Although the term "chronic" is also applied to CML, the disease tends to progress faster than CLL A type of cancer that begins in the lymphocytes of bone marrow and extends into the blood.Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Full Answer
Is CML worse than CLL?
They become myelocytes. Hereof, is CLL or CML worse? CML ( chronic myelogenous leukemia) and CLL ( chronic lymphocytic leukemia) are both cancers that originate from immune-system cells, but that is essentially where their similarities end. Although the term "chronic" is also applied to CML, the disease tends to progress faster than CLL.
What is the best diet for CLL?
- Whole grains
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel)
- Lean poultry
- Olive oil
- Beans, legumes, and lentils
- Eggs (cooked until yolk is hard)
What is the best treatment for CML?
Treatment
- Targeted drug therapy. Targeted drugs are designed to attack cancer by focusing on a specific aspect of cancer cells that allows them to grow and multiply.
- Bone marrow transplant. A bone marrow transplant, also called a stem cell transplant, offers the only chance for a definitive cure for chronic myelogenous leukemia.
- Chemotherapy. ...
- Clinical trials. ...
What does CML stand for in chronic granulocytic leukaemia?
Introduction Chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) is a rare type of leukaemia, or blood cancer. Leukaemias or blood cancers affect the blood cells present in the blood. Chronic myeloid leukaemia is also known as chronic myelogenous and chronic granulocytic leukaemia.

Is CML more serious than CLL?
CLL outlook. The survival rates for CML and CLL are improving as new cancer treatments become available. Currently, the 5-year relative survival rate for CML is around 70 percent and the 5-year relative survival rate for CLL is around 87 percent .
Which form of leukemia is more serious?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) The most common form of acute (fast-developing) leukemia among adults , AML is also the most critical because it progresses rapidly.
Can CLL turn into CML?
In the present study we report an additional patient who developed CML several years after the diagnosis of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Until now, 18 patients have been reported in whom CML developed after the diagnosis of CLL (Table 1).
What is the difference between CML and CML leukemia?
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is also known as chronic myelogenous leukemia. It's a type of cancer that starts in the blood-forming cells of the bone marrow and invades the blood. About 15% of leukemias in adults are CML.
Is CML leukemia is fatal?
Survival statistics Generally for all people with CML: around 90 out of 100 people (around 90%) will survive their leukaemia for 5 years or more after being diagnosed.
What is the most treatable leukemia?
Other drug therapies that have increased remission and cure rates include anthracyclines and gemtuzumab ozogamicin (GO). Because of advances in diagnosis and treatment of this disease, APL is now considered the most curable form of adult leukemia.
How fast does CML progress?
Without effective treatment, CML in chronic phase will eventually move into accelerated phase at first and then into blast phase in about 3 to 4 years after diagnosis.
Can you live a normal life with CML?
Today, the ten year survival rate for the most common form of CML is approximately 85% and patients can expect to live life-spans nearly as long as normal healthy adults.
Does CML reduce life expectancy?
A diagnosis of CML in 1990 in a 55-year-old woman on average reduced her life expectancy by 24.9 years (95% CI, 24.3-25.6), whereas a diagnosis in 2010 for the same woman reduced her life expectancy by only 2.9 years (95% CI, 1.2 to 4.6).
How severe is chronic myeloid leukemia?
In time, the cells can also settle in other parts of the body, including the spleen. CML is a fairly slow growing leukemia, but it can change into a fast-growing acute leukemia that's hard to treat.
Why did I get CML?
Causes of CML CML is caused by a genetic change (mutation) in the stem cells produced by the bone marrow. The mutation causes the stem cells to produce too many underdeveloped white blood cells. It also leads to a reduction in the number of other blood cells, such as red blood cells.
Can you get disability for CML?
A diagnosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), or chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) automatically qualifies you for SSDI benefits. Those are considered to be the "bad" leukemia's by Social Security.
