
Is cell division an example of asexual reproduction?
What is asexual reproduction example? In asexual reproduction, an individual can reproduce without involvement with another individual of that species. The division of a bacterial cell into two daughter cells is an example of asexual reproduction.
What form of cell division creates the sperm?
Meiosis: In this type of cell division, sperm or egg cells are produced instead of identical daughter cells as in mitosis. Binary Fission: Single-celled organisms like bacteria replicate themselves for reproduction.
Can all organisms reproduce using cell division?
The cell cycle allows multiicellular organisms to grow and divide and single-celled organisms to reproduce. All multicellular organisms use cell division for growth and the maintenance and repair of cells and tissues. Single-celled organisms use cell division as their method of reproduction.
What process of cell division that produces sex cells?
When a sperm cell fertilizes an egg cell, the resulting cell has a full set of genetic information again. Sex cells are formed through a particular kind of cell division called meiosis. Unlike in normal cell division (mitosis), the genetic material of the original (parent) cell is divided up twice.
Is cell division same as reproduction?
When cells divide, they make new cells. A single cell divides to make two cells and these two cells then divide to make four cells, and so on. We call this process "cell division" and "cell reproduction," because new cells are formed when old cells divide.
How is cell division related to reproduction?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells. This process is required to produce egg and sperm cells for sexual reproduction.
What type of reproduction is just cell division?
Take the evolution of sex, for instance. To make the move from asexual to sexual reproduction, nature took a system by which parent cells reproduced simply by dividing (asexual reproduction) and altered it to allow two parent cells to combine to create offspring (sexual reproduction).
Is mitosis a form of reproduction?
mitosis, a process of cell duplication, or reproduction, during which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells.
Is mitosis an asexual reproduction?
A mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction as the result of the cell cycle is two identical cells.
What is cell division called?
There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Most of the time when people refer to “cell division,” they mean mitosis, the process of making new body cells. Meiosis is the type of cell division that creates egg and sperm cells.
What are the 3 types of reproduction?
Key TermsTermMeaningSexual reproductionProcess of creating new individual using two parent organismsAsexual reproductionProcess of creating new individual using one parent organismOffspringNew organism that results from reproductionGameteSex cell (in males: sperm; in females: eggs)2 more rows
What are the different types of reproduction?
There are two types of reproduction: asexual and sexual reproduction. Though asexual reproduction is faster and more energy efficient, sexual reproduction better promotes genetic diversity through new combinations of alleles during meiosis and fertilization.
How many types of reproduction are there?
There are basically two types of reproduction: Asexual Reproduction. Sexual Reproduction.
Is reproduction mitosis or meiosis?
Mitosis and meiosis are both processes by which cells reproduce, but there are distinct differences between the two. While new cells are generated during mitosis, meiosis is a special type of cell division that produces sex cells for reproduction.
Is cell division asexual reproduction?
Cell division is part of both sexual and asexual reproduction. The process of mitosis produces cells identical to the parent cells. The diversity of life on Earth is possible because of the combining of genetic materials from two parents in sexual reproduction.
Is human reproduction mitosis or meiosis?
meiosisAs sexually-reproducing, diploid, multicellular eukaryotes, humans rely on meiosis to serve a number of important functions, including the promotion of genetic diversity and the creation of proper conditions for reproductive success.
What is the process of cell reproduction called?
Mitosis is a process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. During cell division, mitosis refers specifically to the separation of the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus.
What is the cell reproduction?
Cellular reproduction is a process by which cells duplicate their contents and then divide to yield multiple cells with similar, if not duplicate, contents. Mitosis. Mitosis- nuclear division resulting in the production of two somatic cells having the same genetic complement (genetically identical) as the original cell ...
What is the most important part of cellular reproduction?
The passage of DNA to daughter cells is an important aspect of cellular reproduction. Because the DNA of cells is extremely long, the DNA is wrapped with proteins into easily managed bundles called chromosomes.
What is the importance of cell division?
