Hypotonic fluid can be lost in osmotic diarrhea but not in secretory diarrhea. In osmotic diarrhea, the fluid lost is hypotonic to plasma because it contains organic osmoles (e.g., lactulose), and hence has a lower concentration of Na+ ions.
What is the difference between isotonic and hypotonic solutions?
5% dextrose in water (D5W)**also used as a hypotonic solution after it is administered because the body absorbs the dextrose BUT it is considered isotonic) Isotonic solutions are used: to increase the EXTRACELLULAR fluid volume due to blood loss, surgery, dehydration, fluid loss that has been loss extracellularly.
What is the most common cause of isotonic dehydration?
The most common cause of isotonic dehydration is diarrhea. Hypotonic dehydration occurs when there is too little salt in the body. Some people are more prone to losing electrolytes like sodium when they sweat, putting them at a higher risk of hypotonic dehydration.
What is the difference between hypotonic and isonatremic dehydration?
If water loss is accompanied by excessive sodium loss, then the serum sodium concentration decreases, resulting in hyponatremic (or hypotonic) dehydration. If water and sodium are lost at the same rate, then the serum sodium concentration remains the same. This is called isonatremic (or isotonic) dehydration.
Can diarrhea cause hypotonic hyponatremia?
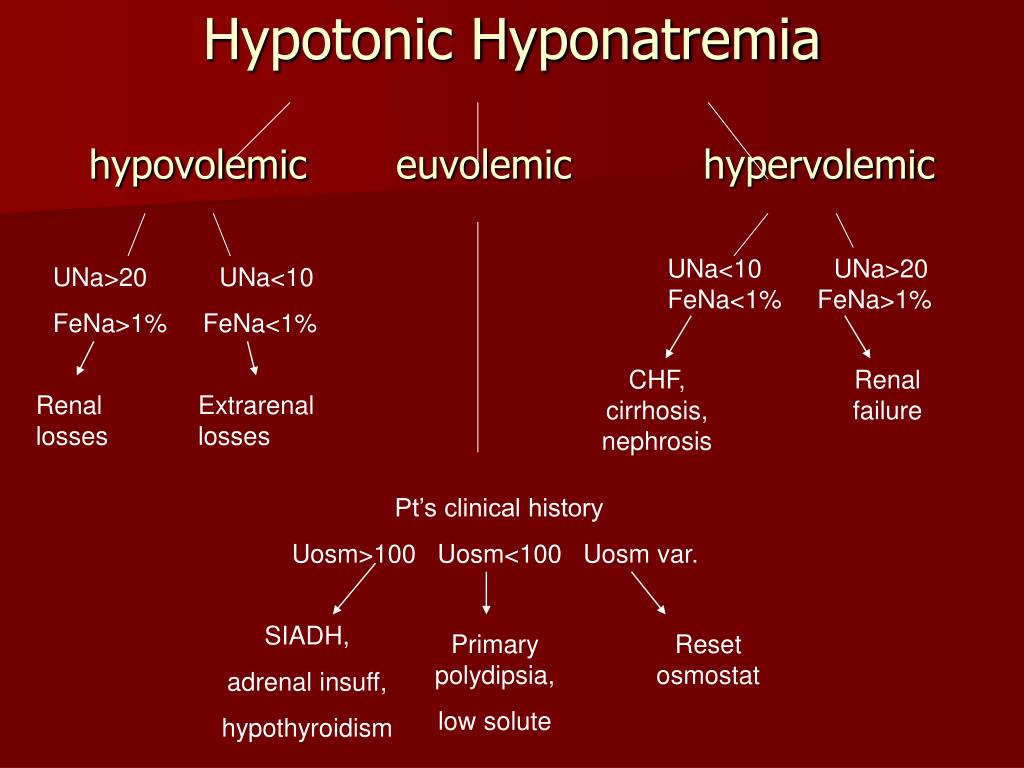
Diarrhea can cause hypotonic hyponatremia and hypernatremia. In Hypotonic hyponatremia - which is true hyponatremia, first check the serum osmolality, if <280 mOsm/kg. Patient always have hypovolemia- (low intravascular volumes). Then, check urine sodium.

Why is diarrhea isotonic?
Under these conditions, diarrhoea can occur when a poorly absorbed, osmotically active substance is ingested. If the substance is taken as an isotonic solution, the water and solute will simply pass through the gut unabsorbed, causing diarrhoea.
Does diarrhea cause isotonic dehydration?
Isotonic dehydration is often caused by diarrhea, vomiting or inadequate intake of fluid. Most commonly seen in infants, hypernatremic dehydration describes a loss of water that is greater than the amount of sodium lost, leading to a rise in blood sodium or hypernatremia.