Which is worse ALL or CLL?
Summary. ALL and CLL are both cancers that affect the bone marrow and blood. ALL is an acute form of leukemia that progresses rapidly, while CLL is slow-growing. Doctors treat ALL more aggressively than CLL because it spreads more rapidly.
Which is worse acute or chronic leukemia?
People with a diagnosis of chronic leukemia can live a normal life, and the outlook is positive. Acute leukemia is more aggressive and develops much more quickly. However, research on treatment is quickly advancing, increasing the number of treatment options and thus improving the outlook.
What are the 4 main types of leukemia?
There are 4 main types of leukemia, based on whether they are acute or chronic, and myeloid or lymphocytic:Acute myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (AML)Chronic myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (CML)Acute lymphocytic (or lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL)Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
IS ALL or AML worse?
Is one more serious than the other? Both ALL and AML are very serious conditions that develop rapidly . According to a 2021 review, AML is the most common type of leukemia among adults, accounting for around 80% of all cases. Authors of the review observe that age plays an important role in survival rates for AML.
What is the Difference Between CML and CLL?
CLL is the commonest form of leukemia , and it occurs in elderly people most of the time. The clonal expansion of small B lymphocytes is the pathological basis of this condition.
What is CLL?
CLL (Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia) is the commonest form of leukemia , and it often occurs in elderly people. The clonal expansion of small B lymphocytes is the pathological basis of this condition.
What is CML in medical terms?
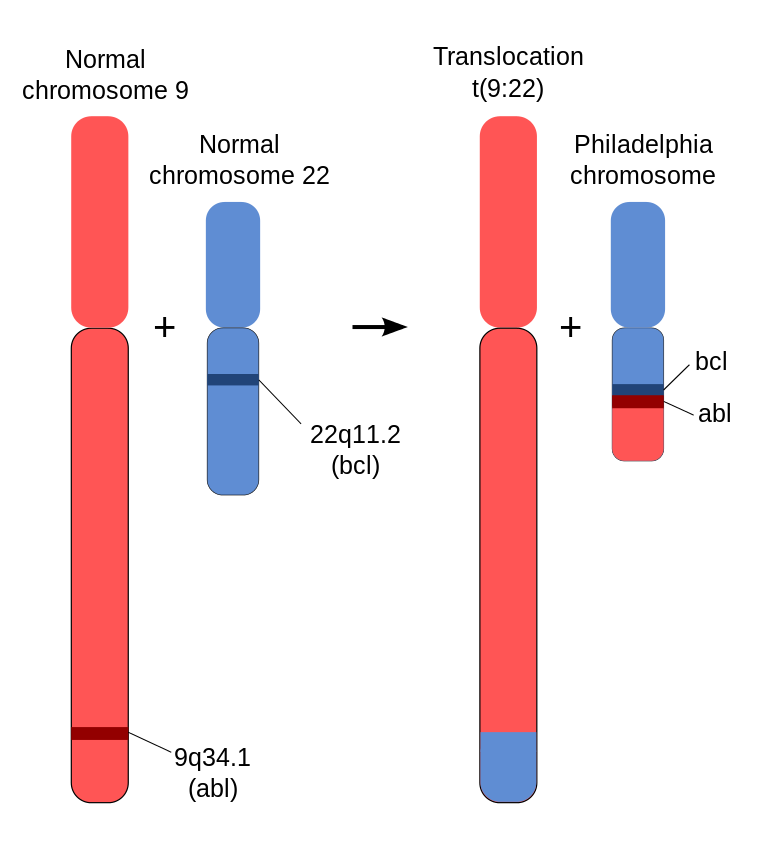
CML (Chronic Myeloid Leukemia) is a member of the family of myeloproliferative neoplasms which occurs exclusively in adults. It is defined by the presence of the Philadelphia chromosome and has a more slowly progressive course than acute leukemia.
What is the treatment for CML?
