
What is a craniopharyngioma?
Craniopharyngioma is a type of benign (noncancerous) brain tumor that arises near the pituitary, a pea-sized gland at the base of the brain that secretes a variety of hormones.
Can craniopharyngioma affect the pituitary gland?
As a craniopharyngioma slowly grows, it can affect the function of the pituitary gland and other nearby structures in the brain. Craniopharyngioma can occur at any age, but it occurs most often in children and older adults. Symptoms include gradual changes in vision, fatigue, excessive urination and headaches.
Can craniopharyngioma recur after surgery?
Craniopharyngiomas are generally benign, but are known to recur after resection. Recent research has demonstrated a malignant (but rare) tendency of craniopharyngiomas. These malignant craniopharyngiomas are very rare, but are associated with poor prognosis.
What is the life expectancy of someone with craniopharyngioma?
At ten years after diagnosis, overall survival rates for adult patients with craniopharyngioma are 85-90%. 2 Outcomes are best if the tumor is removed completely or treated effectively with radiation. Depending on how severe the symptoms are at the time of diagnosis, patients can make a complete recovery.
Are craniopharyngiomas benign?
Craniopharyngioma is a rare type of noncancerous (benign) brain tumor. Craniopharyngioma begins near the brain's pituitary gland, which secretes hormones that control many body functions. As a craniopharyngioma slowly grows, it can affect the function of the pituitary gland and other nearby structures in the brain.
How serious is a craniopharyngioma?
A craniopharyngioma is a serious medical condition that may require life-long medical treatment. About half of all surgically removed tumors come back over time. Craniopharyngiomas cause several medical conditions that remain even after the tumor has been removed.
Is craniopharyngiomas curable?
A craniopharyngioma is a rare type of benign (not cancerous) brain tumor. These tumors usually form close to the pituitary gland and do not spread to other areas. Doctors usually can remove these tumors with surgery or treat them with high doses of radiation. Most people treated for a craniopharyngioma are cured.
What is the difference between pituitary adenoma and craniopharyngioma?
However, pituitary adenomas and craniopharyngiomas differ from each other, as follows: 1) pituitary adenomas are the third most common type of intracranial tumor and represent a significant proportion of brain tumors affecting humans and approximately 80% of sellar lesions, whereas craniopharyngiomas represent only 1 ...
Can craniopharyngioma become malignant?
Many experts consider craniopharyngiomas to be a chronic disease, as they tend to recur even when they have been completely removed (resected) surgically. The tumor itself is usually not dangerous, as it is benign and only very rarely becomes malignant.
How long can you live with craniopharyngioma?
The current survival rate for patients with craniopharyngioma is favorable, with up to 90% of adults and children surviving at 10 years. However, long-term complications such as vision loss and abnormal hormone functioning might decrease quality of life.
What is the survival rate of craniopharyngioma?
The 5-year survival rate for children under the age of 15 with craniopharyngioma is almost 96%. It is important to remember that statistics on the survival rates for children with craniopharyngioma are an estimate. The estimate comes from annual data based on the number of children with this tumor in the United States.
Can craniopharyngioma cause death?
Craniopharyngioma-related death represents the most common cause of early deaths in both pediatric and adult patients.
Do craniopharyngiomas grow back?
The tumor can be fully removed with surgery in 9 out of 10 children. In some cases, there is a chance that the tumor will grow back, especially if all of it is not removed. Most cases of the tumor growing back happen within 2 years of surgery. A child may have other health effects after treatment ends.
Are craniopharyngioma tumor cancerous?
Craniopharyngiomas are rare brain tumors that usually form near the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. They are benign (not cancer) and do not spread to other parts of the brain or to other parts of the body.
How can you tell if a pituitary tumor is benign or malignant?
MRI or CT scans can detect tumors in the pituitary gland. And blood and urine tests can determine hormone levels. Even under a microscope, it's difficult to recognize the difference between a cancerous and a noncancerous pituitary tumor.
What are the risk factors craniopharyngioma?
At present, there are no known causes or proven risk factors for craniopharyngioma. Blood and urine tests can indicate a hormone imbalance that may be caused by a problem with the pituitary gland.