Cell division is necessary to create genetic diversity. In unicellular organisms, cell division is a significant process through which a unicellular organism develops into a new organism.
Where Do Cells Come from?
Sometimes you accidentally bite your lip or skin your knee, but in a matter of days the wound heals. Is it magic? Or, is there another explanation?...
How Many Cells Are in Your body?
You and I began as a single cell, or what you would call an egg. By the time you are an adult, you will have trillions of cells. That number depend...
How Do Cells Know When to Divide?
In cell division, the cell that is dividing is called the "parent" cell. The parent cell divides into two "daughter" cells. The process then repeat...
What is cell division?
Cell division can be defined as a process by which a cell distributes its genetic material and cytoplasm and gives rise to new daughter cells. It is a part of the larger cell cycle and has a direct role in cell reproduction.
How does the cell start cell division?
In the early prophase, the cell initiates cell division by breaking down some cell component and building other components and then the chromosome division starts.
What is the process of a microtubule that separates the poles of a cell?
Microtubules which are not attached to chromosomes elongate and push apart. In doing so they separate the poles and makes the cell longer. These processes are controlled by motor proteins and these proteins carry the chromosomes and microtubules as they move.
How many identical sets of chromosomes are formed in mitosis?
Similar to mitosis the genetic material of the cell is copied and two identical sets of chromosomes are formed.
When does the mitotic spindle organise all chromosomes and lines them up in the middle?
Metaphase starts when the mitotic spindle organises all chromosomes and lines them up in the middle of the cell to divide.
What are the two types of cell division?
In well-developed organisms, there are two types of cell division observed, mitosis and meiosis. These are very complex processes which are carried out through different phases. However, if simplified, mitosis can be defined as the exact duplication of a cell where the daughter cells will have the same genetic information as the parent cell. In meiosis, the daughter cells will only have half of the genetic information of the original cell. The common end phase in both processes is cytokinesis and the division of the cytoplasm. We will discuss both types of cell division in this topic.
How does cell division help unicellular organisms?
In multicellular organisms, cell division assists in the formation of gametes which combine to produce organisms. Cell division also plays a role in the growth and development of an organism and repairs injuries.
What is cell division?
Cell Division Definition. Cell division is the process cells go through to divide. There are several types of cell division, depending upon what type of organism is dividing. Organisms have evolved over time to have different and more complex forms of cell division. Most prokaryotes, or bacteria, use binary fission to divide the cell.
Which type of cell division produces identical cells?
In these cases, organisms need a different method of cell division. Mitosis yields identical cells, but meiosis produces cells with half the genetic information of a regular cell, allowing two cells from different organisms of the same species to combine.
What happens to DNA during mitosis?
The process begins during prophase, when the chromosomes condense. If mitosis proceeded without the chromosomes condensing, the DNA would become tangled and break. Eukaryotic DNA is associated with many proteins which can fold it into complex structures. As mitosis proceeds to metaphase the chromosomes are lined up in the middle of the cell. Each half of a chromosome, known as sister chromatids because they are replicated copies of each other, gets separated into each half of the cell as mitosis proceeds. At the end of mitosis, another process called cytokinesis divides the cell into two new daughter cells.
How do sexually reproducing organisms reproduce?
Humans with even one extra copy of one chromosome can experience detrimental changes to their body. To counteract this, sexually reproducing organisms undergo a type of cell division known as meiosis. As before mitosis, the DNA and organelles are replicated. The process of meiosis contains two different cell divisions, which happen back-to-back. The first meiosis, meiosis I, separates homologous chromosomes. The homologous chromosomes present in a cell represent the two alleles of each gene an organism has. These alleles are recombined and separated, so the resulting daughter cells have only one allele for each gene, and no homologous pairs of chromosomes. The second division, meiosis II, separated the two copies of DNA, much like in mitosis. The end result of meiosis in one cell is 4 cells, each with only one copy of the genome, which is half the normal number.
What happens to DNA after the cell cycle?
