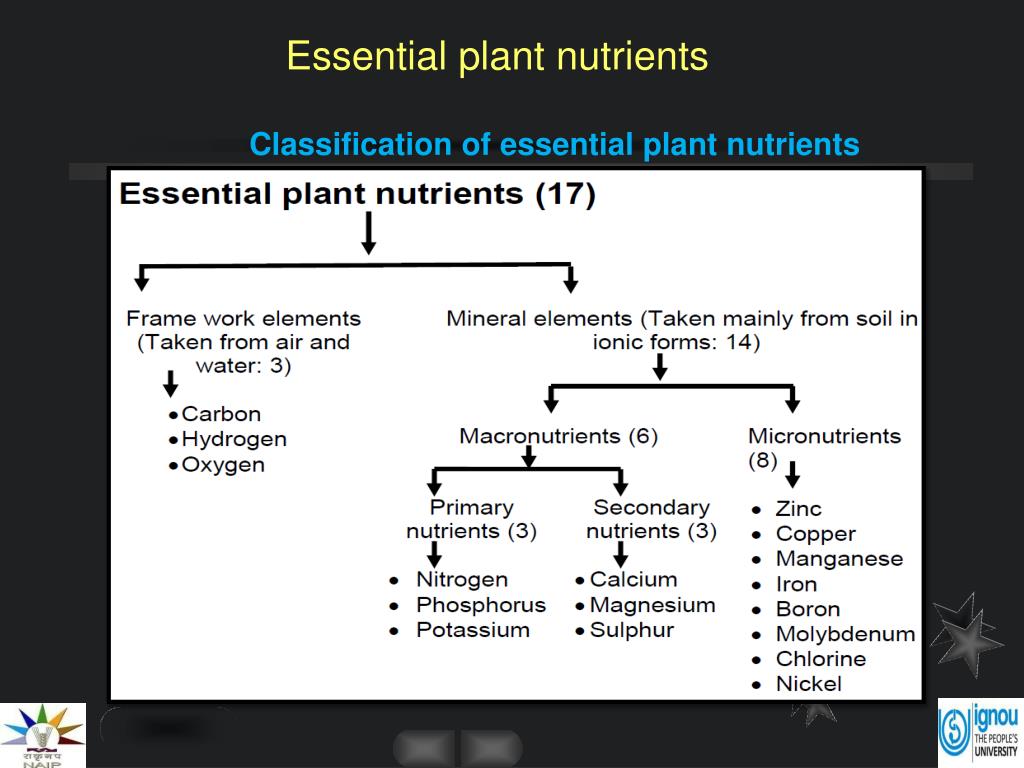
Is carbon a micro or macro nutrient?
There are 16 non-mineral elements; non-mineral elements include carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. In addition, essential mineral elements are called macro or micro nutrients according to the amounts found in plant tissue.
Why is carbon essential life?
The Importance of carbon in living things Is based on the fact that it is the chemical element on which the existence of life is based. Its ability to form polymers makes it an ideal partner for molecules that generate life. Carbon is a key chemical element for life and the natural processes that take place on earth.
What are the main uses of carbon?
Uses of Carbon
- The major use of carbon is in the form of hydrocarbons, mainly methane gas and crude oil. ...
- Cellulose, a natural carbon polymer found in plants, is used in cotton, linen and hemp.
- Plastics are made from synthetic (man made- not naturally occurring) carbon polymers.
- Graphite, a form of carbon, is combined with clays to make the ‘lead’ in pencils. ...
Is CO2 good for the environment?
So, CO 2 and other greenhouse gases are good—up to a point. But CO 2 is so good at holding in heat from the Sun, that even a small increase in CO 2 in the atmosphere can cause Earth to get even warmer. Throughout Earth's history, whenever the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere has gone up, the temperature of Earth has also gone up.
See more

Is carbon considered a nutrient?
Although the four elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, are essential for life, they are so plentiful in food and drink that these are not considered nutrients and there are no recommended intakes for these as minerals.
What type of nutrient is carbon?
Nutrients that plants require in larger amounts are called macronutrients. About half of the essential elements are considered macronutrients: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and sulfur.
Is carbon a nutrient in soil?
Soil carbon is amazingly complex It also improves soil quality in many ways: It gives soil structure, stores water and nutrients that plants need and feeds vital soil organisms. But carbon in soil doesn't exist on its own.
