
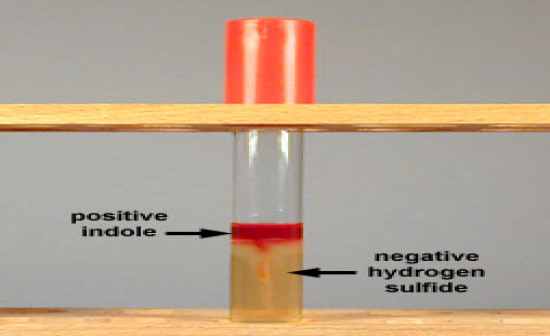
Citrobacter freundii is H2S positive and indole negative. Citrobacter koseri is H2S negative and indole positive. Citrobacter freundii is often the cause of significant opportunistic infections.
What are the characteristics of Citrobacter freundii?
Biochemical Test and Identification of Citrobacter freundii Basic Characteristics Properties ( Citrobacter freundii) Gelatin Hydrolysis Negative (-ve) Gram Staining Negative (-ve) Growth in KCN Positive (+ve) H2S Positive (+ve) 59 more rows ...
What are the 10 H2S positive bacteria?
List of H2S Positive Bacteria 1 Proteus vulgaris 2 Proteus mirabilis 3 Citrobacter freundii 4 Salmonella species ( except Salmonella Paratyphi A) 5 Salmonella arizonae 6 Edwardsiella tarda 7 Edwardsiella hoshinae 8 Erysiphilothrix rhusiopathiae 9 Brucella abortus 10 Brucella suis More items...
When was Citrobacter freundii discovered?
The Citrobacter genus was discovered in 1932 by Werkman and Gillen. Cultures of C. freundii were isolated and identified in the same year from soil extracts [1].
Is Citrobacter freundii a cause of fish disease?
This discovery established C. freundii as a cause of fish disease [11]. In a case study by the Journal of Medical Microbiology, a patient developed peritonitis and tunnel infection due to Citrobacter freundii which is uncommon. The patient was on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.

Does Citrobacter freundii produce gas?
C. freundii was grown in a 51 fermentor under batch anaerobic conditions. The total production of gas was 8.91 in the volumetric ratio of 63% H2 and 37% CO2 in 11 hr from 30.8 g glucose.
Does Citrobacter freundii reduce sulfur?
They mentioned that this strain of Citrobacter is able to reduce sulfate to sulfide. The isolation of bacteria belongs to C. freundii with sulfate reduction capability shows that the diversity of SRB still has the possibility to be expanded (Zhang et al.
What are the characteristics of Citrobacter freundii?
Citrobacter freundii are long rod-shaped bacteria typically 1-5 μm in length [1]. Most C. freundii cells are surrounded by many flagella used to move about, but a few are non-motile. Its habitat includes the environment (soil, water, sewage), food, and the intestinal tracts of animals and humans [1].
Is Citrobacter freundii Mr positive or negative?
rodentium (formerly Citrobacter freundii strain 4280), is a nonmotile, gram-negative rod that ferments lactose but does not utilize citrate or does so marginally (Barthold, 1980; Schauer et al., 1995).
What is Citrobacter freundii sensitive to?
An examination of 99 field and reference strains of Citrobacter freundii showed 79% of them to be resistant to cephaloridine and sensitive to carbenicillin, while 96% of 45 field and reference strains of Citrobacter koseri examined were sensitive to cephaloridine and resistant to carbenicillin.
What is Citrobacter freundii infection?
Citrobacter freundii (genus Citrobacter, family Enterobacteriaceae) is classically considered a ubiquitous and opportunistic pathogen. In humans, C. freundii causes urinary tract infections, diarrhea, pneumonia, and, rarely, meningitis and intracranial abscesses.
Does Citrobacter freundii need oxygen?
Citrobacter freundii characteristics C. freundii contains two membranes – inner and outer – since it's a gram-negative bacteria. It is capable of growing on glycerol as its only carbon and energy source, by fermenting carbon in the absence of oxygen.
What is the morphology of Citrobacter freundii?