After the DNA and organelles are replicated during interphase of the cell cycle, the eukaryote can begin the process of mitosis. The process begins during prophase, when the chromosomes condense. If mitosis proceeded without the chromosomes condensing, the DNA would become tangled and break.
How do prokaryotes replicate?
Prokaryotes replicate through a type of cell division known as binary fission. Prokaryotes are simple organism, with only one membrane and no division internally. Thus, when a prokaryote divides, it simply replicates the DNA and splits in half.
What are plasmids in biology?
Plasmids are small rings of DNA that also get copied during binary fission and can be picked up in the environment, from dead cells that break apart . These plasmids can then be further replicated. If a plasmid is beneficial, it will increase in a population.
How does cell division occur?
Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle. All cells reproduce by splitting into two, where each parental cell gives rise to two daughter cells. These newly formed daughter cells could themselves divide and grow, giving rise to a new cell population that is formed by the division and growth of a single parental cell ...
What are the two types of cell division?
Types of Cell Division. There are two distinct types of cell division out of which the first one is vegetative division , wherein each daughter cell duplicates the parent cell called mitosis. The second one is meiosis, which divides into four haploid daughter cells. Mitosis: The process cells use to make exact replicas of themselves.
Which type of cell division produces sperm instead of identical daughter cells?
Meiosis: In this type of cell division, sperm or egg cells are produced instead of identical daughter cells as in mitosis.
What are the two main phases of the cell cycle?
There are two primary phases in the cell cycle: Interphase: This phase was thought to represent the resting stage between subsequent cell divisions, but new research has shown that it is a very active phase. M Phase (Mitosis phase): This is where the actual cell division occurs.
Why do plant cells divide into two?
The actual division of the cell into two takes place differently in plant and animal cells, since plant cells are surrounded by a stiff outer cell wall. In animal cells, a ring of actin filaments contracts around the center of the cell and pinches it in two. The contraction of the ring is probably due to actin and myosin acting as in muscles.
What is the process of DNA replication?
During the S (synthesis) phase, DNA replication takes place. Chromatin is condensed and each chromosome is duplicated into two copies, sister chromatid s, which are attached at a point called the centromere. DNA replication takes place in much the same way as RNA transcription except that both strands are duplicated, entirely. The cell’s centrosome, the organizing center for microtubules, is also duplicated.
What are the phases of meiosis?
Meiosis is preceded by an interphase, composed of G 1, S and G 2 phases, which travels essentially the same path as in mitosis. Eukaryotic meiosis takes place in two cyclical parts: 1 Meiosis I splits the cell’s DNA into two diploid pairs. 2 Meiosis II splits the pairs into haploid sister chromatids.
How many chromosomes are in a cytokinesis cell?
In the cytokinesis phase, the two cells separate. In our case, chromosomes numbers 1 and 3 remain together, as well as 2 and 4. Each cell contains two chromosomes, but they are sisters, so the cell is considered to be haploid.
How many haploid cells are created in meiosis?
Meiosis, for reproduction, creates two haploid cells from one diplod cell. Then two haploid cells, one from each parent, join to make a child diploid cell. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase, composed of G 1, S and G 2 phases, which travels essentially the same path as in mitosis.
How many diploid pairs does meiosis I split?
Meiosis I splits the cell’s DNA into two diploid pairs.
What is the mitosis phase?
Mitosis. The mitosis phase does all the rest of the replication and localization of organelles, leaving only the actual division of the cell in two. It too is understood to take place in a number of steps. 1. Some sources omit the prometaphase. There is also disagreement as to what goes into each step.
What is the function of cell division in unicellular organisms?
In unicellular organisms, cell division is the means of reproduction; in multicellular organisms, it is the means of tissue growth and maintenance . Survival of the eukaryotes depends upon interactions between many cell types, and it is essential that a balanced distribution of types be maintained. This is achieved by the highly regulated process of cell proliferation. The growth and division of different cell populations are regulated in different ways, but the basic mechanisms are similar throughout multicellular organisms.
What happens during the cell division cycle in eukaryotes?