Is dehydration hypotonic or hypertonic?
Hypertonic dehydration is one of three types of dehydration. Hypotonic dehydration, In contrast with hypertonic dehydration, refers to a decrease in electrolyte concentration in the extracellular fluid.
Which IV fluid is given in diarrhea?
Ringer's lactate IV fluid is preferred. If not available, use normal saline or dextrose solution. It is important to measure the amount of IV fluids delivered and measure the fluid lost as diarrhea and vomitus.
What electrolyte is lost in diarrhea?
Diarrhea can cause dehydration (when your body loses large amounts of water), electrolyte imbalance (loss of sodium, potassium and magnesium that play a key role in vital bodily functions) and kidney failure (not enough blood/fluid is supplied to the kidneys).
Why does diarrhea cause dehydration?
Diarrhea – the most common cause of dehydration and related deaths. The large intestine absorbs water from food matter, and diarrhea prevents this from happening. The body excretes too much water, leading to dehydration. Vomiting – leads to a loss of fluids and makes it difficult to replace water by drinking it.
Is sweating hypotonic or hypertonic?
Sweat is hypotonic to plasma and to some of the electrolyte replacement drinks available.
How does diarrhea cause hypernatremia?
Hypovolemic hyponatremia can result from GI or renal losses of fluid. It was previously noted that vomiting and diarrhea typically involves fluid loss which has sodium + potassium concentration less than that of plasma and may result in hypernatremia.
What is isotonic dehydration?
Isotonic dehydration is loss of water with preserved normal effective osmolality of body fluids. Causes include loss of isotonic fluids via the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, or skin (burns); loss of blood; or as a result of fluid sequestration in the “third space” (eg, the peritoneum).
Which saline is best for diarrhea?
Ringer's Lactate and Normal saline can be used during rapid intravenous rehydration in children with acute diarrhea and severe dehydration.
Does IV fluid help with diarrhea?
If diarrhea has caused you to become dehydrated, IV fluids could help. The saline from an IV enters directly into the bloodstream to rehydrate you quickly. Nausea and vomiting, cramps, and headaches can also accompany diarrhea.
Is saline good for diarrhea?
Normal saline is a safe initial rehydration fluid in children with diarrhea-related hypernatremia.
What are the causes of isotonic dehydration?
There are several forms of dehydration. Isotonic water loss occurs when water and sodium are lost together. Causes of isotonic water loss are vomiting, diarrhea, sweating, burns, intrinsic kidney disease, hyperglycemia, and hypoaldosteronism. Hypertonic dehydration occurs when water losses exceed sodium losses.
Can you dehydrate from diarrhea?
A prolonged bout of diarrhea or vomiting can cause the body to lose more fluid than it can take in. The result is dehydration, which occurs when your body doesn't have the fluid it needs to function properly. Severe dehydration can cause your kidneys to shut down.
Does diarrhea cause hyponatremia or hypernatremia?
Children with malnutrition and diarrhea are more prone to develop hyponatremia and have a higher mortality rate [ 4 ]. On the other hand, most studies revealed that hypernatremia occurs primarily in dehydration associated with diarrhea [ 9 , 10 ].
What electrolytes are lost in vomiting and diarrhea?
Electrolytes and acid-base disorders The vomiting of gastric or intestinal contents most commonly involves the loss of fluid that contains chloride, potassium, sodium, and bicarbonate. The sequelae of these losses include dehydration along with hyponatremia, hypochloremia, and hypokalemia.
Pathophysiology of Dehydration
The total body water is distributed into extracellular and intracellular compartments. The extracellular compartment contains one-third of total bo...
Evaluation of Tbna+ Status
1. Decreased TBNa+ produces signs of volume depletion 1. Dry mucous membranes 2. Decreased skin turgor (i.e. skin tenting when the skin is pinched)...
Signs and Symptoms of Dehydration
Most patients with dehydration present with: 1. Thirst 2. Headaches 3. Fatigue 4. Constipation, dry mouth, dry skin, dizziness and low urine volume...
Isotonic and Hypotonic Fluid Disorders: Summary
1. Hypovolemic shock: Severe dehydration will lead to low blood volume and hypovolemic shock. It can lead to major end organ damage with acidosis a...
Prevention of Dehydration
Adequate hydration is recommended during all activities to prevent dehydration. Water intake is the key to replacing water loss during exercise, in...
When talking about isotonic and hypo/hypertonic, what are we talking about?
Remember when we are talking about isotonic and hypo/hypertonic we are talking about how it looks outside of the cell compared to inside.
When to use hypotonic solution?
