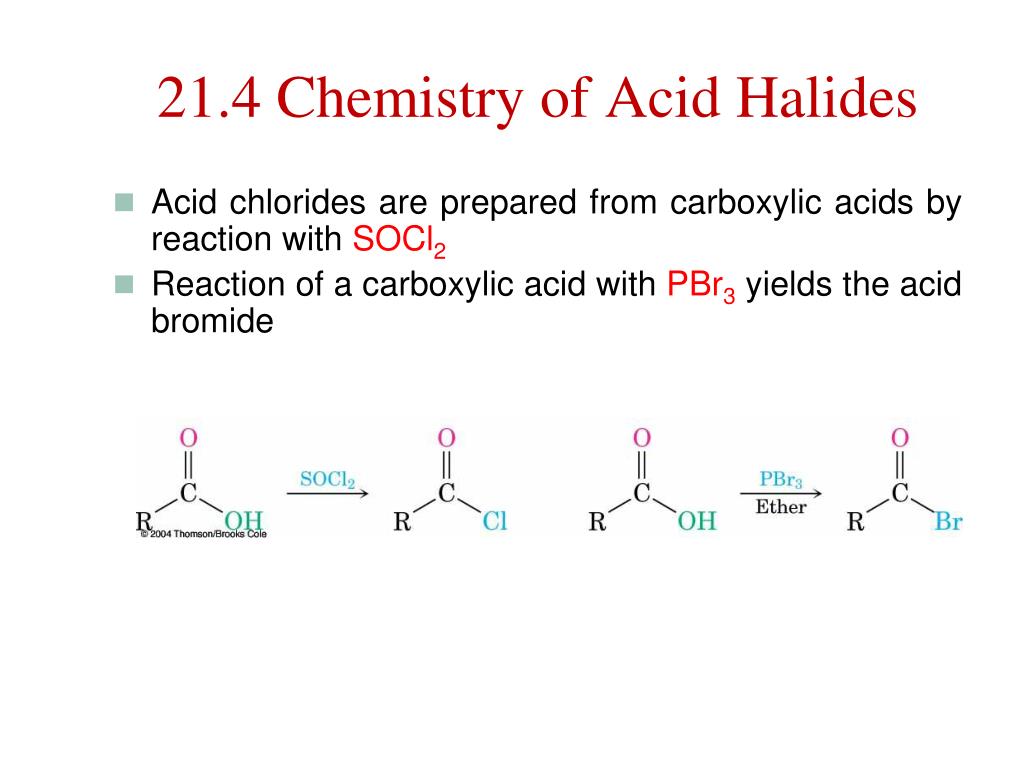
Is BH3 a Lewis base?
So, BH3 cannot be a Lewis base. A Bronsted base must be able to accept a proton, i.e. an H+, like this: An H+ has no electrons to donate, so this is done by having the so-called Lewis base donate an electron pair, which is not possible for BH3 to do...
Is BH3 soft or hard in nature?
Hence it can be clearly concluded that BH3 is soft in nature as it is surrounded by soft H - ions while BF3 , being surrounded by hard F- Ions is a hard acid. Hardness and Softness of an Acid and Base can be explained in terms of HSAB (Hard Soft Acid Base) theory.
Why is BH3 not a Bronsted base?
An H+ has no electrons to donate, so this is done by having the so-called Lewis base donate an electron pair, which is not possible for BH3 to do... Hence, it is not a Bronsted base either.
Is NH3 a base or an acid?
But NH3 is also amphoteric in nature which shows both acid and base character in specific conditions. When we added ammonia in water it takes H+ ions from water and donates its lone electron pair to form OH- ions due to which it shows basic nature.

What type of acid is BH3?
Lewis acidHowever, the molecular species BH3 is a very strong Lewis acid....Borane.NamesChemical formulaBH3Molar mass13.83 g·mol−1Appearancecolourless gasConjugate acidBoronium25 more rows
Is BF3 an acid or base?
Lewis acidBoron trifluoride, BF3 acts as a Lewis acid when it combines with a basic ion or molecule that can donate an electron pair. Such a reaction is shown below. Here, the acid is BF3 and the base is F-. This acid-base reaction allows boron (which is electron-deficient in BF3) to complete its octet.
How BH3 is a Lewis acid?
