
Which other disorders are similar to Bowenoid papulosis?
Symptoms of the following disorders can be similar to those of Bowenoid Papulosis. Comparisons may be useful for a differential diagnosis: Condyloma is a common infectious venereal disease that is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and usually transmitted by direct sexual contact.
What is the prognosis of Bowenoid papulosis?
Despite the malignant pathology, bowenoid papulosis often follows a benign course, resolving with or without treatment. Bowenoid papulosis is said to resolve spontaneously after childbirth in young women. The risk of penile squamous cell carcinoma has been estimated to be 30%, increasing with duration of disease.
How is Bowenoid papulosis (Bowenoid warts) treated?
Bowenoid papulosis may be monitored rather than actively treated. Monitoring in females patients and partners of male patients should include vaginal speculum examination and cervical smear. Treatment is as for anogenital warts. Electrodessication, laser destruction, and cryotherapy are reported to be effective.
How is bowenoid papulosis transmitted?
Bowenoid papulosis lesions are related clinically to genital warts. They share the same age of onset in patients and are transmitted sexually.
Is bowenoid papulosis contagious?
Bowenoid papulosis occurs primarily in young, sexually active adults, with a mean prevalence in the fourth decade of life. Lesions are contagious and are likely transmitted via sexual contact or vertical transmission in the peripartum period.
How serious is bowenoid papulosis?
Bowenoid papulosis is classified as a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) due to a high-risk HPV. It can therefore progress to squamous cell carcinoma particularly in immunocompromised patients, or older patients with large lesions.
Is bowenoid papulosis for life?
Patches that appear on the genitals can cause problems. In that area, Bowen's disease may be called one of the following: Bowenoid papulosis: This affects both men and women and causes lesions in the genital area. They can last from 2 weeks to several years.
How do you get rid of bowenoid papulosis?
The modalities include simple local excision, electrodesiccation, cryosurgery, laser surgery, and use of topical retinoic acid, podophyllum resin, and topical 5-fluorouracil. Immunomodulators have been reported as effective treatment for bowenoid papulosis and may lengthen the remission period of lesions.
Is bowenoid papulosis rare?
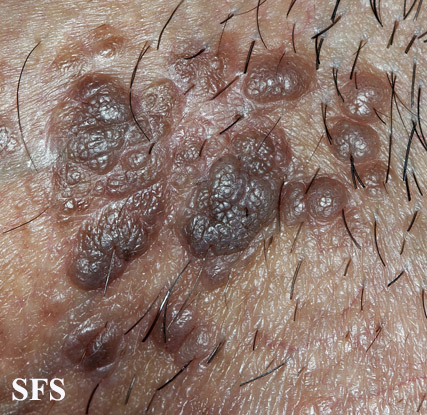
Bowenoid Papulosis is a rare, sexually transmitted disorder thought to be caused by human papillomavirus type 16. This disorder is characterized by lesions that are found on the genitals of males and females. The lesions are reddish brown or violet in color, small, solid, raised and sometimes velvety.
Should I worry about Bowens disease?
Is Bowen's disease serious? Bowen's disease itself is not usually serious. It tends to grow very slowly over months or years, and there are several very effective treatments for it.
Can HPV cause brown spots?
Human papilloma virus (HPV) causes common warts, the small, white, beige or brown skin growths that can appear almost anywhere on the body and on the moist mucous membranes near the mouth, anus and genitals.
Does Bowens disease go away?
A wide variety of treatment options exist for individuals with Bowen disease including topical chemotherapy, cryotherapy, curettage, photodynamic therapy and surgery. Most therapies have an excellent response rate and the prognosis of Bowen disease in most cases is excellent.
Does Bowens disease spread?
If left untreated, there is a small chance that Bowen's disease can spread into the deeper layers of the skin. This means it has become an invasive cancer called squamous cell carcinoma.
Is bowenoid papulosis itchy?
Bowenoid papulosis - Anogenital in Female Adult BP typically occurs in young sexually active adults. There is an equal male-to-female ratio. Lesions are usually asymptomatic, but may be itchy, and occur primarily in the genital and perianal region.
How is Papulosis treated?
Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra TreatmentCryotherapy. One of the most affordable and effective treatment options available. ... Electrodesiccation. Zapping the bumps with an electric current from a probe.Curettage. This procedure involves scraping off the bumps with a small surgical instrument.PDL Laser.
Can hpv16 be transmitted?
You can get HPV by having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has the virus. It is most commonly spread during vaginal or anal sex. It also spreads through close skin-to-skin touching during sex. A person with HPV can pass the infection to someone even when they have no signs or symptoms.
Does Bowens disease spread?
If left untreated, there is a small chance that Bowen's disease can spread into the deeper layers of the skin. This means it has become an invasive cancer called squamous cell carcinoma.