Hypotonic solutions are used when the cell is dehydrated and fluids need to be put back intracellularly. This happens when patients develop diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemia.
How does tonicity work in osmosis?
First, let’s get familiar with the cell and how tonicity works through osmosis. The cell is divided into two parts: ( intracellular & extracellular ). Each part is made up of a solution and depending on the tonicity of the fluid you can having shifting of fluids from outside of the cell to the inside via osmosis.
What is the meaning of tonic?
Tonic: concentration of a solution. The cell has the same concentration on the inside and outside which in normal conditions the cell’s intracellular and extracellular are both isotonic. It is important to be familiar with what fluids are isotonic and when they are given.
Is 5% dextrose hypotonic or isotonic?
5% dextrose in water (D5W)**also used as a hypotonic solution after it is administered because the body absorbs the dextrose BUT it is considered isotonic) Isoto nic solutions are used: to increase the EXTRACELLULAR fluid volume due to blood loss, surgery, dehydration, fluid loss that has been loss extracellularly.
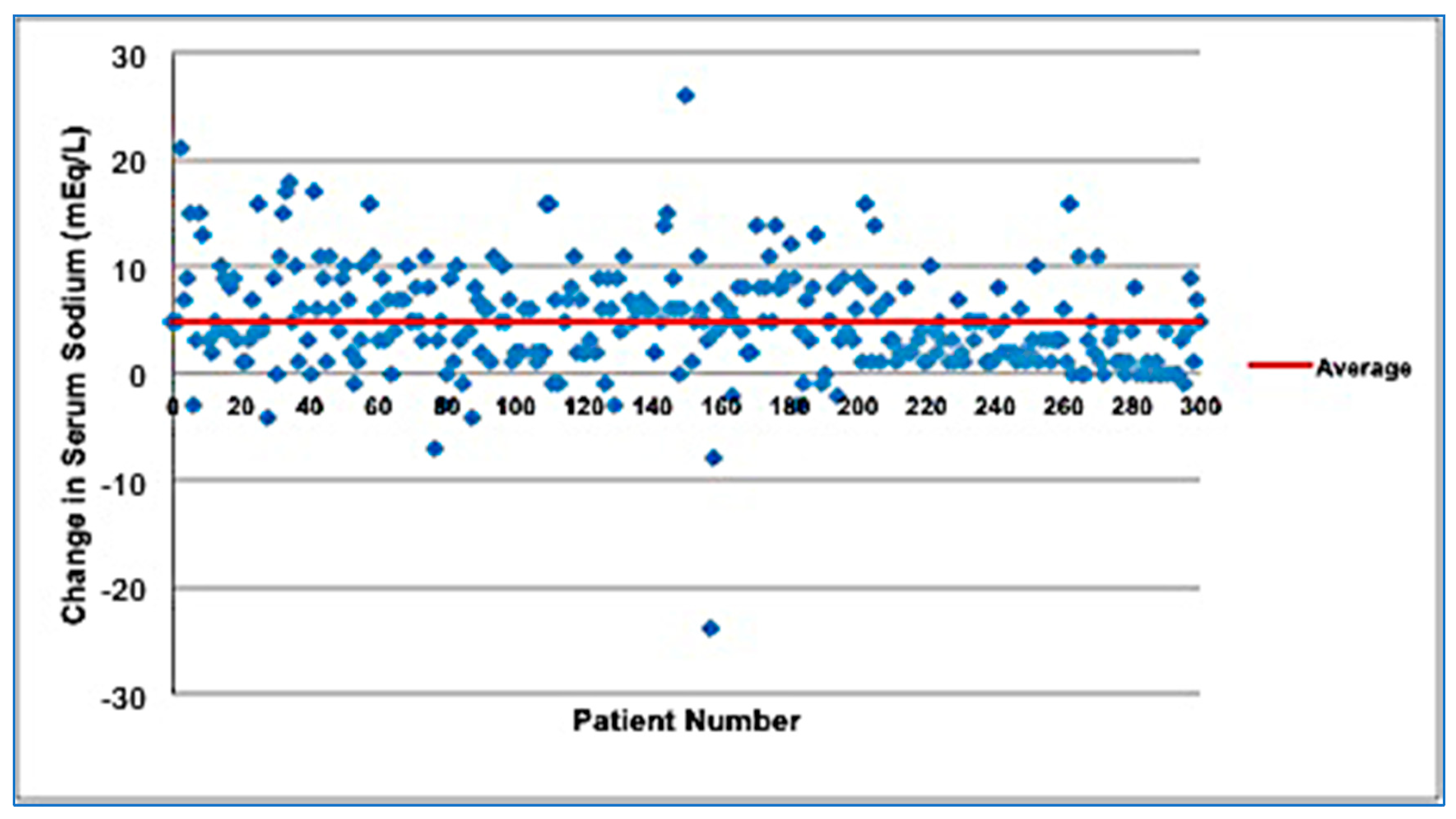
Why does sodium reabsorb more than 10 mEq/L?
