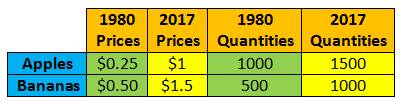
Is GDP deflator more accurate than CPI?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Deflator The fixed basket used in CPI calculations is static and sometimes misses changes in prices of goods outside of the basket of goods. Since GDP isn't based on a fixed basket of goods and services, the GDP deflator has an advantage over the CPI.
Why is CPI a better measure of inflation than GDP deflator?
The CPI measures price changes in goods and services purchased out of pocket by urban consumers, whereas the GDP price index and implicit price deflator measure price changes in goods and services purchased by consumers, businesses, government, and foreigners, but not importers.
Is GDP deflator a better measure of inflation?
Therefore, the GDP deflator is the best index for measuring inflation because it includes all final goods and services produced within a country. Economists and policymakers commonly use the GDP deflator for measuring inflation, while CPI is normally used for measuring standards of living.
What is the most accurate way to measure inflation?
The most well-known indicator of inflation is the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures the percentage change in the price of a basket of goods and services consumed by households.
Why CPI is not a good measure of inflation?
The CPI includes frequently purchased “everyday” goods, such as food and gasoline, and also durable goods, such as cars, furniture, and appliances. Durable goods typically do not increase in price as fast as more frequently purchased goods, and this may lead to an incorrect perception that the CPI is inaccurate.
Is the CPI the best measure for inflation Why or why not?
The "best" measure of inflation depends on the intended use of the data. The CPI is generally the best measure for adjusting payments to consumers when the intent is to allow consumers to purchase at today's prices, a market basket of goods and services equivalent to one that they could purchase in an earlier period.
Why is the GDP deflator not the best measure of inflation & the cost of living for the typical household?
Remember, though, that the GDP deflator is not a good measure of cost of living as it includes prices of many products not purchased by households—aircraft, fire engines, factory buildings, office complexes, and bulldozers, among others.
What is the three major difference between CPI and GDP deflator?
The GDP deflator is a measure of the overall change in prices of the economy. While the CPI reflects movements in the prices of consumer goods and services only, the GDP deflator covers also price changes related to government consumption, investment, and exports and imports of goods and services.
Why is the GDP deflator not an accurate measure of inflation as it impacts a household?
The GDP deflator is not an accurate measure of inflation as it impacts a household is because it includes the production of goods and services rather than consumption or purchase of goods and services.
What are the three reasons why the CPI is hard to measure accurately?
Problems with the CPISubstitution Bias. The first problem with the CPI is the substitution bias. ... Introduction of New Items. The second problem with the CPI is the introduction of new items. ... Quality Changes. The third problem with the CPI is that changes in the quality of goods and services are not well handled.
What is the best indicator of inflation over time?
The most widely watched and reported measure of inflation is the Consumer Price Index (CPI), compiled by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) in the Department of Labor. In June 2022, the headline CPI indicated that prices were 9.1 percent higher than a year earlier—a 40-year high.
What is the accurate inflation rate?
Since the Bureau of Labor Statistics began calculating CPI-E in 1982 through 2021, it averaged 2.96%—a touch higher than CPI-U, which inflated about 2.77% per year, on average, over that same stretch.
Which one is the best measure of inflation rate GDP deflator or CPI?
Because of its comprehensiveness, the GDP deflator is often considered the best measure of the nation's inflation rate. 1. The consumer price index, CPI, is a weighted average of the prices of goods and services purchased by a typical urban household.
Why is the GDP deflator not the best measure of inflation & the cost of living for the typical household?
Remember, though, that the GDP deflator is not a good measure of cost of living as it includes prices of many products not purchased by households—aircraft, fire engines, factory buildings, office complexes, and bulldozers, among others.
What are the three differences between the GDP deflator and the CPI?
The GDP deflator is a measure of the overall change in prices of the economy. While the CPI reflects movements in the prices of consumer goods and services only, the GDP deflator covers also price changes related to government consumption, investment, and exports and imports of goods and services.
What is the difference between CPI and GDP?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the gross domestic product (GDP) price index and implicit price deflator are measures of inflation in the U.S. economy. The CPI measures price changes in goods and services purchased out of pocket by urban consumers, whereas the GDP price index and implicit price deflator measure price changes in goods ...
What is CPI in economics?
The CPI. The CPI is a measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a constant-quality market basket of goods and services— that is, a sample of goods and services that consumers purchase for day-to-day living.
How does the CPI work?
The CPI uses an arithmetic mean (or Laspeyres) formula for all upper level index calculation, but employs a geometric mean for approximately 60 percent of all lower level indexes in terms of weight (a Laspeyres formula is used for the remaining 40 percent). The geometric mean formula allows the CPI to reflect changes in consumer spending patterns among goods and services within item–area combinations—changes that occur in response to changes in relative price. The formula assumes that the change in quantity is equal (in percentage terms), and inversely related, to the change in price. Thus, if the relative price of one brand of bananas in the Boston–Brockton–Nashua metropolitan area increases, then the quantity purchased of that brand is assumed to decrease percentagewise by the same amount. Similarly, if a pint of ice cream increases in (per-unit) price relative to a quart of ice cream, then the quantity purchased of a pint is assumed to decrease by a percentage reflective of the change in relative price. 2
How is CPI calculated?