Lewis acid is a chemical species that reacts with a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. In Borane, boron has only six valence electrons. It is therefore electron deficient and has empty p-orbitals. Hence, it can accept a lone pair.
Is BH3 a live acid?
Diborane thus formed by banana bonds is still an electron deficient compound in nature. Therefore from above we can conclude that $B{H_3}$is a lewis acid as it has empty p orbitals to accept lone pairs of electrons. Hence the correct option is option B.
Why is BF3 an acid?
The boron in BF3 is electron poor and has an empty orbital, so it can accept a pair of electrons, making it a Lewis acid.
Why does BF3 act as an acid?
Boron trifluoride BF3 behaves as Lewis acid because it is an electron-deficient species and it can accept electron pair. Here we see Boron configuration is 1s22s22p1 and vacant p-orbital exist, which indicates that mean BF3 has the tendency to accept lone pair, hence BF3 is lewis acid.
Is BH3 a weak base?
BH3 and NH3 have the tendency to catch H+, so they are weak basic, where NH3 is weaker than BH3.
Is BH3 a good Nucleophile?
BH3 is not a nucleophile. It is an electrophile due to the empty p-orbitals.
How do you tell if it is a Lewis acid or base?
0:286:17How To Identify Lewis Acids and Lewis Bases - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBut the first thing you need to know is that a Lewis acid is defined as a nonbonding electron pairMoreBut the first thing you need to know is that a Lewis acid is defined as a nonbonding electron pair acceptor. So that means that it is able to accept a lone pair of electrons.
Why is Borane a Lewis acid?
Boron reagents are often employed as Lewis acids due to their strongly electrophilic nature granted by a vacant p-orbital into which electrons can be received.
Is BF3 a Lewis acid or base explain the reason?
Boron trifluoride (BF3) is an electron-deficient chemical that can accept electron pairs, hence it behaves as Lewis acid.
Is Borane a Lewis acid?
a) Borane is the Lewis acid. THF has lone pair electrons so it is the Lewis base.
What happens when NH3 acts as a base?
When NH3 acts as a base, it will donate its lone pair to a proton H+ and form its conjugate acid NH 4+ whereas when NH3 acts as an acid, it can give out H+ ion and forms a conjugate base as NH2-. Reactions are given below: (Acting as a Lewis Base) NH3 + H+ ——-> NH4+. (Acting as a Lewis Acid) NH3 ——–> NH2- + H+.
What is NH3 gas?
What is NH3 (Ammonia)? NH3 (Ammonia) is a non-flammable colorless gas that is lighter than the air. It has a very strong bad odor and considered a pungent-smelling gas due to its production by bacterial decomposition of urea.
What is the chemical formula for ammonia?
Ammonia’s chemical formula is NH3 and has a trigonal pyramidal shape with a Nitrogen atom on the pyramid top and 3 hydrogen atoms at the 3 base corners. The atomic number of Nitrogen is 7 and 5 electrons in its valence shell. This means that after the formation of 3 bonds with Hydrogen, Nitrogen carries a lone pair of electron.
What is the reaction of NH3 and Lithium?
It can lose H+ ion and form Amides (NH2-). One of the examples of such reaction is when Lithium reacts with NH3 to form Lithium Amide. (NH3 acting as a weak acid) Li + NH3 ——-> LiNH2 + H2.
What is the reaction of NH3?
NH3 undergoes exothermic combustion to produce Nitrogen gas and water vapor. Following is the combustion reaction of NH3. NH3 + O2 ——-> N2 + H2O ( enthalpy change of this reaction is −1267.20 kJ/mol) Although Nitrogen oxides are unstable with respect to N2 still we can form Nitrogen oxides with the help of some catalysts.
Why does NH3 mix with water?
When put in water, NH3 readily mixes with water due to its polar nature and ability to form hydrogen bonds in water. It helps in the dissociation of H2O molecules in (Hydrogen ions) H+ and (Hydroxyl ions) OH- ions and forms bonding with H+ ions.
What is the molar mass of NH3?
The molar mass of NH3 is around 17.03g and has a bond angle of 107.5 degrees which is slightly less than that in tetrahedral (109.5 degrees). The lone pair provides some repulsion to bonds due to which the angle is slightly less than the tetrahedral.