Are nitrogen and carbon nutrients?
Both C and N nutrients are essential for various cellular functions, and therefore adequate supply of these two nutrients are critical for plant growth, development and response to a wide array of stresses and ultimately for the completion of life cycle and the production of harvestable organs.
Which of these is not a nutrient?
Plasma is not considered a nutrient.
What are types of nutrients?
There are more than 40 different kinds of nutrients in food and they can generally be classified into the following 7 major groups:Carbohydrates.Proteins.Fats.Vitamins.Minerals.Dietary fibre.Water.
Is carbon a plant nutrient?
Carbon is not considered to be a plant nutrient and yet more than 40 percent of a plant is carbon (on a dry matter basis). Compare this with typical macronutrient contents of 1.5 percent nitrogen, 1 percent potassium, and 0.2 percent phosphorus.
Is nitrogen a nutrient?
Nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, are essential for plant and animal growth and nourishment, but the overabundance of certain nutrients in water can cause a number of adverse health and ecological effects. Nitrogen, in the forms of nitrate, nitrite, or ammonium, is a nutrient needed for plant growth.
Is carbon a fertilizer?
Carbon fertilizer The answer is … no. Although the carbon content of the atmosphere is far less than 1%, plants capture it efficiently; it is their mission in life.
What are six basic nutrients?
There are six major nutrients – water, carbohydrates, protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals. Each plays a unique and important role in how our bodies function.
What are the 4 nutrient cycles?
ADVERTISEMENTS: Some of the major biogeochemical cycles are as follows: (1) Water Cycle or Hydrologic Cycle (2) Carbon-Cycle (3) Nitrogen Cycle (4) Oxygen Cycle. The producers of an ecosystem take up several basic inorganic nutrients from their non-living environment.
Is soil a carbon or nitrogen?
Soil organic carbon is a component of soil organic matter. Organic matter is primarily made up of carbon (58%), with the remaining mass consisting of water and other nutrients such as nitrogen and potassium.
Is carbon a plant nutrient?
Carbon is not considered to be a plant nutrient and yet more than 40 percent of a plant is carbon (on a dry matter basis). Compare this with typical macronutrient contents of 1.5 percent nitrogen, 1 percent potassium, and 0.2 percent phosphorus.
What are macro nutrients?
Carbohydrates, fat and protein are called macronutrients. They are the nutrients you use in the largest amounts. “Macronutrients are the nutritive components of food that the body needs for energy and to maintain the body's structure and systems,” says MD Anderson Wellness Dietitian Lindsey Wohlford.
What class of nutrient does not contain carbon?
inorganic nutrientsThe nutrients that contain carbon in their structural makeup are referred to as organic nutrients, whereas those that do not contain carbon are called inorganic nutrients. Therefore, the organic nutrients are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and vitamins. These nutrients are important for energy.
What is the function of carbon?
Carbon is the chemical backbone of life on Earth. Carbon compounds regulate the Earth's temperature, make up the food that sustains us, and provide energy that fuels our global economy. Most of Earth's carbon is stored in rocks and sediments. The rest is located in the ocean, atmosphere, and in living organisms.
What are the sources of organic C in soil?
Crop residues, green manures and animal wastes can be significant sources of organic C in the soil.
What is the primary energy source and building block for plant tissues?
Carbon is the primary energy source and building block for plant tissues.
What is carbon chemistry?
Modern carbon chemistry dates from the development of coals, petroleum, and natural gas as fuels and from the elucidation of synthetic organic chemistry, both substantially developed since the 1800s. bituminous coal.
What is carbon made of?
Carbon is the cosmic product of the “burning” of helium, in which three helium nuclei, atomic weight 4, fuse to produce a carbon nucleus, atomic weight 12. Britannica Quiz. The Stuff That Things Are Made Of.
How is carbon determined?
Carbon, either elemental or combined, is usually determined quantitatively by conversion to carbon dioxide gas, which can then be absorbed by other chemicals to give either a weighable product or a solution with acidic properties that can be titrated.
What is the name of the group 14 element?
Carbon (C), nonmetallic chemical element in Group 14 (IVa) of the periodic table. Although widely distributed in nature, carbon is not particularly plentiful—it makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth’s crust—yet it forms more compounds than all the other elements combined. In 1961 the isotope carbon-12 was selected to replace oxygen as ...
