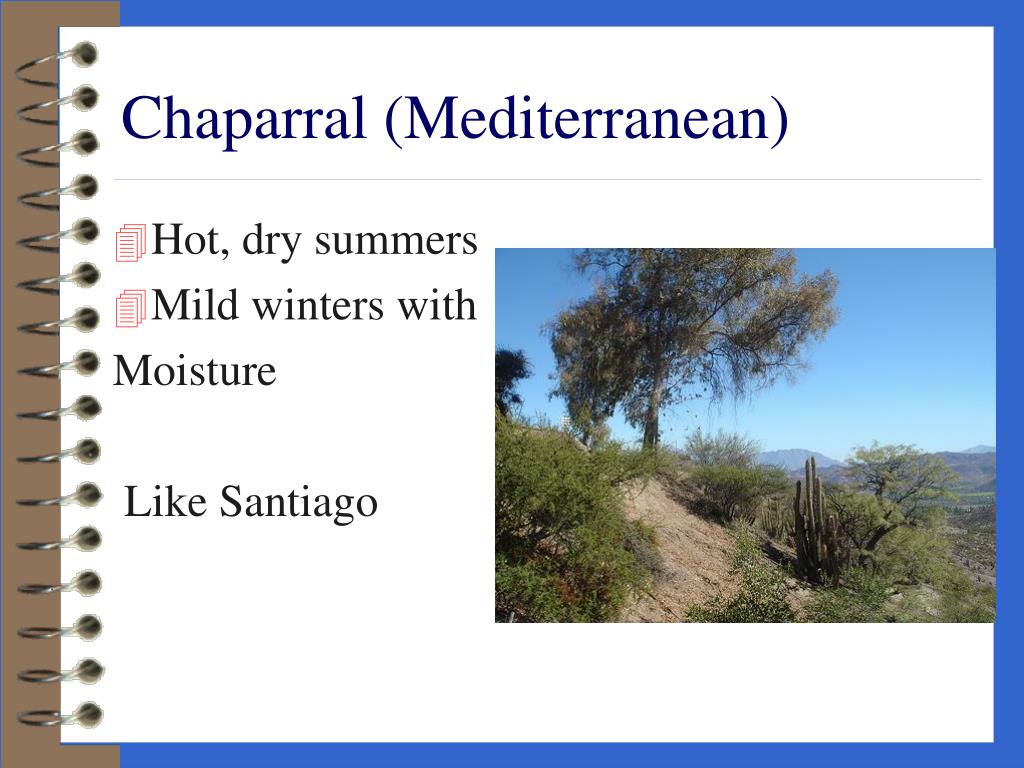
Chaparral is found in regions with a climate similar to that of the Mediterranean area, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. What is another name for Chaparral? In Europe it is called the maquis, Australia has the mallee, Chile the matorral, and South Africa calls it fynbos.
What is the Mediterranean chaparral biome?
Chaparral is found in regions with a climate similar to that of the Mediterranean area, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. What is another name for Chaparral? In Europe it is called the maquis, Australia has the mallee, Chile the matorral, and South Africa calls it …
What is chaparral?
· It is also called the Mediterranean Forest, Woodland, and Scrub biome. The chaparral biome has many different types of terrain. Some examples are flat plains, rocky hills and mountain slopes. CLIMATE. The chaparral is characterized as being very hot and dry. The winter is very mild and is usually about 10°C.
What is the difference between chaparral and cismontane?
Chaparral is found in regions with a climate similar to that of the Mediterranean area, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. What is another name for Chaparral? In Europe it is called the maquis, Australia has the mallee, Chile the matorral, and South Africa calls it …
What is the difference between a shrubland and a chaparral?
Chaparral is the California name for this biome.Chaparral, or Sclerophyll forest biomes, occur in Europe, Africa, Asia Minor, North America, and South America. This subtropical Mediterranean biomeMediterranean biomeMediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub is a biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The biome is generally characterized by dry summers and …

Is chaparral a Mediterranean climate?
In the winter the Chaparral climate, also known as the Mediterranean climate, is mild and moist, but not rainy. During the summer it is very hot and dry. The temperature is usually mild but it can get very hot or nearly freezing. The temperature range is between 30° and 100° F.
What is another name for chaparral biome?
It is also called the Mediterranean Forest, Woodland, and Scrub biome. The chaparral biome has many different types of terrain. Some examples are flat plains, rocky hills and mountain slopes. WEATHER: The chaparral is characterized as being very hot and dry.
