What is critical path and how does it help me?
The critical path method is one of the most frequently used and effective techniques in project planning. When you’re managing dozens of tasks, dependencies, and people, the critical path method helps you keep your project on track and on budget, providing visibility into your project.
What is critical path method and why it's important?
Key Takeaways
- Critical path analysis is a project planning method that focuses on identifying tasks that are dependant on other tasks for their timely completion.
- Understanding the dependencies between tasks is key to setting a realistic deadline for a complex project.
- Critical path analysis is used in most industries that undertake highly complex projects.
How to use the critical path method for complete beginners?
The Ultimate Guide to the Critical Path Method
- Choose a Gantt Chart Template. Go to Smartsheet.com and login to your account (or start a free 30 day trial ). ...
- List Your Task Information. A pre-made, formatted template will open with sample content filled in for reference. ...
- Provide Start and End Dates. ...
- Add % Complete and Assigned To Information. ...
- Establish Predecessors. ...
- Identify the Critical Path. ...
How to identify critical path?
The elements required for identifying the Critical Path are the following:
- The WBS (Work Breakdown Structure), that is, the full list of activities included in your project
- The duration of each of these activities
- The dependencies involved in your project activities
- Milestones and deliverable dates (logical end point)
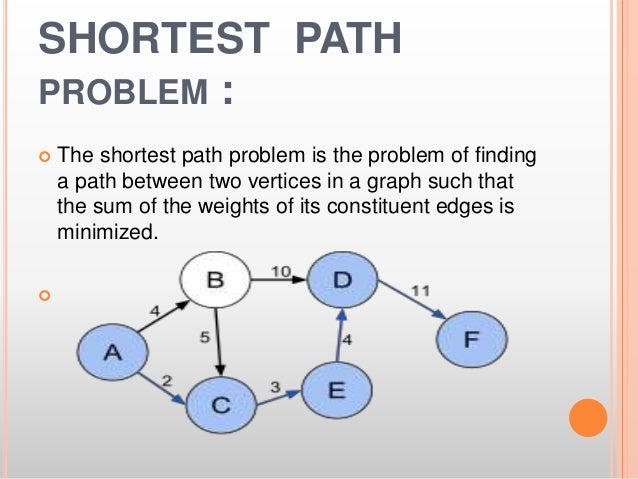
Is the critical path the longest path?
The critical path (or paths) is the longest path (in time) from Start to Finish; it indicates the minimum time necessary to complete the entire project.
Why is the critical path the longest and not the shortest?
Critical Path is the longest path through the project because that's the only path with no (positive) float / wiggle room. Other (non-critical) paths on the schedule network diagram have (positive) float / wiggle room.
Is critical path the shortest time to complete the project?
Yes, the critical path is the longest overall duration for the sequenced activities. It is not the shortest project duration and it is the shortest time possible to complete the project.
How do you determine the critical path?
5. Calculate the critical pathStep 1: Write down the start and end time next to each activity.Step 2: Look at the end time of the last activity in the sequence to determine the duration of the entire sequence.Step 3: The sequence of activities with the longest duration is the critical path.More items...•
Which is the longest path?
A longest path between two given vertices s and t in a weighted graph G is the same thing as a shortest path in a graph −G derived from G by changing every weight to its negation. Therefore, if shortest paths can be found in −G, then longest paths can also be found in G.
What is the longest distance path through the project which determines the shortest duration?
What is Critical Path? Your Critical Path is the longest distance between the start and the finish of your project, including all the tasks and their duration, which gives you a clear picture of the project's actual schedule.
What is the duration of the critical path?
The network path with longest total duration is the critical path! Critical path is the shortest duration required to complete the project successfully. In our example this is the second path: A -> B -> C -> D -> G -> H, which comes to 49 minutes.
What is project critical path?
The critical path is a chain of linked tasks that directly affects the project finish date. If any task on the critical path is late, the whole project is late. The critical path is a series of tasks (or sometimes only a single task) that controls the calculated start or finish date of the project.
Why is critical path Important?
Using the critical path method is important when managing a project because it identifies all the tasks needed to complete the project, then determines the tasks that must be done on time, those that can be delayed if needed and how much float or slack you have.
What is critical path example?
A simplified example of critical path project management is this project plan for building a house. All the tasks in the project are listed in the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), then the dependencies between the tasks are determined, and the duration of each task is calculated.
What is critical path and float?
The longest path through the network is the critical path. The difference between the early end date and the required completion date of the project is the total project float, and the start date of each activity is the early start date.
What is the critical path in a network diagram?
The critical path is the longest path of the network diagram. The activities in the critical path have an effect on the deadline of the project. If an activity of this path is delayed, the project will be delayed.
What is the longest path of tasks through a project?
The Longest Path is the path through a project network from start to finish where the Total Duration is longer than any other path. It makes sense to focus on a project's Longest Path as it is definitely the path where deviations from plan will affect the project's finish date.
