
What is the formula for equilibrium?
What is equilibrium formula? Keq is the equilibrium constant at given temperature. Keq = [C] × [D] / [A] × [B] This equation is called equation of law of chemical equilibrium. At equilibrium, the concentration of reactants is expressed as moles/lit so Keq = Kc and if it expressed as partial pressure then Keq = Kp.
How to find the equilibrium?
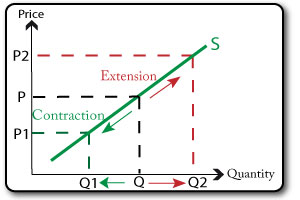
The equilibrium in a market occurs where the quantity supplied in that market is equal to the quantity demanded in that market. Therefore, we can find the equilibrium by setting supply and demand equal and then solving for P. 03. of 04.
How do I calculate equilibrium quantity?
How Do You Calculate Equilibrium In Microeconomics? You can find the supply line by using the supply function, Qs = x + yP, or by using a graph or algebra. The quantity function should be used for quantity. You should set the prices for the two quantities equally. The equilibrium price can be solved by solving the equation.
How to calculate equilibrium price?
Calculating the equilibrium price becomes simple when you know the supply function, demand function, and equilibrium price formula. The linear supply function is-Qs = x + yP, where Qs= supplied quantity, x= quantity, P= price. The demand function is-Qd = x + yP, where Qd= demanded quantity, x= quantity, P= price. Finally, the equilibrium price formula is-Qs = Qd
IS curve represent the equilibrium of?
The IS Curve represents various combinations of interest and income along which the goods market is in equilibrium.
IS-LM curve equilibrium?
The Keynesian IS-LM model is a model of disequilibrium, not equilibrium. The IS curve does not represent the condition that demand equals supply for goods. Instead the IS curve represents the condition that demand equals product. There is excess supply, with demand and product less than supply.
What is meant by IS curve?
Describing the real sector of the economy, the IS curve represents the condition that aggregate demand equals national product. Whereas in the Keynesian cross model aggregate demand depended only on national income, now it depends as well on the interest rate. 1.
IS curve an economic discussion?
The IS curve is negatively sloped because a higher level of the interest rate reduces investment spending, thereby reducing aggregate demand and thus the equilibrium level of income.
WHAT IS IS curve and LM curve?
The IS stands for Investment and Savings. The LM stands for Liquidity and Money. On the vertical axis of the graph, 'r' represents the interest rate on government bonds. The IS-LM model attempts to explain a way to keep the economy in balance through an equilibrium of money supply versus interest rates.
Is the curve a shift?
Movements along the IS curve: As interest rates rise, output falls. Shifts in the IS curve: As government spending increases, output increases for any given interest rate. IS Curve: At lower interest rates, equilibrium output in the goods market is higher. An increase in government spending shifts out the IS curve.
What are the properties of IS curve?
The IS curve slopes downwards to the right. Or it has a negative slope. Its slope depends on the saving function and investment function. The IS curve will be relatively steep (flat) if investment is less (more) sensitive to interest rate changes.
What are the types of curves?
Answer: The different types of curves are Simple curve, Closed curve, Simple closed curve, Algebraic and Transcendental Curve.
IS curve a slope?
Downward-Sloping IS Curve The IS curve is downward sloping. When the interest rate falls, investment demand increases, and this increase causes a multiplier effect on consumption, so national income and product rises.
IS-LM equilibrium in economics?
The LM curve shows the combinations of interest rates and levels of real income for which the money market is in equilibrium. It shows where money demand equals money supply. For the LM curve, the independent variable is income and the dependent variable is the interest rate.
IS-LM curve theory?
The basis of the IS-LM model is an analysis of the money market and an analysis of the goods market, which together determine the equilibrium levels of interest rates and output in the economy, given prices. The model finds combinations of interest rates and output (GDP) such that the money market is in equilibrium.
Which curve shows the goods market equilibrium?
Answer: The IS-LM curve model shows the goods market equilibrium. It also shows the interaction between the goods markets and money markets.
What is the equation of IS curve?
The Derivation of IS Curve: Algebraic Method: ADVERTISEMENTS: Consumption demand is function of disposable income. Disposable income is level of income minus taxes (Yd = Y – T) where Yd stands for disposable income and T for taxes.
WHAT IS IS curve and how it is derived?
The IS curve is derived from goods market equilibrium. The IS curve shows the combinations of levels of income and interest at which goods market is in equilibrium, that is, at which aggregate demand equals income.
What causes the IS curve to shift?
Any change (decrease in government consumption, increase in taxes, decrease in consumer confidence - proxied by c0) that, for a given interest rate, decreases the demand for goods creates a shift of the IS curve to the left.
IS curve a note?
The IS Curve is derived from the negative relation of Autonomous Planned Spending (mainly Autonomous Consumption and Investment) with the level of interest rates, and the positive relationship between the level of Autonomous Spending with the level of real income.
What is the IS curve?
