
Does CH3Cl have dipole dipole intraction?
It mean, it generate dipole moment between C-Cl and C-H. this type of intraction is called dipole-dipole intraction. therefore, you can say that, ch3cl has dipole dipole intraction. and carbon-chlorine bonds are slightly stronger then carbon-hydrogen. Read More:- NH3 intermolecular forces, types, Polarity, and FAQ?
Is CH3Cl a polar or nonpolar molecule?
CH3Cl is polar molecules because carbon are attached with three hydrogen, it is non polar, and london dispersion forces occurs non polar molecules but carbon – chlorine is polar molecules. because chlorine has more electronegative charge then carbon. So, it hold electron on it.
What type of Bond has a high dipole-dipole attraction?
Hydrogen bonding (Molecules with F-H,O-H, or N-H have highly concentrated partial charges that allow for a very strong dipole-dipole attraction to develop known as hydrogen bonding) Which of the following is the strongest intermolecular force? - hydrogen bonding - dipole-dipole attractions - dispersion forces - covalent bonding
Where do dipole dipole attractions occur between molecules?
polar/polar molecules (Dipole-dipole attractions occur between the partially positive end of one polar molecule and the partially negative end of another polar molecule) The hydrogen bond occurring between which two molecules would be the strongest?
How do dipole-dipole interactions work?
When do polar covalent bonds and dipole moments occur?
What color is the electron density of a polar covalent bond?
What are the main types of intermolecular interactions responsible for the physical properties of compounds?
What is the weakest intramolecular interaction?
How to find the direction of polarity in a bond?
Why is the C-I bond reactive?
See 2 more
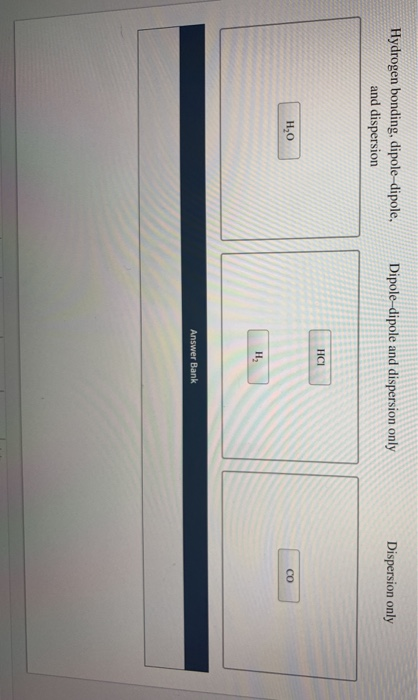
Is CH3Cl hydrogen bonding or dipole dipole?
dipole-dipoleIn CH3Cl, there is a polar bond between carbon and chlorine. So the molecule has dipole-dipole and dispersion.
Is CH3Cl a dipole dipole?
Due to this electronegativity difference, the C atom has a slightly positive (ẟ+) charge and the Cl atom has a slightly negative (ẟ-) charge. This results in the presence of dipole-dipole interaction between the CH3Cl molecules as a dipole moment is generated between the C-H bond and the C-Cl bond.
Does CH3Cl show hydrogen bonding?
Hence, CH3Cl is a hydrogen bond.
Is CHCl3 a dipole dipole or dispersion?
due to this charge it interact each other and the direction of bond dipole between carbon and chlorine is upwards. It mean, it generate dipole moment between C-Cl and C-H. this type of intraction is called dipole-dipole intraction. therefore, you can say that, ch3cl has dipole dipole intraction.
What type of intermolecular is CH3Cl?
dipole-dipole forcesSo, the intermolecular forces that will be present in CH3Cl C H 3 C l are London forces(as these forces are present in all the molecules) and dipole-dipole forces. Among London forces and dipole-dipole forces, the dominant intermolecular forces in CH3Cl C H 3 C l is dipole-dipole forces.
What type of intermolecular bond is CHCl3?
Two inter molecular forces that are active between two molecules of CHCl3 are Dipole Dipole, because it is a polar molecule, and London dispersion, because all molecules use them. non polar covalent bond.
Is CHCl3 a dispersion force?