MICROSCOPIC APPEARANCEGram Stains:Gram-negative.Morphology:Straight rods, occurring singly and in pairs.Size:Approximately 1 micrometer in diameter by 2.0-6.0 micrometers in length.Motility:Usually motile by peritrichous flagella.Capsules:None.1 more row
What antibiotics work for Citrobacter freundii?
Carbapenems, cefpirome, amikacin, and quinolones are still reliable agents for treating C. freundii bacteremia.
How can you tell the difference between E coli and Citrobacter freundii?
H2S-negative Citrobacter may be confused with other Enterobacteriaceae. The main features differentiating between Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Citrobacter freundii biogroup b are the citrate and KCN tests, and the citrate, malonate, and adonitol tests are the differentiating features between E.
Is Citrobacter freundii positive for methyl red?
They ferment glucose and other carbohydrates with the production of acid and gas. They are oxidase negative, catalase and methyl red positive, Voges-Proskauer negative, and do not decarboxylate lysine. Taxonomically, the genus Citrobacter is most closely related to Salmonella and Escherichia.
Is Citrobacter aerobic or anaerobic?
Citrobacter species are straight, facultative anaerobic, Gram-negative bacilli and are typically motile by means of peritrichous flagellae. This genus was proposed in 1932 by Werkman and Gillen (61).
Is Citrobacter a lactose fermenter?
Lactose usually is fermented rapidly by Escherichia, Klebsiella and some Enterobacter species and more slowly by Citrobacter and some Serratia species.
What antibiotic treats Citrobacter Freundii?
Carbapenems, cefpirome, amikacin, and quinolones are still reliable agents for treating C. freundii bacteremia.
Is Citrobacter catalase positive?
They are oxidase negative, catalase and methyl red positive, Voges-Proskauer negative, and do not decarboxylate lysine. Taxonomically, the genus Citrobacter is most closely related to Salmonella and Escherichia.
Can Citrobacter cause Sibo?
SIBO is often not alone. Many of my clients' test results also reveal the existence of serious gut infections. These can include parasites like Blastocystis hominis and Dientamoeba fragilis or bacterial infections like H. pylori or Citrobacter.
How long is a C. freundii rod?
The bacteria have a long rod shape with a typical length of 1–5 μm. Most C. freundii cells generally have several flagella used for locomotion, but some do not and are non-motile. C. freundii is a soil organism, but can also be found in water, sewage, food and in the intestinal tracts of animals and humans. The genus Citrobacter was discovered in ...
What is the name of the gram-negative bacteria that is a rod-shaped organism?
Citrobacter freundii. Ci trobacter freundii is a species of facultative anaerobic gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The bacteria have a long rod shape with a typical length of 1–5 μm. Most C. freundii cells generally have several flagella used for locomotion, but some do not and are non-motile.
What is the gram negative name of C. freundii?
Citrobacter. Species: C. freundii. Binomial name. Citrobacter freundii. (Braak 1928) Werkman and Gillen 1932. Citrobacter freundii is a species of facultative anaerobic gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The bacteria have a long rod shape with a typical length of 1–5 μm. Most C. freundii cells generally have several flagella ...
What is the role of C. freundii in the soil?
This microbe plays an important role in the nitrogen cycle in the environment. C. freundii is responsible for reducing nitrate to nitrite in the environment. This conversion is an important and crucial stage in the nitrogen cycle.
When was Citrobacter discovered?
The genus Citrobacter was discovered in 1932 by Werkman and Gillen. Cultures of C. freundii were isolated and identified in the same year from soil extracts. C. freundii is a common component of the gut microbiome of healthy humans.
Does C. freundii grow on glycerol?
C. freundii has also been investigated for biodegradation of tannic acid used in tanneries. C. freundii has the ability to grow on glycerol, and use it as its sole source of carbon and energy. The organism contains a bacterial microcompartment which is capable of processing propanediol.
What is the amino acid sequence of OS60?