Thus, the IS curve is the locus of those combinations of rate of interest and the level of national income at which goods market is in equilibrium. How the IS curve is derived is illustrated in Fig. 20.1. In panel (a) of Fig. 20.1 the relationship between rate of interest and planned investment is depicted by the investment demand curve II.
What determines the position of the IS curve?
It is important to understand what determines the position of the IS curve and what causes shifts in it. It is the level of autonomous expenditure which determines the position of the IS curve and changes in the autonomous expenditure cause a shift in it. By autonomous expenditure we mean the expenditure, be it investment expenditure, the Government spending or consumption expenditure, which does not depend on the level of income and the rate of interest.
What accounts for the downward-sloping nature of the IS curve?
What accounts for the downward-sloping nature of the IS curve. As seen above, the decline in the rate of interest brings about an increase in the planned investment expenditure. The increase in investment spending causes the aggregate demand curve to shift upward and therefore leads to the increase in the equilibrium level of national income.
What is the steepness of the IS curve?
The steepness of the IS curve also depends on the magnitude of the multiplier. The value of multiplier depends on the marginal propensity to consume (mpc). It may be noted that the higher the marginal propensity to consume, the aggregate demand curve (C + I) will be more steep and the magnitude of multiplier will be large.
When is the goods market in equilibrium?
The goods market is in equilibrium when aggregate demand is equal to income. The aggregate demand is determined by consumption demand and investment demand. ADVERTISEMENTS: In the Keynesian model of goods market equilibrium we also now introduce the rate of interest as an important determinant of investment. With this introduction of interest as ...
What is the elasticity of investment demand?
The elasticity of investment demand signifies the degree of responsiveness of investment spending to the changes in the rate of interest. Suppose the investment demand is highly elastic or responsive to the changes in the rate of interest, then a given fall in the rate of interest will cause a large increase in investment demand which in turn will produce a large upward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
What is equilibrium curve?
The equilibrium curve of a given structure represents, to some extent, its behavior. This curve is constructed in an (n + 1) dimensional space if the system is of finite dimensions; otherwise, for continuum systems (such as beams, plates, shells, and deformable bodies in general), the corresponding space is infinite. Hence, all the plane curves that plot the loading parameter versus the displacement of some point of the body are only projections of the multidimensional deformation curve onto some plane spanned by the load parameter q and the displacement component ξ that we select to draw the plot. Thus, such planar curves of deformation contain only partial, incomplete information about the behavior of the system. One should be aware of these limitations, because, otherwise it is possible to come to serious miscalculations. For example, if a planar equilibrium curve of a multi-degree of freedom system intersects itself, this does not imply that at this point a bifurcation occurs. Only in the case of a system of one degree of freedom is the deformation curve complete in the plane ( q, ξ), and only in this case does it contain all the information about the response of the system.
What is the intersection point of an equilibrium curve?
11 ). The intersection point is called the pinch point and may occur at the bottom ( 11a ), at the top ( 11b ), or at a tangent point ( 11c ). The solvent rate leading to this intersection is the minimum solvent flow required to absorb the specified amount of solute.
What is the peculiarity of a closed loop?
The peculiarity of a closed loop (isola) is that the equilibrium states they represent cannot be reached by a process of loading (quasi-static) starting from any equilibrium state of the structure that does not belong to this loop (for example, the undeformed state). Such special sets of solutions were discovered many years ago in the course of an investigation into the postbuckling behavior of bars (see the classical dissertation of M. Born [1906] ).
What temperature is the catalyst bed in Problem 11.4?
In Problem 11.4, you prepared a heatup path for the same gas (fed into the catalyst bed at 675 K).
What does it mean when the solvent rate is higher than the minimum?
The higher the solvent rate specified, the greater is the distance between the operating line and the equilibrium curve, and the smaller is the number of stages required.
What is the heavy curve in Figure 3.11?
In Figure 3.11, the heavy curve 4 describes the dependence of the upper limit load, in dimensionless terms given by η +, the definition of which is given by
Can a transition take place that does not correspond to bifurcation from one stable equilibrium state to the next stable?
Because of this difference, a transition cannot take place that does not correspond to bifurcation from one stable equilibrium state to the next stable state without overcoming an energy barrier determined by the difference between the energies of the stable state and the in-between unstable state.
What does a shift in the position and shape of the IS and LM curves represent?
Shifts in the position and shape of the IS and LM curves, representing changing preferences for liquidity, investment, and consumption, alter the equilibrium levels of income and interest rates.
Why does the LM curve slope upward?
The LM curve slopes upward because higher levels of income (GDP) induce increased demand to hold money balances for transactions, which requires a higher interest rate to keep money supply and liquidity demand in equilibrium. The intersection of the IS and LM curves shows the equilibrium point of interest rates and output when money markets and ...
What is the intersection of IS and LM curves?
The intersection of the IS and LM curves shows the equilibrium point of interest rates and output when money markets and the real economy are in balance. Multiple scenarios or points in time may be represented by adding additional IS and LM curves.
What is the IS-LM graph?