Rituximab in combination with Fludarabine and cyclophosphamide show a dramatic response rate. First line drug in the treatment of CML is Imatinib (Glivec), which is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Where does leukemia originate?
Leukemia can be described in lay terms as the malignancies of blood. However, in reality, the origin of leukemia happens in the bone marrows where the precursor stem cells that produce various blood cells lie.
Symptoms
CML and CLL share several symptoms, most of which are vague and may be shared by a variety of other conditions. However, they each have some unique symptoms.
Causes
In both CLL and CML, experts don’t know the exact cause of the disease. Gene changes likely play a role. Neither form of leukemia is inherited. Instead, the changes responsible for these types of cancers are typically acquired during a person's lifetime. 5
Diagnosis
Neither form of leukemia can be diagnosed during a physical exam. A doctor needs to perform additional tests to confirm a diagnosis of CML or CLL.
Treatment
A proper diagnosis is vital because the treatments for different types of cancer may not be the same. The first-line treatments for CML and CLL differ.
Prevention
Because little is known about what exactly causes either of these cancers, experts don’t know how to prevent them. 17
Summary
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have many similarities in their symptoms. It’s essential to get a proper diagnosis because treatment differs for these types of leukemia.
A Word From Verywell
If you have either of these types of leukemia, the good news is that they are highly treatable. Both also have a good prognosis. The five-year survival rate for CLL is about 87%. 19 For CML, it’s about 70%. 20
How to not feel guilty about cancer?
Don’t feel guilty for how you feel about your cancer journey. Don’t try and deny or surpress the emotions your experiences bring up. This cancer story you are in the middle of is most likely the most challenging thing you have ever faced. Do not make it harder on yourself by judging yourself and trying to decide if you are coping “well” or “badly”.
What is C in cancer?
C is for Chronic or Indolent. This means a slow growing form of blood cancer that may not need treatment straight away but can often be harder to cure. Often people are put onto “watch and wait” which can sometimes mean “watch and worry”. This phase of not needing to be treated can sometimes last many years. When treated the cancer often responds well, but may well return months or years later. Chronic blood cancers may need repeated treatments, but patients will often live for many years living in a kind of truce with the cancer. Examples of these types of blood cancer include some types of non Hodgkin’s lymphoma including follicular lymphoma, and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), as well as Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML).
Is blood cancer dangerous?
When you hear the word “acute” it can be very scary and of course these cancers are dangerous and there is an immediate risk to your health and even your life when you get such a diagnosis. But the doctors are also going to want to start treatment quickly and will usually offer you hope that the aggressive treatment these forms of blood cancer require will be well worth it.
Is blood cancer a type of non-Hodgkins lymphoma?
One type of blood cancer that seems to cause a lot of confusion has two names. For more than twenty years what was once thought to be two different diseases has been considered as one. And to make matters worse this disease is both a leukemia and a type of non Hodgkins lymphoma (NHL). No wonder it gets confusing! Some people even think the doctor told them they have four different diseases (Leukemia, Lymphoma, CLL and SLL).
What is the difference between CML and CLL?
The main difference between CML and CLL is that in CML , granulocytes are the malignant cells but lymphocytes are the malignant cells in CLL.
Where does leukemia originate?
Leukemia can be described in lay terms as the malignancies of blood. However, in reality, the origin of leukemia happens in the bone marrows where the precursor stem cells that produce various blood cells lie. CML (Chronic Myeloid Leukemia) and CLL (Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia) are two such varieties of leukemia that occur due to abnormalities in the stem cells in the bone marrows. CML is a member of the family of myeloproliferative neoplasms whereas CLL is the commonest type of leukemia whose pathological basis is the clonal expansion of B
What are the factors that affect your outlook on leukemia?
Other factors that will affect your outlook are: your age. your general health. how much the leukemia has spread in your body.
How to treat leukemia?
