Is Lyme disease considered viral?
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection spread to humans by infected ticks. It's also known as Lyme borreliosis. Ticks are tiny spider-like creatures found in woodland and moorland areas. They feed on the blood of birds and mammals, including humans.
Is Borrelia a bacteria?
Borrelia mayonii are a type of bacteria recently found in North America that can cause Lyme disease.
How is Borrelia burgdorferi classified?
Borrelia burgdorferi is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus Borrelia, and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans.
Is Lyme disease and Borrelia the same thing?
Borreliosis, also known as Lyme disease, is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and is transmitted to humans by the bite of infected ticks. Ticks become infected when they feed on birds or mammals that carry the bacterium in their blood.
Is Borrelia a parasite?
The spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi is a tick-borne obligate parasite whose normal reservoir is a variety of small mammals [1]. Whereas infection of these natural hosts does not lead to disease, infection of humans can result in Lyme disease, as a consequence of the human immunopathological response to B.
What part of the body does Borrelia burgdorferi infect?
Animal studies have shown that Borrelia burgdorferi can be found in many tissues and organs including the skin, joints, heart, brain, bladder and other sites of untreated animals as well as in animals who receive antibiotic treatment (Barthold, 2012, and Embers, Barthold, Borda et.
How long does Borrelia burgdorferi live?
Lyme bacteria survive 28-day course of antibiotics months after infection: Living B. burgdorferi spirochetes were found in ticks that fed upon primates and in multiple organs after treatment with 28 days of doxycycline.
What kind of bacteria is Borrelia burgdorferi?
Borrelia burgdorferi is a spirochete bacteria that causes Lyme disease. It is similar in shape to the spirochetes that cause other diseases, such as relapsing fever and syphilis.
How is Borrelia burgdorferi treated?
A 14- to 21-day course of antibiotics is usually recommended, but some studies suggest that courses lasting 10 to 14 days are equally effective. Intravenous antibiotics. If the disease involves the central nervous system, your doctor might recommend treatment with an intravenous antibiotic for 14 to 28 days.
Does Lyme disease stay with you forever?
No. Patients treated with antibiotics in the early stages of the infection usually recover rapidly and completely. Most patients who are treated in later stages of the disease also respond well to antibiotics, although some may have suffered long-term damage to the nervous system or joints.
What does a positive Borrelia burgdorferi test mean?
A positive blood test result means that antibodies to fight the Lyme disease bacteria were found in your blood. In this case, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends a second blood test on the same blood sample.
What organs are affected by Lyme disease?
Lyme disease can affect different body systems, such as the nervous system, joints, skin, and heart. The symptoms of Lyme disease are often described as happening in three stages.
What kind of bacteria is Borrelia?
Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and rarely, Borrelia mayonii. It is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks. Typical symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic skin rash called erythema migrans.
What kind of bacteria is Borrelia burgdorferi?
Borrelia burgdorferi is a spirochete bacteria that causes Lyme disease. It is similar in shape to the spirochetes that cause other diseases, such as relapsing fever and syphilis.
What bacteria species causes Lyme disease?
Overview. Lyme disease is caused by four main species of bacteria. Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia mayonii cause Lyme disease in the United States, while Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii are the leading causes in Europe and Asia.
Which bacterial cells causes Lyme disease?
Lyme disease is an infectious disease caused by Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria. The bacteria are transferred to humans by tick bite, specifically by blacklegged ticks (commonly known as deer ticks).
What is Borrelia Burgdorferi?from borreliaburgdorferi.org
B. burgdorferi sl (a total of 12 species) belongs to the genus Borrelia, family Spirochaetaceae. According to current knowledge, four species are pathogenic to humans: B. burgdorferi sensu stricto (ss), B.garinii, and B.afzelii B.spielmanii. These are gram-negative spiral bacteria, a culture of bacteria is possible in special media. Presumably, the transition takes place in round body for spirochetal survival in the tissue has a significant role.
What happens to Borrelia burgdorferi after it is transmitted?from en.wikipedia.org
After the pathogen is transmitted, it will acclimate to the mammalian conditions. Borrelia burgdorferi will change its glycoproteins and proteases on its plasma membrane to facilitate its dissemination throughout the blood. While infecting, B. burgdorferi will express proteins that will interact with endothelial cells, platelets, chondrocytes, and the extracellular matrix. This interaction inhibits proper function of the infected areas, leading to the pathological manifestations of Lyme disease. In response, the host will initiate an inflammatory response to attempt to remove the infection.