In eukaryotes the processes of DNA replication and cell division occur at different times of the cell division cycle. During cell division, DNA condenses to form short, tightly coiled, rodlike chromosomes.
What happens to the chromosomes in prophase?
In prophase the mitotic spindle forms and the chromosomes condense. In prometaphase the nuclear envelope breaks down (in many but not all eukaryotes) and the chromosomes attach to the mitotic spindle. Both chromatids of each chromosome attach to the spindle at a specialized chromosomal region called the kinetochore.
How does DNA replication work?
In the circular DNA of prokaryotes, replication starts at a unique site called the origin of replication and then proceeds in both directions around the molecule until the two processes meet, producing two daughter molecules. In rapidly growing prokaryotes, a second round of replication can start before the first has finished. The situation in eukaryotes is more complicated, as replication moves more slowly than in prokaryotes. At 500 to 5,000 nucleotides per minute (versus 100,000 nucleotides per minute in prokaryotes), it would take a human chromosome about a month to replicate if started at a single site. Actually, replication begins at many sites on the long chromosomes of animals, plants, and fungi. Distances between adjacent initiation sites are not always the same; for example, they are closer in the rapidly dividing embryonic cells of frogs or flies than in adult cells of the same species.
Why is DNA replication important?
Accurate DNA replication is crucial to ensure that daughter cells have exact copies of the genetic information for synthesizing proteins. Accuracy is achieved by a “proofreading” ability of the DNA polymerase itself. It can erase its own errors and then synthesize anew. There are also repair systems that correct genetic damage to DNA. For example, the incorporation of an incorrect nucleotide, or damage caused by mutagenic agents, can be corrected by cutting out a section of the daughter strand and recopying the parental strand.
How does mitosis grow?
Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Most tissues of the body grow by increasing their cell number, but this growth is highly regulated to maintain a balance between different tissues. In adults most cell division is involved in tissue renewal rather ...
Why do cells need to duplicate DNA?
Before a cell can divide, it must accurately and completely duplicate the genetic information encoded in its DNA in order for its progeny cells to function and survive. This is a complex problem because of the great length of DNA molecules. Each human chromosome consists of a long double spiral, or helix, each strand of which consists of more than 100 million nucleotides ( see above The nucleus ).

What Is Cell Division?
- Cell division can be defined as a process by which a cell distributes its genetic material and cytoplasm and gives rise to new daughter cells. It is a part of the larger cell cycleand has a direct role in cell reproduction. In well-developed organisms, there are two types of cell division observed, mitosis and meiosis. These are very complex proces...
Cell Division- Mitosis and Meiosis
- The two well-documented types of cell division are: 1.Mitosis 2. Meiosis 3. Binary Fission Mitosis It is the type of cell division where one cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells. A great majority of cell divisions that take place in our body is mitosis. The process is integral to an organism's body growth and development, and it takes place throughout the organ…
Early and Late Prophase
- In the early prophase, the cell initiates cell division by breaking down some cell components and building other components and then the chromosome division starts.
- In this stage, the chromosomes start to condense which helps them to separate easily in later stages
- Afterwards, the mitotic spindle starts to form, a structure made of microtubules. It organizes …
- In the early prophase, the cell initiates cell division by breaking down some cell components and building other components and then the chromosome division starts.
- In this stage, the chromosomes start to condense which helps them to separate easily in later stages
- Afterwards, the mitotic spindle starts to form, a structure made of microtubules. It organizes the chromosomes and moves them around during mitosis. The mitotic spindle grows between the centrosome...
- The nucleolus then disappears which is a sign that the nucleus is getting ready to break down.
Metaphase
- Metaphase starts when the mitotic spindle organizes all chromosomes and lines them up in the middle of the cell to divide.
- All chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
- At this stage of metaphase, the two kinetochores of each chromosome should be attached to microtubules from opposite spindle poles. Before proceeding forward to anaphase, the cell w…
- Metaphase starts when the mitotic spindle organizes all chromosomes and lines them up in the middle of the cell to divide.