What biome is chaparral?
Lay of the land: The chaparral biome has many different types of terrain. Some examples are flat plains, rocky hills and mountain slopes. It is sometimes used in movies for the "Wild West". Chaparral is characterized as being very hot and dry.
Is Greece a chaparral?
There are chaparral biomes along the west coasts in the mid-latitudes of Europe, Australia, the Americas, and South Africa. The entire Mediterranean Basin — which includes coastal areas in Italy, Greece, Turkey, Syria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Spain, and Portugal — is considered Mediterranean forest.
What biome is the Mediterranean?
Chaparral, or Mediterranean Forests, and shrub is a temperate biome, characterized by hot-dry summers and mild and rainy winters.
Where is the Mediterranean chaparral located?
Mediterranean Chaparral biome is localized in the coastal areas surrounding the Mediterranean Sea including parts of Europe, North Africa, and Asia Minor. This subtropical Mediterranean biome, composed of shrub lands and woodlands is called the maquis in Europe.
What means chaparral?
Definition of chaparral 1 : a thicket of dwarf evergreen oaks broadly : a dense impenetrable thicket of shrubs or dwarf trees. 2 : an ecological community composed of shrubby plants adapted to dry summers and moist winters that occurs especially in southern California.
What is the difference between chaparral and desert?
Subtropical deserts are characterized by their dry environments, while chaparrals are characterized by the presence of shrubs.
What countries have chaparral?
The chaparral is on the west coast of continents in these two areas. These continents include North America, South America, South Africa, and Australia. The chaparral is also along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea.
What climate is the Mediterranean?
Mediterranean climate, major climate type of the Köppen classification characterized by hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters and located between about 30° and 45° latitude north and south of the Equator and on the western sides of the continents.
What countries are near the Mediterranean Sea?
Today 21 countries, with surface areas from 2 km2 to 2.4 million km2, have coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea. They are Albania, Algeria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Cyprus, Egypt, France, Greece, Israel, Italy, Lebanon, Libya, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, Morocco, Slovenia, Spain, Syria, Tunisia, and Turkey.
Where is Chaparral located?
Chaparral / ˌʃæp.əˈræl, ˌtʃæp -/ is a shrubland plant community found primarily in the U.S. state of California, in southern Oregon, and in the northern portion of the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico.
What is a desert chaparral?
Desert chaparral is a regional ecosystem subset of the deserts and xeric shrublands biome, with some plant species from the California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion. Unlike cismontane chaparral, which forms dense, impenetrable stands of plants, desert chaparral is often open, with only about 50 percent of the ground covered. Individual shrubs can reach up to 10 feet (3.0 m) in height.
Where is the Cismontane Chaparral?
Cismontane chaparral ("this side of the mountain") refers to the chaparral ecosystem in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome in California, growing on the western (and coastal) sides of large mountain range systems, such as the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada in the San Joaquin Valley foothills, western slopes of the Peninsular Ranges and California Coast Ranges, and south-southwest slopes of the Transverse Ranges in the Central Coast and Southern California regions.
How can chaparral be eliminated?
Though adapted to infrequent fires, chaparral plant communities can be eliminated by frequent fires. A high frequency of fire (less than ten years) will result in the loss of obligate seeding shrub species such as Manzanita spp. This high frequency disallows seeder plants to reach their reproductive size before the next fire and the community shifts to a sprouter-dominance. If high frequency fires continue over time, obligate resprouting shrub species can also be eliminated by exhausting their energy reserves below-ground. Today, frequent accidental ignitions can convert chaparral from a native shrubland to non-native annual grassland and drastically reduce species diversity, especially under drought brought about by climate change.
Is the Chaparral biome dry?
Chaparral is a coastal biome with hot, dry summers and mild, rainy winters. The chaparral area receives about 38–100 cm (15–39 in) of precipitation a year. This makes the chaparral most vulnerable to fire in the late summer and fall.
What are the main components of the biome?
Shrubs and low growing vegetation are the main components of this biome. In some areas the growth extends to larger trees and hard leaf forests, as well as aromatic plants. The vegetation must be hardy and drought resistant and will include evergreens, cacti, olive and fruit trees, and cork oak, among others.
Do cactus need water?
Ca ctus and other water storing plants do well in this environment. The cacti often form dense thickets. Most of the plant growth is leafy and relatively short, less than eight feet tall. It is important for plants to be drought resistant, to survive the short wet winters and long dry summers.