Trichloromethane is composed of a hydrogen atom, a carbon atom, and three chlorine atoms. There are two intermolecular forces of attraction present in trichloromethane. These are London dispersion forces and dipole-dipole forces.
Why is CH3Cl a dipole moment?
CH3Cl (1. 94D) has more dipole moment than CH3F (1. 82D), because the charge separation is larger in CH3Cl compared to CH3F. This is due to greater C−Cl bond length than C−F bond length.
Why is CHCl3 a dipole moment?
In case of CHCl3 resultant of TWO Cl bonds cancel each other and the remaining H and Cl gives the dipole moment .
Why is CHCl3 a dipole moment?
In case of CHCl3 resultant of TWO Cl bonds cancel each other and the remaining H and Cl gives the dipole moment .
Does CHCl3 have a dipole moment?
CHCl3 has a tiny dipole moment of 1.08 D as a result of this. The resultant of the dipole moments of two C – Cl bonds, on the other hand, is enhanced by the resultant of the dipole moments of two C – H bonds in CH2Cl2.
How do you identify a dipole dipole bond?
1 Answer. You have a dipole moment when there is a difference in electronegativity between two atoms.
Why CHCl3 has a dipole moment?
1-This is due to in CH3Cl chlorine is EWG and it is in one direction and no other group present for cancelling/decreasing its dipole moment. 2- In CH2Cl2 dipole moment of H-H atoms and Cl-Cl atoms do not cancel each other because angle are not 180° so they are not linear.
How do dipole-dipole interactions work?
To understand the nature of dipole-dipole interactions, remember that when two atoms with different electronegativities are connected, we have a polar covalent bond, and the shared electron pair of the covalent bond is not in the middle of the two atoms. There is a higher density towards the more electronegative element and as a result, both elements have partial charges. Mainly, the more electronegative atom bears a partial negative, and the other atom has a partial positive charge which are indicated by the delta plus (δ+) and delta minus (δ-) symbols:
When do polar covalent bonds and dipole moments occur?
Polar covalent bonds and dipole moment originate when there is a significant difference in the electronegativities of the two bonded atoms. Now, the ionic bonding occurs when the difference in electronegativities is very large and one of the atoms completely takes the bonding electrons.
What color is the electron density of a polar covalent bond?
The electron density of a polar covalent bond can also be shown with electrostatic maps. These are simply color-coded clouds where the blue usually corresponds to the most electron-deficient, and the red, to the most electron-rich region.
What are the main types of intermolecular interactions responsible for the physical properties of compounds?
Dipole-dipole, London dispersion (also known as Van der Waals) interactions, hydrogen bonding, and ionic bonds are the main types of intermolecular interactions responsible for the physical properties of compounds. All of them are electrostatic interactions meaning that they all occur as a result of the attraction between opposite charges ...
What is the weakest intramolecular interaction?
These are the weakest intramolecular interactions and occur as an electrostatic interaction of temporary dipole moments formed in the molecule right at the time when they get in a close enough distance.
How to find the direction of polarity in a bond?
The direction and magnitude of polarity in a bond are given by the dipole moment which is indicated by an arrow. The arrow starts from the less electronegative element and points toward the more electronegative element as shown above.
Why is the C-I bond reactive?
This is because of polarizability which is the characteristic of how the electron cloud around an atom responds to changes in the electronic environment.
Why does hydrogen bonding increase the boiling point?
These are all due to the strong intermolecular forces present in such a substance, making the molecules harder to separate)
Which molecule has the best ability to participate in dispersion forces?
CI4 is the largest molecule, as iodine atoms are larger than the other halogens listed. As the largest molecule, it will have the best ability to participate in dispersion forces. Intermolecular forces occur between particles in a substance. These particles can be: atoms or separate molecules.
Which compound has the highest boiling point?
CH3COOH (Compounds with stronger intermolecular forces will have higher boiling points (ion-ion > hydrogen bonding > dipole-dipole > london dispersion). CH3COOH is the only one that is capable of hydrogen bonding, so it will have the highest boiling point)
Which atoms are electronegative?
electronegative atoms (Hydrogen bonds are formed between hydrogen and the three most electronegative atoms (nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine). The relatively large difference in the partial charges of each atom in N−H, O−H and F−H bonds allow for very strong dipole-dipole attractions between molecules that contain them)
Is ICl polar or nonpolar?