Once price and expenditure data are collected, price indexes can be calculated with the use of price index formulas. The CPI uses a hybrid of geometric and arithmetic mean calculation, depending on whether “lower level” or “upper level” indexes are being constructed. Currently, the CPI measures price change for 211 item categories (e.g., breakfast cereal) in 38 geographic areas (e.g., Boston–Brockton–Nashua), forming 8,018 basic item–area index cells (211 × 38) that serve as the building blocks from which aggregate indexes are constructed. These building blocks are the so-called lower level indexes. Aggregate indexes constructed from them are the so-called upper level indexes. For example, the intermediate upper level index for cereals and cereal products is constructed from three item categories: (1) flour and prepared flour mixes; (2) breakfast cereal; and (3) rice, pasta, and cornmeal. The index for cereals and cereal products can be computed for the Boston–Brockton–Nashua metropolitan area, for a set of cities that make up the Northeast urban geographic area, or for all cities in which prices are collected. The last forms an index at the level of the U.S. city average. In total, the CPI consists of thousands of indexes that measure price change for narrow and broad categories of goods and services across multiple geographic areas. The result is a set of CPI indexes that measure the average change over time in the price paid specifically by urban consumers for a constant-quality market basket of goods and services.
How is the GDP price index calculated?
The GDP price index is calculated with a Fisher ideal index formula, which is able to pick up changes in the allocation of expenditures by consumers across the broad categories of consumer goods and services covered by GDP. The GDP price index is similar in concept to the chained CPI-U, or CPI for All Urban Consumers. 11
What is the CPI index?
In total, the CPI consists of thousands of indexes that measure price change for narrow and broad categories of goods and services across multiple geographic areas.
What are the inputs for CPI?
The CPI has two primary inputs: prices and expenditure weights. Data on prices are collected from the BLS Commodities and Services (C&S) Survey and Housing Survey. The C&S survey collects price data on approximately 80,000 goods and services per month in roughly 23,000 retail establishments in 87 urban areas around the United States. The Housing Survey collects approximately 6,000 rent quotes per month in the same 87 urban areas. Retail establishments for which price data are collected are selected primarily via a sampling process that uses data from the Telephone Point-of-Purchase Survey (TPOPS), administered quarterly by the U.S. Census Bureau on behalf of BLS. Once retail establishments are selected for price collection, field staff employed by BLS visit the establishments, select a unique item for pricing, and continue to collect the price data monthly or bimonthly, unless the item is no longer sold or a different retail establishment is selected in the next TPOPS rotation. Housing units are selected by means of a different survey process, one that relies on data from both the decennial census and the U.S. Census Bureau’s American Community Survey for sampling.
What does the CPI deflator mean?
The CPI indicates the impact of inflation on average consumers. The GDP deflator tracks price changes on all goods and services throughout the entire economy and not just those purchased by average consumers.
Why is CPI used to measure inflation?
The CPI is the most commonly used measure of inflation because it is believed to be an accurate reflection of how price changes impact average citizens. That is because it tracks price changes in a market basket of goods bought by average urban consumers.
Why is the dramatic increase in nominal GDP misleading?
The dramatic increase in nominal GDP is somewhat misleading because there were also dramatic price increases between 1980 and 2017. To get a more accurate picture of what happened to this country’s output calculate and compare real GDP (adjusting for inflation) for both years.
How does consumer price index work?
The consumer price index tracks price changes in a market basket of goods instead of all goods within an economy. To calculate the index, the quantities will never change but you calculate the value of that basket in both the base year’s prices and the current year’s prices.
What is it called when prices fall?
When prices fall, that is called deflation . Deflation can also wreak havoc on an economy as it causes a decrease in real wages and increases debt burdens.
What happens to the value of money when inflation is high?
When inflation rates are high, the value of saved money diminishes, decreasing the real value of people’s wealth. An important goal of macro-economy is stable prices.
What is the CPI for 2017?
That means the CPI for 2017 is 141.67 ($17/$12 x 100).
How does the CPI compare to the GDP deflator?
The third difference concerns how the two measures aggregate the many prices in the economy. The CPI or RPI assigns fixed weights to the prices of different goods, whereas the GDP deflator assigns changing weights. In other words, the CPI or RPI is computed using a fixed basket of goods, whereas the GDP deflator allows the basket ...
What is the difference between GDP and CPI?
The first difference is that the GDP deflator measures the prices of all goods and services produced, whereas the CPI or RPI measures the prices of only the goods and services bought by consumers.
How does the CPI work?