Is chaparral found on multiple continents?
Note: Since the chaparral is found on multiple continents, not all plant life is the same depending on the region! This is a general list; if you are researching for a report make sure you confirm where the plant is found!
How long is the summer in Chaparral?
Summer lasts about 5 months, with temperatures ranging from 15–30°C (60–85°F), and highs reaching up to 38°C (100°F). Winter temperature in the chaparral ranges from 4° to 20°C (40–65°F). An overall annual average would be about 18°C (64°F). This mild climate is what draws so many people to live in these areas.
What is the climate of the chaparral biome?
You will find this biome in the temperate regions between 30° and 50° north and south latitude, from sea level up to around 1500 m (~4900 ft) above sea level. This biome is often found where cool, moist air from the ocean hits dry, warm land masses, typically along the west coast, forming this semi-arid mediterranean climate. The chaparral covers somewhere between 2-5% of terrestrial earth and is found on multiple continents, each with its own name: 1 North America: Chaparral 2 Greece: Phrygana 3 Israel: Batha 4 Portugal: Matagal or Mato 5 Southern Europe (France and Italy): Maquis 6 Southwest Australia: Kwongan or mallee 7 South Africa: Fynbos 8 Spain, Mexico and Chile: Matorral
Where are scrublands found?
These low, soft-leaved scrublands around the Mediterranean are known as phrygana in Greece, batha in Israel, tomillares in Spain, and garrigue in France.
Where is coastal scrub found?
Meanwhile, northern coastal scrub and coastal sage scrub, or soft chaparral, occur near the California coast. This is also known as coastal matorral in central Chile, strandveld in the Western Cape of South Africa, and sand-heath and kwongan in Southwest Australia.
What are the ecosystems in California?
In California specifically, there are also pine woodlands and walnut woodlands. Savanna and grassland: The California Central Valley grasslands are the largest Mediterranean grassland ecoregion, although these grasslands have mostly been converted to agriculture. Your content goes here.
How many species of fynbos are there in Africa?
For example, the fynbos in Africa is said to have as many as 6,000 endemic species! These facts not only make chaparral ecosystems important to world plant biodiversity, but also shows that they provide a very important habitat to various animals.
Mediterranean Shrublands (Chaparral Biome)
Mediterranean Shrublands or Chaparral biome is found along the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea, California, Central Chile, south-western part of South Africa and south-western parts of Australia.
Comments
even the sirocco winds from sahara desert cause a sort of blood rain over the adriatic and aegean sea!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!

Overview
Chaparral is a shrubland plant community found primarily in the U.S. state of California, in southern Oregon, and in the northern portion of the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. It is shaped by a Mediterranean climate (mild wet winters and hot dry summers) and infrequent, high-intensity crown fires. Chaparral features summer-drought-tolerant plants with hard sclerophyllousevergreen le…
Introduction
In its natural state, chaparral is characterized by infrequent fires, with natural fire return intervals ranging between 30 years and over a hundred years. Mature chaparral (at least 50 years since time of last fire) is characterized by nearly impenetrable, dense thickets (except the more open chaparral of the desert). These plants are flammable during the late summer and autumn months when conditions are characteristically hot and dry. They grow as woody shrubs with thick, leathe…
California chaparral
The California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion, of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, has three sub-ecoregions with ecosystem—plant community subdivisions:
• California coastal sage and chaparral: In coastal Southern California and northwestern coastal Baja California, as well as all of the Channel Islandsoff Ca…
Fire
Chaparral is a coastal biome with hot, dry summers and mild, rainy winters. The chaparral area receives about 38–100 cm (15–39 in) of precipitation a year. This makes the chaparral most vulnerable to fire in the late summer and fall.
The chaparral ecosystem as a whole is adapted to be able to recover from naturally infrequent fire (fires occurring a minimum of 30 years apart); indeed, …
See also
• California Chaparral Institute
• California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion
• Heath (habitat)
• Fire ecology
Bibliography
• Haidinger, T.L., and J.E. Keeley. 1993. Role of high fire frequency in destruction of mixed chaparral. Madrono 40: 141–147.
• Halsey, R.W. 2008. Fire, Chaparral, and Survival in Southern California. Second Edition. Sunbelt Publications, San Diego, CA. 232 p.
• Hanes, T. L. 1971. Succession after fire in the chaparral of southern California. Ecol. Monographs 41: 27–52.
External links
• The California Chaparral Institute website