ICl is a polar molecule and Br2 is a non-polar molecule. Which molecule will have a higher boiling point?
Does CH3OCH3 have OH bonds?
CH3OCH3. (The ether does not have OH bonds, it has only CO bonds and CH bonds, so it will be unable to participate in hydrogen bonding) hydrogen bonding results in: higher boiling points (Hydrogen bonding increases a substance's boiling point, melting point, and heat of vaporization.
Is hydrogen a covalent bond?
covalent bond. Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces, not bonds, so they are much weaker than covalent bonds, but much stronger than other dipole-dipole attractions and dispersion forces. Dispersion forces result from the formation of: ion-dipole attractions. dipole-dipole attractions.
What atoms add up to give CH3Cl a dipole moment?
In CH3Cl the polarity vectors of 3 H atoms and Cl atoms add up and give it a large dipole moment ...
Which is greater, CH3Cl or CHCl3?
Dipole moment of CH3Cl is GREATER than CHCl3.
How many Cl atoms cancel each other's effect?
In CH3Cl the polarity vector of only one H atom adds up and 3 Cl atoms cancel each others effect and give it a much smaller dipole m
What is dipole moment?
A dipole moment is the product of charge and separation. The distance between the C and the Cl atom is so much larger than the distance between the C and the F that even though it is multiplied by a smaller charge difference it is still ending up the larger of the two dipoles.
What scales up with the aforementioned difference in electronegativity?
the magnitude of a dipole moment scales up with the aforementioned difference in electronegativity: the larger it is, the larger the dipole moment.
Which dipole moment has the lowest value?
Tetrachloro methane has the lowest value of dipole moment .
Which atoms cancel each other's dipole moments?
In the structure it is clear that the two chlorine atoms present opposite to each other cancel each other’s dipole moments . Hydrogen has a lower electronegativity than Carbon and Carbon is less electronegative than Chlorine and so a net dipole moment acts towards the right giving it a high dipole which is 1/2^ (1/2) times that of the dipole moment of dichloromethane .
How do dipole-dipole interactions work?
To understand the nature of dipole-dipole interactions, remember that when two atoms with different electronegativities are connected, we have a polar covalent bond, and the shared electron pair of the covalent bond is not in the middle of the two atoms. There is a higher density towards the more electronegative element and as a result, both elements have partial charges. Mainly, the more electronegative atom bears a partial negative, and the other atom has a partial positive charge which are indicated by the delta plus (δ+) and delta minus (δ-) symbols:
When do polar covalent bonds and dipole moments occur?
Polar covalent bonds and dipole moment originate when there is a significant difference in the electronegativities of the two bonded atoms. Now, the ionic bonding occurs when the difference in electronegativities is very large and one of the atoms completely takes the bonding electrons.
What color is the electron density of a polar covalent bond?
The electron density of a polar covalent bond can also be shown with electrostatic maps. These are simply color-coded clouds where the blue usually corresponds to the most electron-deficient, and the red, to the most electron-rich region.
What are the main types of intermolecular interactions responsible for the physical properties of compounds?
Dipole-dipole, London dispersion (also known as Van der Waals) interactions, hydrogen bonding, and ionic bonds are the main types of intermolecular interactions responsible for the physical properties of compounds. All of them are electrostatic interactions meaning that they all occur as a result of the attraction between opposite charges ...
What is the weakest intramolecular interaction?
These are the weakest intramolecular interactions and occur as an electrostatic interaction of temporary dipole moments formed in the molecule right at the time when they get in a close enough distance.
How to find the direction of polarity in a bond?
The direction and magnitude of polarity in a bond are given by the dipole moment which is indicated by an arrow. The arrow starts from the less electronegative element and points toward the more electronegative element as shown above.
Why is the C-I bond reactive?
This is because of polarizability which is the characteristic of how the electron cloud around an atom responds to changes in the electronic environment.