Is cancerous HPV contagious?
HPV passes easily between sexual partners. It can be transmitted through any intimate skin-to-skin contact, including vaginal–penile sex, penile–anal sex, penile–oral sex, vaginal–oral sex, and use of sex toys or other objects. The infection passes easily between sexual partners.
How long is HPV Transmissable?
Is HPV Contagious Forever? Most cases of HPV clear up on their own after one to two years, and you'll no longer be contagious once it leaves your system. However, the virus can remain dormant for years, and some people experience infections that stick around for much longer.
What is bowenoid papulosis?
Bowenoid papulosis is a sexually transmitted infection that presents as pigmented genital papules due to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection with histology closely resembling squamous cell carcinoma - in-situ ( Bowen disease ). It is now classified as a vulval or penile high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and 'bowenoid papulosis' is no longer used by pathologists in the WHO Classification of Tumours, 2020 5th edition.
What are the clinical features of bowenoid papulosis?
Although the glans penis, foreskin, and vulval labia are the most common sites affected, bowenoid papulosis may present on other parts of the genitals, around the anus, or oral cavity. It is usually asymptomatic but lesions can become inflamed, itchy, and painful.
How is bowenoid papulosis diagnosed?
Bowenoid papulosis may be suspected based on its typical clinical appearance and dermoscopy.
What is the risk of penile squamous cell carcinoma?
Bowenoid papulosis is said to resolve spontaneously after childbirth in young women. The risk of penile squamous cell carcinoma has been estimated to be 30%, increasing with duration of disease. See smartphone apps to check your skin.
Where is bowenoid papulosis most common?
Although the glans penis, foreskin, and vulval labia are the most common sites affected, bowenoid papulosis may present on other parts of the genitals, around the anus, or oral cavity. It is usually asymptomatic but lesions can become inflamed, itchy, and painful. See Bowenoid papulosis images.
Is Bowenoid Papulosis a STI?
Bowenoid papulosis is a sexually transmitted infection ( STI) so sexual partners can be infected with the high-risk HPV, increasing their risk of cervical, vaginal, vulval, or penile intraepithelial neoplasia or invasive squamous cell carcinoma. Concurrent HPV-related intraepithelial neoplasia in other anogenital sites can occur. Infection of extragenital sites usually follows genital disease.
Is vulval papulosis a HSIL?
It is now classified as a vulval or penile high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and 'bowenoid papulosis' is no longer used by pathologists in the WHO Classification of Tumours, 2020 5th edition.
Who is Bowenoid Papulosis named after?
The term bowenoid papulosis was coined in 1977 by Kopf and Bart and is named after dermatologist John Templeton Bowen. The term “intraepithelial neoplasia” defines a premalignant intraepithelial change.
What is the condition of the penis called?
Dermatology. Bowenoid papulosis is a cutaneous condition characterized by the presence of pigmented verrucous papules on the body of the penis. They are associated with human papillomavirus, the causative agent of genital warts.
Can Bowen's disease be used for anogenital lesions?
The terminology has been very confusing and it is now recommended that the terms Bowen's disease, erythroplasia of Queyrat, and bowenoid papulosis should not be used for lesions in the anogenital area.
Cause
- Human papillomavirus (HPV), the cause of genital warts and some genital cancers, has been closely linked to bowenoid papulosis. Although most cases of bowenoid papulosis are benign (harmless) a small percentage may transform into invasive squamous cell carcinoma (penile or vulvar cancer). Sexually active people may be at risk of getting bowenoid pa...
Epidemiology
- Men and women are equally at risk and the peak incidence is in sexually active persons under 30 years of age.
Signs and symptoms
- Small red, brown or flesh-coloured flat or warty lesions appear most commonly on the shaft of the penis or labia of females. They may also be present on other parts of the genitals as well as in and around the anus. The condition is usually symptomless but occasionally lesions may become inflamed, itchy and painful. The diagnosis is usually made by skin biopsy.
Prognosis
- Bowenoid papulosis tends to spontaneously disappear within several months and if a young woman is pregnant when it is diagnosed it will often disappear after delivery. If it is persistent this is an indication for active treatment because of the chance of developing skin cancer. Once infected with HPV you may become a lifelong carrier of the virus and recurrence of bowenoid pa…
Diagnosis
- Bowenoid papulosis may be diagnosed by its typical clinical appearance, especially with the aid of dermoscopy, or by skin biopsy. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ pathology is diagnostic on skin biopsy.
Treatment
- Because bowenoid papulosis usually runs a benign course with many cases spontaneously regressing, treatment is often unnecessary. Lesions should be re-examined every 3 to 6 months so that any changes may be picked up early. If the lesions are persistent, treatment of bowenoid papulosis is the same as for genital warts. This is usually destruction of the lesions via several …