In other words, the CPI or RPI is computed using a fixed basket of goods, whereas the GDP deflator allows the basket of goods to change over time as the composition of GDP changes. To see how this works, consider an economy that produces and consumes only apples and oranges.
What is the difference between a price index and a Paasche index?
A price index with a fixed basket of goods is called a Laspeyres index and a price index with a changing basket is called Paasche index. Economists have studied the properties of these different types of price indexes to determine which is better. The answer is that neither is clearly superior.
What is the purpose of price index?
The purpose of any price index is to measure the cost of living — that is, how much it costs to maintain a given standard of living. When prices of different goods are changing by different amounts, a Laspeyres index tends to overstate the increase in the cost of living, whereas a Paasche index tends to understate it.
Does Toyota affect the GDP deflator?
affects the CPI or RPI, because the Toyota is bought by consumers in the U.K., but it does not affect the GDP deflator. The third difference concerns how the two measures aggregate the many prices in the economy.
How does the GDP price deflator work?
What this means is that the GDP price deflator captures any changes in an economy's consumption or investment patterns.
Why is CPI used in inflation?
The CPI, which measures the level of retail prices of goods and services at a specific point in time, is one of the most commonly used inflation measures because it reflects changes to a consumer's cost of living.
Why is the PCE index used instead of the CPI?
6 It is used instead of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) because the PCE Index is composed of a broad range of expenditures that exceeds the limited basket of goods used in CPI.
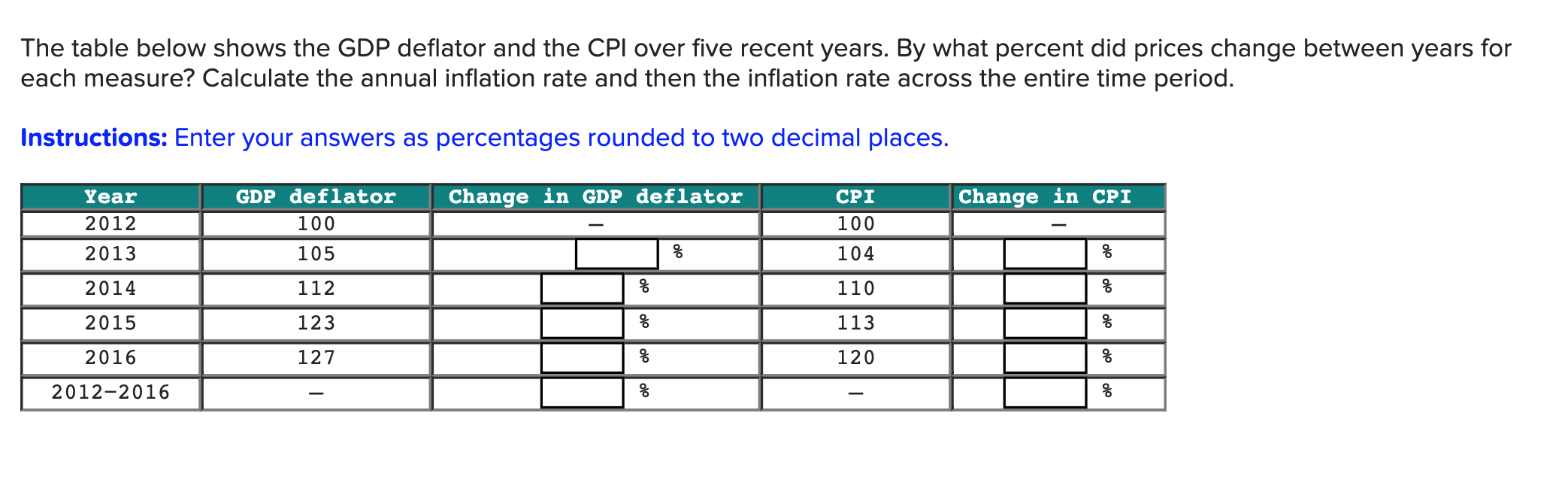
What does a CPI of 100 mean?
It is based upon the index average for the period from 1982 through 1984 (inclusive) which was set to 100. So a CPI reading of 100 means that inflation is back to the level that it was in 1984 while readings of 175 and 225 would indicate a rise in the inflation level of 75% and 125% respectively. The quoted inflation rate is actually ...
What does it mean when the inflation rate is quoted?
The quoted inflation rate is actually the change in the index from the prior period, whether it is monthly, quarterly or yearly. Changes in the CPI reflect price changes in the economy. When there is an upward change in the CPI, this means there has been an increase in the average change in prices over time.
What is the most widely watched and used measure of the U.S. inflation rate?
While the CPI is the most widely watched and used measure of the U.S. inflation rate, many economists differ on how they believe inflation should be measured.
What is the CPI used for?
As such, the CPI is an economic indicator that is most frequently used for identifying periods of inflation (or deflation) in the U.S. But, some economists question whether CPI is the best measure of inflation. For several years, there has been some controversy about whether ...