- All chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
- At this stage of metaphase, the two kinetochores of each chromosome should be attached to microtubules from opposite spindle poles. Before proceeding forward to anaphase, the cell will check if all...
- The spindle checkpoint ensures that the sister chromatids are split equally into two daughter cells.
Anaphase
- In this stage, the sister chromatids separate from each other and move towards the opposite poles of the cell. The protein glue that holds them breaks and allows them to separate.
- Microtubules that are not attached to chromosomes elongate and push apart. In doing so they separate the poles and makes the cell longer. These processes are controlled by motor proteins and these...
Telophase
- In this stage, the cell is almost divided and starts to re-establish its normal cellular structures as cytokinesis takes place.
- The mitotic spindle breaks down into its building blocks and two new nuclei are formed, one for each set of chromosomes.
- The nuclear membrane and the nucleoli then reappear and the chromosomes begin to de- co…
- In this stage, the cell is almost divided and starts to re-establish its normal cellular structures as cytokinesis takes place.
- The mitotic spindle breaks down into its building blocks and two new nuclei are formed, one for each set of chromosomes.
- The nuclear membrane and the nucleoli then reappear and the chromosomes begin to de- condense to return to their normal form.
Cytokinesis
- In animal cells, cytokinesis is contractile. There's a pinch-like formation within the cell which divides it in two like a coin purse with a 'drawstring'. The "drawstring" is a band of actin protei...
- Plant cells can't be divided like this as they have a rigid cell wall and are too stiff. A cell plate forms down the middle of the cell which splits the daughter cells.
Meiosis
- In meiosis, a single cell divides twice to produce four cells that contain half of the original amount of genetic material. It can be observed in sperm cells in males and egg cells in females. There are 9 meiotic cell division phases. These are discussed below: Interphase 1. Similar to mitosis the genetic material of the cell is copied and two identical sets of chromosomes are formed. 2. The …
Meiosis II
- Prophase II 1. At the end of meiosis, there are two daughter cells with 23 chromosomes 2. The chromosomes condense again and form visible X-shaped structures 3. The nuclear membrane will dissolve releasing the chromosomes. 4. The centrioles duplicate and the meiotic spindle is formed. Metaphase II 1. Similar to metaphase I, the sister chromatid align along the center of th…
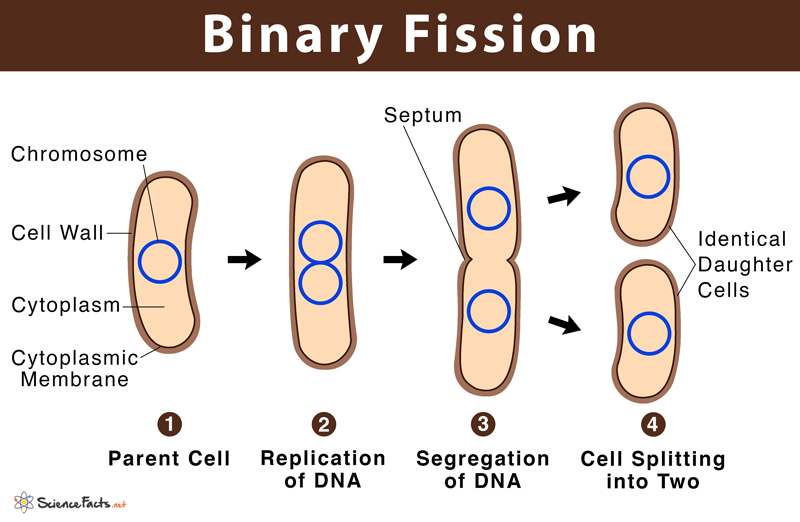
Binary Fission
- When a cell divides, it first duplicates its DNA, then divides. This is how the day-to-day growth of the human body occurs, which requires new cells to be created for tissue repair and maintenance through cell division. For prokaryotes (bacteria), the process of binary fission is a simple duplication of the DNA followed by division into two cells. For eukaryotes (plants and animals), t…