If (less than 10 mEq/L) this implies that the kidneys are increasing sodium reabsorption to retain more Sodium in order to compensate for extrarenal losses such as diarrhea, vomiting, nasogastric suction, burns or pancreatitis. )
Can hypernatremia be caused by diarrhea?
Caveat: In Hypernatremia induced by diarrhea; always check the if the patient is drinking enough fluids to replace lost fluids enterally
Can diarrhea cause hypotonic hyponatremia?
Diarrhea can cause hypotonic hyponatremia and hypernatremia. In Hypotonic hyponatremia - which is true hyponatremia, first check the serum osmolality, if <280 mOsm/kg.
Does diarrhea cause hypovolemia?
Therefore, diarrhea causes excess sodium and water loss in the gut causing hypovolemia and hypotonic hyponatremia.
How to understand hypertonic, isotonic, and hypotonic?
To understand hypertonic, isotonic, and hypotonic, you must understand the process of osmosis. With osmosis, just remember LOW to HIGH. Osmosis is the process of molecules moving from a less concentrated solution to a higher concentrated solution by passing through a semipermeable membrane.
Why is isotonic solution used?
Isotonic solution is given to ensure that the cells remain in the extracellular compartment. Goal is to increase the intravascular volume. We want to treat low extracellular fluid so it makes sense that we’d use isotonic solution to keep cells in the extracellular compartment.
What are the symptoms of hypovolemia?
You should know understand and be aware of signs and symptoms of hypovolemia: Poor urine output. Poor skin turgor. Tachycardia. Hypotension. Dehydration. Fluid therapy can be lifesaving and is given when there is a loss of body water. Remember that it can cause a lot of harm when give in the wrong situation.
Does hypotonic solution lower sodium levels?
Hypotonic solutions lower serum sodium levels so it’s essential to monitor sodium levels.
What are the effects of isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic extracellular environments on plants and?
The effects of isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic extracellular environments on plant and animal cells is the same. However, due to the cell walls of plants, the visible effects differ. Although some effects can be seen, the rigid cell wall can hide the magnitude of what is going on inside.
What is hypertonic solution?
Hypertonic Solution. In Latin, the prefix hyper means over or above. Hypertonic solutions have a higher solute concentration than inside the cell. This causes water to rush out making the cell wrinkle or shrivel. This is clearly seen in red blood cells undergoing a process called crenation.
What happens if you leave an animal cell in hypertonic solution?
The cell wall helps keep the cell from bursting. However, if left in a highly hypertonic solution, an animal cell will swell until it bursts and dies.
What is the osmolality of hypotonic hyponatremia?
Hypotonic Hyponatremia (Serum osmolality of less than 275 mOsm/kg)
What is the difference between hyponatremia and total body water?
Hyponatremia represents an imbalance in this ratio where total body water is more than total body solutes. Total body water (TBW) has two main compartments, extracellular fluid (ECF) accounting for one-third and intracellular fluid (ICF), accounting for the remaining two-thirds. Sodium is the major solute of ECF and potassium for ICF. ...
What is the major solute of ECF and potassium?
Sodium is the major solute of ECF and potassium for ICF. Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 mEq/L but can vary to some extent depending upon the set values of varied laboratories.[1] . Hyponatremia is a common electrolyte abnormality caused by an excess of total body water in comparison to that ...
What is SIADH in kidney?
SIADH is a diagnosis of exclusion, as there is no single test to confirm the diagnosis. Patients are hyponatremic and euvolemic. [9]
What is the most common electrolyte disorder?
Hyponatremia is the most common electrolyte disorder, with a prevalence of 20% to 35% among hospitalized patients. The incidence of hyponatremia is high among critical patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) and also in postoperative patients.
What drugs cause hyponatremia?
Medications that cause hyponatremia such as carbamazepine or its analogs, vincristine, nicotine, antipsychotics, chlorpropamide, cyclophosphamide, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Illicit drugs such as methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA or ecstasy). Epidemiology.
What is pseudohyponatremia?
Pseudo-hyponatremia is a laboratory artifact. It is usually caused by hypertriglyceridemia, cholestasis (lipoprotein X), and hyperproteinemia (monoclonal gammopathy, intravenous immunoglobulin [IVIG]). Two-thirds of clinical labs in use still use indirect ion-selective electrode technology, and therefore this problem is still present.