The IS-LM graph examines the relationship between output, or gross domestic product (GDP), and interest rates. The entire economy is boiled down to just two markets, output and money; and their respective supply and demand characteristics push the economy towards an equilibrium point.
What are the three critical exogenous variables in the IS-LM model?
The three critical exogenous, i.e. external, variables in the IS-LM model are liquidity, investment, and consumption. According to the theory, liquidity is determined by the size and velocity of the money supply. The levels of investment and consumption are determined by the marginal decisions of individual actors.
What Is the IS-LM Model?
The IS-LM model, which stands for "investment-savings" (IS) and "liquidity preference-money supply" (LM) is a Keynesian macroeconomic model that shows how the market for economic goods (IS) interacts with the loanable funds market (LM) or money market. It is represented as a graph in which the IS and LM curves intersect to show the short-run equilibrium between interest rates and output.
What is equilibrium in the goods market?
Equilibrium in the goods market occurs when expenditure equals production. It is graphically represented by the Keynesian cross which is the graph of expenditure and output level. E1 is the initial equilibrium of the goods market. It is the point of intersection of the aggregate expenditure curve AD1 and the 45-degree line ...
Why does the IS curve slope downward?
The IS curve slopes downward. It is because when the interest rate is high, output is low because investment is low and vice versa.
When does aggregate demand curve shift?
Since the investment spending is a function of interest rate, the aggregate demand curve shifts when there is a change in interest rate which in turn results in a change in total output corresponding to the new equilibrium E2.
What is consumption C?
Consumption (C) depends on disposable income which equals autonomous spending (c 0 ), spending that occurs even at zero income, plus the product of marginal propensity to consume (c) and disposable income. Disposable income equals total income (Y) minus taxes (t).
What is equilibrium in economics?
What Is Equilibrium? Equilibrium is the state in which market supply and demand balance each other, and as a result prices become stable.
What is the opposite of equilibrium?
Disequilibrium is the opposite of equilibrium and it is characterized by changes in conditions that affect market equilibrium.
Why is the coffee market in disequilibrium?
At times disequilibrium can spillover from one market to another—for instance, if there aren’t enough transport companies or resources available to ship coffee internationally then the coffee supply for certain regions could be reduced, effecting the equilibrium of coffee markets. Economists view many labor markets as being in disequilibrium due to how legislation and public policy protect people and their jobs, or the amount they are compensated for their labor.
What are the characteristics of a market in equilibrium?
A market in equilibrium demonstrates three characteristics: the behavior of agents is consistent, there are no incentives for agents to change behavior, and a dynamic process governs equilibrium outcome.
When does a market reach equilibrium?
A market is said to have reached equilibrium price when the supply of goods matches demand. A market in equilibrium demonstrates three characteristics: the behavior of agents is consistent, there are no incentives for agents to change behavior, and a dynamic process governs equilibrium outcome.
Is the food market in equilibrium?
Markets can be in equilibrium, but it may not mean that all is well. For example, the food markets in Ireland were at equilibrium during the great potato famine in the mid-1800s. Higher profits from selling to the British made it so the Irish and British market was at an equilibrium price that was higher than what consumers could pay, and consequently many people starved.
Is equilibrium a good thing?
As noted by Paul Samuelson in his 1983 work Foundations of Economic Analysis, the term equilibrium with respect to a market is not necessarily a good thing from a normative perspective and making that value judgment could be a misstep. 1 . Markets can be in equilibrium, but it may not mean that all is well.
What is the IS curve?
The IS curve represents all combinations of income (Y) and the real interest rate (r) such that the market for goods and services is in equilibrium. That is, every point on the IS curve is an income/real interest rate pair (Y,r) such that the demand for goods is equal to the supply of goods (where it is implicitly assumed that whatever is demanded is supplied) or, equivalently, desired national saving is equal to desired investment. The graphical derivation of the IS curve is given below.
What does a plus above the exogenous variables mean?
Pluses (+) above the exogenous variables indicate that increases in the variables shift the IS curve up and to the right (increases demand).

What Is The IS-LM Model?
Understanding The IS-LM Model
- British economist John Hicks first introduced the IS-LM model in 1936,1 just a few months after fellow British economist John Maynard Keynes published "The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money."2 Hicks's model served as a formalized graphical representation of Keynes's theories, though it is used mainly as a heuristicdevice today. The three critical exogen…
Characteristics of The IS-LM Graph
- The IS-LM graph consists of two curves, IS and LM. Gross domestic product (GDP), or (Y), is placed on the horizontal axis, increasing to the right. The interest rate, or (i or R), makes up the vertical axis. The IS curve depicts the set of all levels of interest ratesand output (GDP) at which total investment (I) equals total saving (S). At lower i...
Limitations of The IS-LM Model
- Many economists, including many Keynesians, object to the IS-LM model for its simplistic and unrealistic assumptions about the macroeconomy. In fact, Hicks later admitted that the model's flaws were fatal, and it was probably best used as "a classroom gadget, to be superseded, later on, by something better."3 Subsequent revisions have taken place for so-called "new" or "opti…