You may not be diagnosed until symptoms, such as enlarged lymph nodes, appear. Chemotherapy, corticosteroids, and monoclonal antibodies may be used to control the cancer. Your doctor may use blood transfusions and platelet transfusions to treat the decrease in red blood cells and platelets. Radiation may help reduce the size of your lymph nodes.
Why does leukemia develop so quickly?
Acute leukemia develops quickly. This is because the cancerous cells multiply fast. Chronic leukemia is most commonly diagnosed after a routine blood test. You may have low-level symptoms for years before it’s diagnosed. The symptoms may be vague and could occur due to many other medical conditions.
What tests are done to determine if leukemia is killing cells?
Your doctor will do regular blood and bone marrow tests to determine how well your treatment is killing the leukemia cells. They may try various mixtures of drugs to see what works best.
How to diagnose leukemia?
All types of leukemia are diagnosed by examining blood samples and bone marrow. A complete blood count will show the levels and types of: white cells. leukemia cells. red cells. platelets. Bone marrow and other tests will give your doctor further information about your blood to confirm a diagnosis of leukemia.
What are the risk factors for acute leukemia?
exposure to chemicals such as benzene or Agent Orange. exposure to high levels of radiation. Some risk factors for developing acute leukemia include: smoking cigarettes. having chemotherapy and radiation therapy for other cancers. exposure to very high radiation levels.
What are the causes of leukemia?
Both environmental and genetic factors are thought to be involved. Leukemia may occur due to changes in the DNA of your cells. Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) may also be associated with a gene mutation called the Philadelphia chromosome. This gene mutation isn’t inherited.
What does CLL mean in blood tests?
Lymphocytes become a type of white blood cell, which helps your body fight off infections. But with CLL, the lymphocytes grow out of control. Blood tests often show a high white blood cell or lymphocyte level. You’d get more tests to find out if this is leukemia.
When do people get CLL?
CLL is the most common leukemia in adults. Most people get diagnosed in their 60s and 70s. As you age, your risk increases. Other types, such ALL and AML, mainly happen in childhood. Kids usually don’t get slow-growing forms of leukemia.
Where does leukemia start?
Two other types of leukemia -- acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) -- start in myeloid cells in your bone marrow. Myeloid cells develop into white blood cells other than lymphocytes, red blood cells (which carry oxygen), and platelets (which form clots to help stop bleeding).
Which type of leukemia grows faster?
In contrast, types of leukemia that have “acute” in their name (acute lymphocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia) grow much faster than most chronic leukemia. People with these types are usually very sick and need treatment right away.
Where does CLL start?
CLL and ALL begin in the bone marrow, where blood cells are usually made. Specifically, it starts in a type of bone marrow cell called lymphocytes. (That’s what the first “L” in CLL and ALL refers to.) Lymphocytes become a type of white blood cell, which helps your body fight off infections.
Can you have CLL for years?
If, like most people with CLL, you have the slow-growing kind, you might not notice any symptoms for years. A routine blood test might be the first clue that something’s wrong. You may not need treatment right away. (Your doctor will closely follow your health, of course.)
Can a doctor test for CLL?
Doctors can test for common and uncommon proteins on the surface of CLL cells. The results help diagnose and treat it, as well as check on the prognosis (how the condition may affect you).
Where does CML grow?
The leukemia cells grow and divide, building up in the bone marrow and spilling over into the blood. In time, the cells can also settle in other parts of the body, including the spleen. CML is a fairly slow growing leukemia, but it can change into a fast-growing acute leukemia that's hard to treat. CML occurs mostly in adults, ...
Where does CML start?
It's a type of cancer that starts in certain blood-forming cells of the bone marrow. In CML, a genetic change takes place in an early (immature) version of myeloid cells -- the cells that make red blood cells, platelets, and most types of white blood cells (except lymphocytes).
What is leukemia?