The C. freundii OS60 AmpC β-lactamase gene has also been sequenced and it is composed of 1197 nucleotides. It encodes a 380 amino acid long precursor and contains a 19 residue signal peptide in the 5’ end [6]. This gene encodes a mature protein that has a molecular mass of 39 781 Daltons. The amino acid positions in these precursor are suprisinlgy identical to residues in the E. coli K12 chromosomal AmpC β-lactamases [6].
What is the habitat of Citrobacter freundii?
freundii cells are surrounded by many flagella used to move about, but a few are non-motile. Its habitat includes the environment (soil, water, sewage), food, and the intestinal tracts of animals and humans [1].
How long is a C. freundii cell?
The cell structure of C. freundi is long and rod-shaped usually 1-5 μm in length. The outside of the cell contains many flagella used for motality [1]. Since C. freundii is gram-negative bacteria, it contains two membranes (inner and outer).The periplasmic space lies in between the two membranes.
How does C. freundii grow?
For metabolism, C. freundii has an amazing ability to grow on glycerol as the sole carbon and energy source. In this process, glycerol is fermented by a dismutation process. This process requires two pathways [8]. In the first pathway, glycerol is dehydrogenated by a NAD1-linked glycerol dehydrogenase to dihydroxyacetone. The dihydroxyacetone is then phosphorylated and funneled to glycolysis by dihydroxyacetone kinase [8]. In the second pathway, glycerol is dehydrated by the coenzyme B12-dependent glycerol dehydratase to form 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde [8]. This product is reduced to the major fermentation product 1,3-propanediol by the NADH-linked 1,3-propanediol dehydrogenase, which regenerates NAD1. The dha regulon encodes the four essential enzymes of these two pathways. Amazingly, the expression of the dha regulon is only induced when glycerol is present [8].
Why are C. freundii sequenced?
freundii genome are being sequenced is in order to find antibiotics that can fight these opportunistic infections. Surprisingly, this infectious microbe in humans plays a positive role in the environment.
Where is Citrobacter freundii found?
Citrobacter freundii are commonly found in the environment, mainly in soil, water, and sewages. They are an indicator of potential contamination of water. They are also found on different organs of diseased animals, including mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians [1]. They are not known to interact with other organims.
When was the Citrobacter genus discovered?
The Citrobacter genus was discovered in 1932 by Werkman and Gillen. Cultures of C. freundii were isolated and identified in the same year from soil extracts [1].
What is the name of the bacteria that causes diarrhea?
Shigella are genus of Enterobacteriaceae family of bacteria and causing an infectious disease called Shigellosis. Shigella is named after the Japanese microbiologist Kiyoshi Shiga who isolated the first member of the group in 1896 from epidemic dysentery in Japan which was then called Shigella shiga and is now called as S. dysenteriae. Most who are infected with Shigella develop diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps starting a day or two after they are exposed to the bacteria. Shigellosis usually resolves in 5 to 7 days. Some people who are infected may have no symptoms at all, but may still pass the Shigella bacteria to others. The spread of this organisms can be stopped by frequent and careful hand washing with soap and taking other hygiene measures because of being mode of infection feco-oral route.
Why does lactose fermenting produce yellow slants?
Bacteria that are non lactose fermenting initially produce a yellow slant due to the production of acid from the glucose. The small amount of glucose is rapidly depleted.
How long does it take for a shigellosis to spread?
Infection mainly occurs because of the ingestion of contaminated food or water. Incubation period is 12-48 hours but may vary between 1-7 days. Through the ingestion the bacilli will reaches to the large intestine of the humans. The multiplication occurs in the epithelial cells of the large intestine. Then the bacteria spreads to adjacent cells and to the lamina propria (is a thin layer of loose connective tissue which lies beneath the epithelium) where the colonization occurs. After the growth and multiplication, it starts to produce toxins.The lamina propria and sub mucosa develops an acute inflammatory reaction with formation of abscess on the mucosal surface along with capillary thrombosis by the production of toxins. The necrosed epithelium become soft and sloughed out and causing superficial ulcers and bleeding. The toxin produced by the shigella bacteria have both enterotoxic effect and neurotoxic effect. Thus their combined action leads to severe diarrhea,poly neuritis, coma and meningitis.