What is the isotope used in radiocarbon dating?
In 1961 the isotope carbon-12 was selected to replace oxygen as the standard relative to which the atomic weights of all the other elements are measured. Carbon-14, which is radioactive, is the isotope used in radiocarbon dating and radiolabeling.
How many elements are in the periodic table?
The periodic table is made up of 118 elements. How well do you know their symbols? In this quiz you’ll be shown all 118 chemical symbols, and you’ll need to choose the name of the chemical element that each one represents.
Where does the word carbon come from?
The word carbon probably derives from the Latin carbo, meaning variously “coal,” “charcoal,” “ember.” The term diamond, a corruption of the Greek word adamas, “the invincible,” aptly describes the permanence of this crystallized form of carbon, just as graphite, the name for the other crystal form of carbon, derived from the Greek verb graphein, “to write,” reflects its property of leaving a dark mark when rubbed on a surface. Before the discovery in 1779 that graphite when burned in air forms carbon dioxide, graphite was confused with both the metal lead and a superficially similar substance, the mineral molybdenite.
What is the only source of carbon?
The atmospheric carbon dioxide is virtually the only source of carbon. The carbon cycle is the process through which carbon elements are interchanged between the biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere in the Earth.
How is carbon absorbed by plants?
Carbon present in the atmosphere is absorbed by the plants through photosynthesis.
What is the nutrient cycle?
Q.1. What is the nutrient cycle simple definition?#N#Ans: Circulation or exchange of nutrient elements between the living and nonliving components of an ecosystem is called the nutrient cycle or biogeochemical cycle.
What is the process of exchange of nutrient elements between living and nonliving components of an ecosystem?
Circulation or exchange of nutrient elements between the living and nonliving components of an ecosystem is called the nutrient cycle or biogeochemical cycle. The term biogeochemical cycles represent the interactions among the organic (bio-) and inorganic (geo-) components and concentrate on the chemistry (chemical-) and movement (cycles) of chemical elements and compounds. Nutrient cycling represents the movement of elements through various forms and their return to their original state.
What are the elements in a living organism?
All biotic components, cells and living organisms are made up of elements such as carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, sulphur and Phosphorus. These elements are essential in life. The flow of elements is regulated as the nutrient cycles are passed through each sphere, namely, biosphere, lithosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere. Each sphere has a particular rate at which the flow of elements is calculated by the viscosity and density of the medium. Hence, the elements present in the nutrient cycles flow at different rates, and this maintains the flow of elements in those cycles. Ecosystems restore the equilibrium state to function properly through the nutrient cycles.
How many types of nutrient cycles are there in an ecosystem?
There are three types of nutrient cycles that are observed in an ecosystem-based on their reservoirs.
What is the process of absorbing nitrogen from plants?
This process is called Nitrogen fixation.
Why is it important to cycle nutrients?
These elements are essential for life. It is important to recycle and continuously replenish nutrients into the environment for life to exist.
How does nutrient cycling differ from energy flow?
How nutrient cycling differs from energy flow? The energy flow refers to the transfer of energy from one trophic level to another in the food chain and food web. It is unidirectional and energy is lost from one trophic level to another in the form of heat. Sunlight is the ultimate energy source.
How do nutrient cycles help the ecosystem?
air to soil or water. Nutrient cycles keep the ecosystem in equilibrium and help in storing nutrients for future uptake. Through nutrient cycling, living organisms interact with the abiotic components of their surroundings.
What is the nutrient cycle?
A nutrient cycle is defined as the cyclic pathway by which nutrients pass-through, in order to be recycled and reutilised. The pathway comprises cells, organisms, community and ecosystem. In the process, nutrients get absorbed, transferred, released and reabsorbed. It is a natural recycling system of mineral nutrients.
What is the role of soil microbes in nutrient recycling?
Soil microbes play an important role in nutrient recycling. They decompose organic matter to release nutrients.
Why are soil microbes important?
Soil microbes play an important role in nutrient recycling. They decompose organic matter to release nutrients. They are also important to trap and transform nutrients into the soil, which can be taken up by plant roots.
What is the ultimate energy source?
Sunlight is the ultimate energy source. Nutrient cycling is a cyclic process that encompasses the movement of nutrients from the physical environment to living organisms and back to the environment. Nutrients are present on the earth where they are recycled, transformed into different forms and reutilized.