What is the survival rate of craniopharyngioma?
The 5-year survival rate for children under the age of 15 with craniopharyngioma is almost 96%. It is important to remember that statistics on the survival rates for children with craniopharyngioma are an estimate. The estimate comes from annual data based on the number of children with this tumor in the United States.
How long does it take to recover from craniopharyngioma surgery?
Recovering from craniopharyngioma surgery can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months. Some patients need to take hormone replacements after undergoing surgery. This largely depends on whether the tumors have damaged the pituitary gland. In some cases, surgery may not remove all of the tumors.
How fast does craniopharyngioma grow?
They are slow-growing tumours that can take two to three years or longer to manifest themselves before a diagnosis is made. They can cause serious problems by interfering with important structures near them.
How common is craniopharyngioma in adults?
Craniopharyngiomas are slow growing benign tumors of the sellar and parasellar region with an overall incidence rate of approximately 1.3 per million. During adulthood there is a peak incidence between 40 and 44 years. There are two histopathological types, the adamantinomatous and the papillary type.
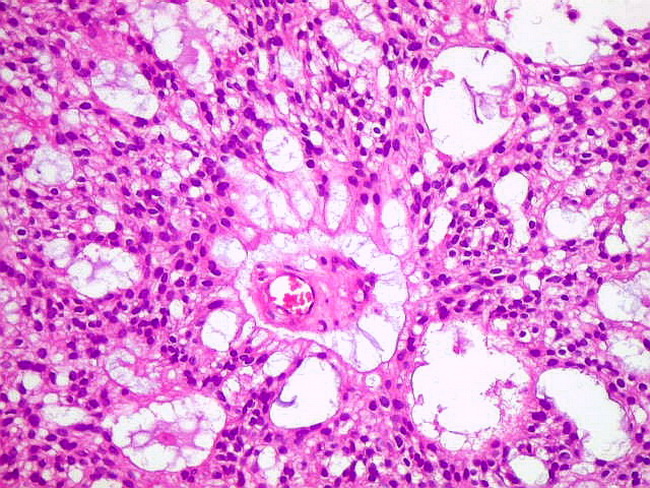
What is a low magnification micrograph of an adamantinomatous craniopharyn?
Craniopharyn gioma. Very low magnification micrograph of an adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma. HPS stain. A craniopharyngioma is a rare type of brain tumor derived from pituitary gland embryonic tissue that occurs most commonly in children, but also affects adults.
What causes a child to have a delayed puberty?
Often occurs to some degree because craniopharyngiomas develop in the area of the pituitary stalk, which can affect the function of the pituitary gland and many other hormones.
Why does prolactin increase in large pituitary tumors?
This elevation occurs as a result of the compression of the pituitary stalk, which interferes with the brain's control of prolactin production.
Where do cranial odontogenic tumors come from?
They arise from the cells along the pituitary stalk, specifically from nests of odontogenic (tooth-forming) epithelium within the suprasellar/diencephalic region, so contain deposits of calcium that are evident on an X-ray .
What are the symptoms of a keratin pearl?
Of a long list of possible symptoms, the most common presentations include headaches, growth failure, and bitemporal hemianopsia . CT scan showing a craniopharyngioma.
What is the procedure for a craniopharyngioma?
Endoscopic surgery through the nose often performed by a joint team of neurosurgeons and ENT, is increasingly being considered as an alternative to transcranial surgery done by making an opening in the skull. Because of the location of the craniopharyngioma near the brain and skullbase, a surgical navigation system might be used to verify the position of surgical tools during the operation.
When does craniopharyngioma occur?
It may present at any age, even in the prenatal and neonatal periods, but peak incidence rates are childhood-onset at 5–14 years and adult-onset at 50–74 years.
How does craniopharyngioma affect the pituitary gland?
Because craniopharyngioma arises in the brain near the pituitary, tumor growth can affect pituitary function. Depending on which hormones are affected, the following symptoms may occur: Short stature or slow growth, in children. Delayed puberty, in children. Excessive thirst and/or urination.
What is the name of the tumor that is located near the pituitary gland?
