s considered gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Along with heartburn or GERD, it’s typical for those with Barrett’s esophagus to experience regurgitation of stomach contents. 2.
How old is the average age to get Barrett's esophagus?
Age. Barrett’s esophagus is more common in middle-aged and older adults than any other age group, and 55 is the average age at diagnosis. Sex.
What is the best way to relieve heartburn?
Those who experience worse heartburn at night may find relief by raising their head or sleeping on their left side. In addition, a doctor may prescribe a medication called a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that reduces the amount of acid in the stomach. Complications of Barrett’s Esophagus.
How to stop acid reflux?
There are lifestyle changes that can ease acid reflux. Changing diet, smoking cessation, wearing loose-fitting clothes, and more are all at-home remedies.
What is Barrett's esophagus?
What Is Barrett’s Esophagus? B arrett’s esophagus is a medical condition that develops after a series of health complications affect the function of the intestines and or esophagus. Barrett’s esophagus transforms the lining of the esophagus into a lining similar to that of the small intestine.
How does GERD lead to Barrett’s esophagus?
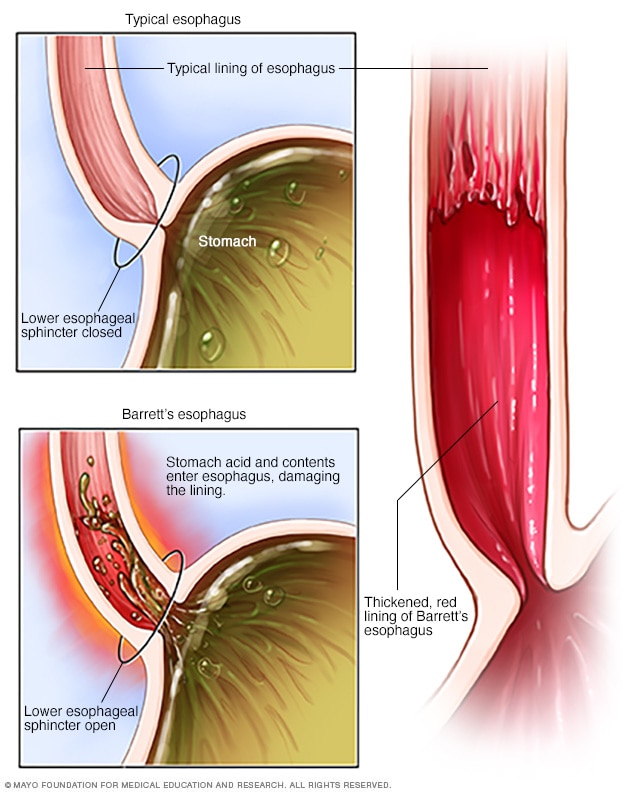
The sphincter is responsible for controlling the flow of food and acid in the stomach/esophagus area. When the sphincter is working properly , food passes through the esophagus to the stomach. All the acids and bile in the stomach are locked out of the esophagus by the lower esophageal sphincter. A weak or compromised esophageal sphincter will stop filtering out food and acids/bile. The acids and bile flow back into the stomach area causing acid reflux, heartburn, and other similar conditions.
How to tell if you have reflux?
An ENT can determine if the patient is suffering from laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR). This is a specific type of acid reflux in which the acid travels right through the esophagus up to the throat and mouth. Frequently, patients with LPR experience these symptoms: 1 Frequent coughing 2 Excess mucus 3 Burning sensation 4 Post-nasal drip 5 Regurgitation 6 Belching
How to tell if you have laryngopharyngeal reflux?
An ENT can determine if the patient is suffering from laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR). This is a specific type of acid reflux in which the acid travels right through the esophagus up to the throat and mouth. Frequently, patients with LPR experience these symptoms: Frequent coughing. Excess mucus.
Why is it so hard to swallow food?
Another condition, dysphagia, is the result of scar tissue growing within the esophageal lining, making hard for a person to swallow food.
What happens when the sphincter is working properly?
When the sphincter is working properly, food passes through the esophagus to the stomach. All the acids and bile in the stomach are locked out of the esophagus by the lower esophageal sphincter. A weak or compromised esophageal sphincter will stop filtering out food and acids/bile.
What is Barrett's esophagus?
Overview. Barrett’s esophagus is a change in the lining of the esophagus, the tube that connects your mouth and stomach. Having this condition means that tissue in the esophagus has changed to a type of tissue that is found in the intestine. Barrett’s esophagus is thought to be caused by long-term acid reflux or heartburn.
How to prevent Barrett's esophagus from worsening?
Fiber. Getting plenty of fiber in your daily diet is good for your overall health. Medical research shows that it may also help prevent Barrett’s esophagus from worsening and lower your risk of cancer in the esophagus. Add these and other fiber-rich foods to your daily diet: fresh, frozen, and dried fruit.
How to prevent cancer of the esophagus?
There are several lifestyle changes you can make to help prevent cancers of the esophagus. This is especially important if you have Barrett’s esophagus. Healthy changes that prevent acid reflux and other factors that irritate the lining of the esophagus may keep this condition under control.
What foods cause Barrett's esophagus to get worse?
Your trigger foods for acid reflux might vary. Common foods that cause heartburn include fried foods, spicy foods, fatty foods, and some beverages.
How many people with acid reflux develop Barrett's esophagus?
About 10 to 15 percent of people with acid reflux develop Barrett’s esophagus. The risk of getting cancer due to Barrett’s esophagus is even lower. Only 0.5 percent of people with Barrett’s are diagnosed with esophageal cancer per year. Being diagnosed with Barrett’s esophagus shouldn’t cause alarm.
How to control acid reflux?
Control your acid reflux to help improve your overall quality of life. Find out what foods trigger your acid reflux by keeping a food and symptom journal. Also try eliminating certain foods to see if your heartburn improves. Talk to your doctor about the best diet and treatment plan for your acid reflux.
Why does Barrett's esophagus increase?
This may happen because too much sugar in the diet causes your blood sugar levels to spike.