Leukemia is a cancer that starts in the blood-forming cells of the bone marrow. When one of these cells changes and becomes a leukemia cell, it no longer matures the way it should. Often, it divides to make new cells faster than normal. Leukemia cells also don't die when they should. They build up in the bone marrow and crowd out normal cells. At some point, leukemia cells leave the bone marrow and spill into the bloodstream, often causing the number of white blood cells (WBCs) in the blood to increase. Once in the blood, leukemia cells can spread to other organs, where they can keep other cells in the body from working properly.
What is a myeloid leukemia?
Whether leukemia is myeloid or lymphocytic depends on which bone marrow cells the cancer starts in.
What is CMML in medical terms?
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is another chronic leukemia that starts in myeloid cells. For more information, see Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia.
What is the difference between acute leukemia and lymphoma?
Other types of acute leukemia have a less favorable outlook. Lymphocytic leukemias start in the cells that become lymphocytes. Lymphomas are also cancers that start in those cells. The main difference between lymphocytic leukemias and lymphomas is that in leukemia, the cancer cell is mainly in the bone marrow and blood, ...
What is the term for a person who has a bone marrow cell that cannot mature?
Acute lymphocytic (or lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) In acute leukemias, the bone marrow cells cannot mature the way they should. These immature cells continue to reproduce and build up. Without treatment, most people with acute leukemia would only live a few months.
How long do people live with CLL?
This does not mean that life expectancy for a person with CLL is 5 years. Researchers typically collect data for survival rates at 1, 5, or 10 years after diagnosis.
What happens after CLL treatment?
After treatment, a person is likely to have periods of time when they have few or no symptoms of CLL. This is often known as remission. At the current time, medical professionals do not know if a person can reduce their risk of CLL coming back.
What happens when a person has lymphocytic leukemia?
When a person has lymphocytic leukemia, white blood cells become leukemia cells, which can spread into the blood and other parts of the body. CLL happens when white blood cells do not fully mature. They cannot fight infection properly, and they build up in the bone marrow. This means healthy white blood cells do not have as much room to thrive.
What are the factors that affect CLL survival?
Other factors that can affect survival rates include: 1 whether CLL has come back or improved with treatment 2 how cancer cells have spread in the bone marrow 3 if there are changes to a person’s DNA and what they are 4 a person’s general health
How long can you live with chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
Although doctors cannot often cure the disease, a person can live with this form of leukemia for many years with treatment.
How old do you have to be to get CLL?
Often, people do not require treatment for a while. Older adults are more likely than others to be affected by CLL, with 70 years being the average age of diagnosis. Those under the age of 40 years old are very unlikely to experience this type of cancer.
Is CLL a second form?
One form of CLL progresses very slowly, and a person may not need treatment for some time. The second form progresses more quickly and is considered to be more severe.

Symptoms
Causes
Diagnosis
- Neither form of leukemia can be diagnosed during a physical exam. A doctor needs to perform additional tests to confirm a diagnosis of CML or CLL.
Treatment
- A proper diagnosis is vital because the treatments for different types of cancer may not be the same. The first-line treatments for CML and CLL differ.
Prevention
- Because little is known about what exactly causes either of these cancers, experts don’t know how to prevent them.17 However, avoiding exposure to high amounts of radiation or radon can lower your risk of developing CML and CLL, respectively. That said, most people don’t knowingly or purposely expose themselves to these substances.18
Summary
- Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have many similarities in their symptoms. It’s essential to get a proper diagnosis because treatment differs for these types of leukemia. For example, the treatment of choice for CML involves targeted therapy drugs. In contrast, CLL treatment may involve a combination of chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and m…
A Word from Verywell
- If you have either of these types of leukemia, the good news is that they are highly treatable. Both also have a good prognosis. The five-year survival rate for CLL is about 87%.19 For CML, it’s about 70%.20 You can do very little to prevent these types of cancer. But you can visit a doctor if you notice any out-of-the-ordinary symptoms, including ...