What is the primary vector of Lyme disease?from en.wikipedia.org
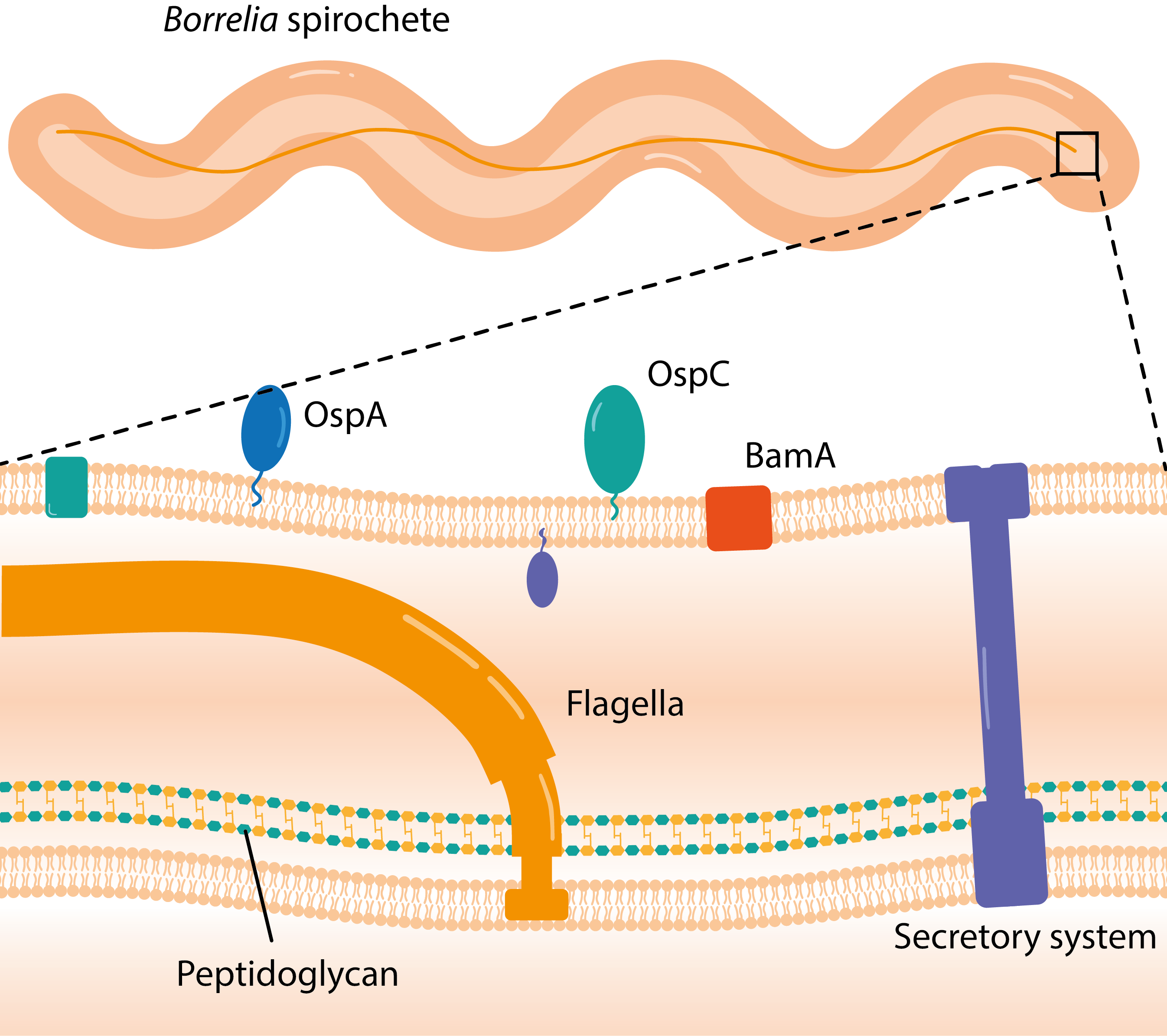
Ixodes scapularis, the primary vector of Lyme disease in eastern North America. Tick Ixodes ricinus, developmental stages. Lyme disease is caused by spirochetes, spiral bacteria from the genus Borrelia. Spirochetes are surrounded by peptidoglycan and flagella, along with an outer membrane similar to Gram-negative bacteria.
How does B. Burgdorferi maintain genetic diversity?from en.wikipedia.org
burgdorferi strains, as defined by the sequence of ospC, are maintained within the Northeastern United States. Balancing selection may act upon ospC or a nearby sequence to maintain the genetic variety of B. burgdorferi. Balancing selection is the process by which multiple versions of a gene are kept within the gene pool at unexpectedly high frequencies. Two major models that control the selection balance of B.burgdorferi is negative frequency-dependent selection and multiple-niche polymorphism. These models may explain how B. burgdorferi have diversified, and how selection may have affected the distribution of the B. burgdorferi variants, or the variation of specific traits of the species, in certain environments.
Why is lyme disease a long lived disease?from en.wikipedia.org
Exposure to the Borrelia bacterium during Lyme disease possibly causes a long-lived and damaging inflammatory response, a form of pathogen-induced autoimmune disease. The production of this reaction might be due to a form of molecular mimicry, where Borrelia avoids being killed by the immune system by resembling normal parts of the body's tissues.
Why is lyme disease a pathogen?from en.wikipedia.org
Exposure to the Borrelia bacterium during Lyme disease possibly causes a long-lived and damaging inflammatory response, a form of pathogen-induced autoimmune disease. The production of this reaction might be due to a form of molecular mimicry, where Borrelia avoids being killed by the immune system by resembling normal parts of the body's tissues.
What is the most common tick-borne disease in Europe and Asia?from mayoclinic.org
Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia mayonii cause Lyme disease in the United States, while Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii are the leading causes in Europe and Asia. The most common tick-borne illness in these regions, Lyme disease is transmitted by the bite of an infected black-legged tick, commonly known as a deer tick.