Why is Kligler's Iron Agar different from Triple Sugar Iron Agar?
Kligler’s Iron Agar (KIA) test only differs from the Triple Sugar Iron agar (TSI) test due to lacking sucrose in its composition.
What is TSI in agar?
Hydrogen sulfide production by the bacteria. TSI stands for triple sugar iron and it is agar medium recommended for use in the differentiation of Enterobacteriaceae by their ability to ferment glucose, lactose, and sucrose, and their ability to produce hydrogen sulfide.
What bacteria have H2S?
H2S positive bacteria Proteus vulgaris and Salmonella Typhi from left to right respectively as shown above picture. H 2 S positive bacteria have the ability to produce hydrogen sulfide from substrates such as sulfur-containing amino acids or inorganic sulfur compounds. The sulfur is used as the final hydrogen acceptor leading to the formation of H 2 S. Sulfur-containing amino acids ( e.g. methionine, cysteine, cysteine, or an inorganic compound such as sodium thiosulphate, etc.) should be present in the medium to detect the presence of H2S. It is being gassed, will escape from the test medium. Therefore, the indicators such as heavy metal ions are incorporated into the test medium, which supports the growth of bacteria. Organisms that are tested for the production of hydrogen sulfide must contain an enzyme system that releases sulfide from the sulfur source. Sulfides combine with the hydrogen ion to form H 2 S and H 2 Scombines with heavy metals to form insoluble black precipitate as shown above picture.
What is sulfur used for?
The sulfur is used as final hydrogen acceptor leading to the formation of H 2 S. Sul fer containing aminoacids ( e.g. methonine, cysteine, cysteine or inorganic compound such as sodium thiosulphate , etc.) should be present in the medium to detect the presence of H2S. It is being gas, will escape from the test medium.
Overview
Cell morphology and features
Exopolysaccharides from C. freundii target the hydroxyl radical, demonstrating antioxidant activity. These antioxidant properties are related to many different physical and chemical properties.
C. freundii can also have a positive impact when it comes to the treatment of some cancers; specifically, it has been found to be helpful in killing and treating cervical carcinoma. Certain isol…
Phylogeny and genome evolution
C. freundii is more phylogenetically diverse than the clades of E. coli and Salmonella spp., indicating C. freundii to be a polyphyletic genus. Due to the phenotypic diversity that C. freundii contains, it makes it very difficult to identify, especially because it is versatile not only in its antigenic and pathogenic behaviors, but also in its cell morphology.
C. freundii contains high degrees of nucleotide diversity due to the two different lineages with de…
Metabolic details
C. freundii has the ability to grow on glycerol, and use it as its sole source of carbon and energy. The organism contains a bacterial microcompartment capable of processing propanediol. C. freundii creates a positive MR and negative VP test along with a positive catalase and negative oxidase test. C. freundii cannot hydrolyze starch, lipids, or gelatin. C. freundii has also been investigated for biodegradation of tannic acid used in tanneries.
Relevance to broader system
C. freundii is also commonly found to be a member of the soil microbiome. This microbe plays an important role in the nitrogen cycle in the environment. C. freundii is also a nitrogen-fixing bacteria, a process demonstrated in the living tissues of sassafras trees. This process provides evidence that they are partly responsible for reducing nitrate to nitrite in the environment.
C. freundii can also be found in the intestinal tracts of humans and other animals from diverse e…
External links
• "Citrobacter freundii". NCBI Taxonomy Browser. 546.
• Type strain of Citrobacter freundii at BacDive - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase
Classification
Description and Significance
Genome Structure
Cell Structure and Metabolism
Ecology
Pathology
- As an opportunistic pathogen, Citrobacter freundii is often the cause of significant opportunistic infections, meaning that it does not generally cause disease in healthy human hosts. They only affect patients with a weak immune system, signifying that they need an "opportunity" to infect the person . Therefore, in patients with a suppressed immune...
Application to Biotechnology
Current Research
Antibiotic Resistance
References