Is there always a critical path?
The critical path in project management may contain all the important activities associated with a project, or it may not. In fact, the activities on the critical path are not always the most important parts of the project.
Can the critical path be changed if yes then under what circumstances and if no then the valid reasons for that?
The critical path of a project will not remain static throughout its life, it can change during the course of project completion. Unforeseen circumstances sometimes may cause estimated duration of one or more activities to change.
What happens when the critical path changes?
The critical path can change as critical tasks are completed, or as tasks in another series of tasks are delayed. There is always one overall critical path for any project schedule. The new critical path then becomes the series of tasks you track more closely to ensure the finish date you want.
Critical Path
Critical path project management (CPM) is a technique used to complete projects on time by focusing on key tasks. One path through all the inter-connected tasks is the fastest avenue to take when completing any project.
Longest Path
The Longest Path is the longest continuous path of activities through a project, which controls project early completion. It is possible for otherwise defined critical path activities to not be on the longest path and longest path activities to not show calculated critical float.
Is there overlap between Longest Path and Critical Path?
Let say it this way – the Longest Path is a Critical Path, but not all Critical Paths are the Longest.
Which one should I use?
I would strongly suggest you get to know your project’s Longest Path and monitor it. What the client wants to see might be something else, but the timely completion of Longest Path activities leads to your project finishing on time.
What is critical path activity?
Slack: How long a task can be delayed without interrupting other tasks or the whole project. Critical Path Activity: An activity where no slack is available. Lead Time: The time it will take realistically to complete a task without delaying or interfering with the next task.
Why is critical path important?
Critical Path is called “critical” because it’s the “red alert” of paths.
What is a PERT chart?
A PERT chart is an activity-on-arrow visual outline of a project’s schedule. It shows the sequence of tasks on a path and determines the time it will take to complete each, and which of those may be completed simultaneously.
What are the three main types of anticipated dependencies in a project?
EDITOR’S NOTE: There are usually three main types of anticipated dependencies in a project. Mandatory dependencies – dependencies due to the physical limitations of the task. Often tasks in research and development projects are labeled as compulsory.
What is late start and late finish?
Late start and late finish are the adverse. They’re the latest beginning, and ending dates a task can be assigned without derailing the other tasks on the path or the whole project altogether. Begin with the project plan’s completion date, then the critical path, then paths of descending order of completion dates.
Which chart is best for smaller projects?
Gantt charts are best for smaller projects, linking dependent tasks instead of establishing a network diagram showing interconnecting independent tasks as a PERT chart does for larger, more complex projects.
What is early start in a project?
Beginning a task on its early start is conditional upon the completion of tasks on the same path. If the prior task can finish on it’s early finish time and it completes the last task on the path, the team can begin with an early start on the next task, freeing up more time to use on other, more unpredictable tasks.
What is critical path?
In project management, a critical path is the sequence of project network activities which add up to the longest overall duration, regardless if that longest duration has float or not. This determines the shortest time possible to complete the project. There can be 'total float' (unused time) within the critical path.
How long is the drag of a critical path?
If a critical path activity has nothing in parallel, its drag is equal to its duration. Thus A and E have drags of 10 days and 20 days respectively. If a critical path activity has another activity in parallel, its drag is equal to whichever is less: its duration or the total float of the parallel activity with the least total float.
What is the CPM method?
The critical path method (CPM) is a project modeling technique developed in the late 1950s by Morgan R. Walker of DuPont and James E. Kelley Jr. of Remington Rand. Kelley and Walker related their memories of the development of CPM in 1989. Kelley attributed the term "critical path" to the developers of the PERT which was developed at about the same time by Booz Allen Hamilton and the U.S. Navy. The precursors of what came to be known as Critical Path were developed and put into practice by DuPont between 1940 and 1943 and contributed to the success of the Manhattan Project.
What is total float in critical path?
There can be 'total float' (unused time) within the critical path. For example, if a project is testing a solar panel and task 'B' requires 'sunrise', there could be a scheduling constraint on the testing activity so that it would not start until the scheduled time for sunrise.
What is the crash duration?
'Crash duration' is a term referring to the shortest possible time for which an activity can be scheduled. It can be achieved by shifting more resources towards the completion of that activity, resulting in decreased time spent and often a reduced quality of work, as the premium is set on speed. Crash duration is typically modeled as a linear relationship between cost and activity duration; however, in many cases a convex function or a step function is more applicable.
What is a parallel path in a project?
A project can have several, parallel, near critical paths; and some or all of the tasks could have 'free float' and/or 'total float'. An additional parallel path through the network with the total durations shorter than the critical path is called a sub-critical or non-critical path.
When was CPM used?
CPM was used the first time in 1966 for the major skyscraper development of constructing the former World Trade Center Twin Towers in New York City. Although the original CPM program and approach is no longer used, the term is generally applied to any approach used to analyze a project network logic diagram.