Craniopharyngioma is a type of benign (noncancerous) brain tumor that arises near the pituitary, a pea-sized gland at the base of the brain that secretes a variety of hormones. Craniopharyngiomas can be divided into two types: adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma which mainly occurs in children, and papillary craniopharyngioma which mainly occurs in ...
What happens if a complete resection is not complete?
If a complete resection (or, gross total resection) cannot be accomplished, then a partial resection (subtotal resection) is done, leaving a small amount of craniopharyngioma behind.
How to treat craniopharyngioma?
The treatment of craniopharyngioma is complex because many factors affect whether the tumor can be removed or prevented from growing. In general, the initial approach is to perform surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible. Depending on the size and location of the tumor, patients with craniopharyngioma may be a candidate for minimally invasive skull base surgery. This approach involves removing the tumor endoscopically, using special tools and scopes that pass through small openings–in this case, the nasal passages. Because many craniopharyngioma can be removed through the patient’s nose, this type of procedure does not require drilling into the skull, or making facial or scalp incisions. For very large tumors, larger operations (i.e. craniotomy) may be necessary.
What causes a person to lose vision?
Unusual sleepiness. Weight gain. In addition, because the optic nerves (which connect the eyes to the brain) are located above the pituitary gland, craniopharyngioma may cause the following: Progressive loss of vision. Sometimes, very large craniopharyngioma can block normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain.
What type of radiation therapy is used for a tumor?
The type of radiation used depends upon the location of the residual tumor: If there is a larger amount of tumor remaining after surgery, or if vital structures are close by, then 3D conformal radiation therapy or intensity modulated radiation therapy may be used.
How long does it take to recover from craniopharyngioma?
At ten years after diagnosis, overall survival rates for adult patients with craniopharyngioma are 85-90%. 2. Outcomes are best if the tumor is removed completely or treated effectively with radiation. Depending on how severe the symptoms are at the time of diagnosis, patients can make a complete recovery.
Abstract
Craniopharyngiomas are histologically and cytologically benign epithelial tumors of the central nervous system that may be locally aggressive and tend to recur after excision. Malignant change in craniopharyngiomas is extremely rare; we found only 4 such reports in the literature.
REPORT OF A CASE
In 1982, at 27 years of age, the patient presented with bilateral hemianopsia and underwent transphenoidal resection of a typical craniopharyngioma. Three years later the craniopharyngioma recurred. Open craniotomy was performed with subtotal removal of the tumor and cyst drainage.
PATHOLOGIC FINDINGS
Tissue sections submitted from the previous resections in 1994 and 1996 and from the most recent resection in 1998 for histologic examination were reviewed. The 1994 and 1996 resections showed histopathologic features characteristic of a classic adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma ( Figure 2 ).
CLINICAL FOLLOW-UP
An extensive clinical workup showed no evidence of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Palliative systemic chemotherapy (paclitaxel and carboplatin) was administered.
COMMENT
Patients with craniopharyngiomas generally present with 3 major clinical syndromes related to ( a) increased intracranial pressure, ( b) endocrine dysfunction caused by compression of the hypothalamic-hypophyseal axis, or ( c) visual problems resulting from direct compression of the optic pathways by the tumor, secondary intracranial hypertension, or both.
Overview
Diagnosis
Symptoms and signs
Mechanisms
Prevention
Treatment
A physician can conduct a few scans and tests to diagnose a person with craniopharyngioma. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is valuable because it allows the neuroradiologist to view the tumor from different angles.
In some cases, a powerful 3T (Tesla) MRI scanner can help define the location …
Prognosis
Craniopharyngiomas are almost always benign. However, as with many brain tumors, their treatment can be difficult, and significant morbidities are associated with both the tumor and treatment.
• Headache (obstructive hydrocephalus)
• Hypersomnia
Recent research
Craniopharyngioma is a rare, usually suprasellar neoplasm, which may be cystic, that develops from nests of epithelium derived from Rathke's pouch. Rathke's pouch is an embryonic precursor of the anterior pituitary.
Craniopharyngiomas are typically very slow-growing tumors. They arise from the cells along the pituitary stalk, specifically from nests of odontogenic (tooth-forming) epithelium within the supras…