What is the definition of electron domain?
In chemistry, the electron domain refers to the number of lone pairs or bond locations around a particular atom in a molecule. Electron domains may also be called electron groups. Bond location is independent of whether the bond is a single, double, or triple bond.
What are the electron domains?
Key Takeaways: Electron Domain An atom's electron domain is the number of lone pairs or chemical bond locations that surround it. It represents the... By knowing the electron domain of each atom in a molecule, you can predict its geometry. This is because electrons... Electron repulsion is not the ...
How to determine electron pair geometry?
Steps Used to Find the Shape of the Molecule
- Draw the Lewis Structure.
- Count the number of electron groups and identify them as bond pairs of electron groups or lone pairs of electrons. ...
- Name the electron-group geometry. ...
- Looking at the positions of other atomic nuclei around the central determine the molecular geometry. ...
What is the electron geometry of CH3OH?
What is the electron pair electronic geometry for CH3OH? CH3OH has sp3 hybridization, therefore it should depict a tetrahedral shape. But CH3OH depicts both tetrahedral and bent tetrahedral shape instead of tetrahedral throughout. There is one reason for that — the presence of lone pairs on the Oxygen atom.

What is the definition of electron geometry?
Definition. Electron Geometry: Electron geometry is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering both bond electron pairs and lone electron pairs. Molecular Geometry: Molecular geometry is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering only bond electron pairs.
What is the number of lone electron pairs?
Number of lone electron pairs = 3 – 3 = 0. Therefore, the electron geometry = trigonal planar. Sometimes, the electron geometry and the molecular geometry are the same. That is because only bonding electrons are considered in the determination of geometry in the absence of lone electron pairs.
What is the electron geometry?
The electron geometry gives the spatial arrangement of all the bonds and lone pairs of a molecule. The electron geometry can be obtained using VSEPR theory.
What is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering both bond electron pairs and lone electron pairs?
Electron geometry is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering both bond electron pairs and lone electron pairs. The VSEPR theory states that electron pairs located around a certain atom repel each other. These electron pairs can be either bonding electrons or non-bonding electrons.
How is electron geometry determined?
The main difference between electron geometry and molecular geometry is that electron geometry is found by taking both lone electron pairs and bonds in a molecule where as molecular ...
What is the geometry of a molecule?
The geometry of a molecule determines the reactivity, polarity and biological activity of that molecule. The geometry of a molecule can be given as either the electron geometry or the molecular geometry. The VSEPR theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory) can be used to determine the geometries of molecules.
Why is the molecular geometry bent or angular?
The geometry there is “bent or angular” because the lone electron pair needs more space than two bonding electron pair.
What is a lone pair?
A lone (non-bonding) pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bond. And a bond pair is a pair of electrons in a bond.
What is the difference between electronic geometry and molecular geometry?
The difference between electronic geometry and molecular geometry/shape is the inclusion of lone pair (s) of electrons in determining the geometry of a molecule.
How to determine the molecular geometry of ozone?
The molecular geometry of Ozone (O 3) can be determined by knowing the electron pairs on the central oxygen atom. Having 5 valence electrons (positive formal charge on the central oxygen), the central O atom forms a double bond with one of the terminal O atoms and a single bond with the other terminal O atom. It is also left with a lone pair of electrons (A phenomenon called resonance occurs).
How many valence electrons does NH3 have?
The electron geometry of ammonia (NH3) is tetrahedral because the central nitrogen atom, having 5 valence electrons, bonds 3 of its electrons with 3 hydrogen atoms, and the remaining 2 electrons act as a single lone pair.
How to determine the geometry of an electron?
Electron geometry can be determined by finding out the number of electron pairs, both bonding and non-bonding pairs around the central atom (s).
How many electron pairs are there in the central nitrogen atom?
So there are a total of 4 electron pairs around the central nitrogen atom. A tetrahedral electron geometry results, with an ∠HNH bond angle of 107° rather than 109.5° due to more repulsion from the lone pair as compared to a bond pair.
What is the shape of a molecule?
The shape of a molecule is the structure predicted using only bond pairs around the central atom (Molecular geometry) whereas the geometry of a molecule uses both bond pairs and lone pairs in determining the structure (Electron geometry): but are often used interchangeably, especially when there are no lone pairs.
What is the difference between electron geometry and molecular geometry?
Electron geometry teaches us about the arrangement of different electron groups. Molecular geometry, on the other hand, helps us understand the entire atom and its arrangement. It is the 3D arrangement of all the atoms in a particular molecule. So, when you compare them, you will note that atoms have different arrangements in electron geometry ...
How many valence electrons are in a central atom?
Example of electron geometry. The central atom here is C, and there are 4 valence electrons. Hydrogen atoms donate 4 electrons, which means there are a total of 8 electrons around C. The single bonds, in this case, are 4 and the number of lone pairs is 0.
How many electrons does hydrogen have?
Hydrogen donates a total of 2 electrons, making the total 8. So there are 4 electron groups and 2 lone electron pairs. There are also 2 single bond pairs. Thus, the molecular geometry here is bent. In such a way we can draw the structure of different molecules quite easily.
Do atoms have different arrangements in electron geometry?
So, when you compare them, you will note that atoms have different arrangements in electron geometry and molecular geometry.
Can we draw the structure of molecules?
In such a way we can draw the structure of different molecules quite easily.
Is chemistry fun?
Interesting and intriguing – chemistry is always fun! While understanding what matter is made of, we learn about so many new things that we simply lose ourselves in the beautiful world of chemistry.
What is AX 3?
AX 3 - The three electron domain system describes a trigonal planar geometry of a molecule where four atoms are arranged to form triangles with respect to each other. The angles add up to 360 degrees. An example of a molecule with this configuration is boron trifluoride (BF 3 ), which has three F-B bonds, each forming 120-degree angles.
What is the electron domain arrangement of a molecule?
When the electron domain arrangement is used to describe around the central atom of a molecule, it may be called the molecule's electron domain geometry. The arrangement of atoms in space is the molecular geometry. Examples of molecules, their electron domain geometry, and molecular geometry include:
Why do we know the electron domain of each atom in a molecule?
This is because electrons distribute around an atom to minimize repulsion with one another. Electron repulsion is not the only factor that affects molecular geometry.
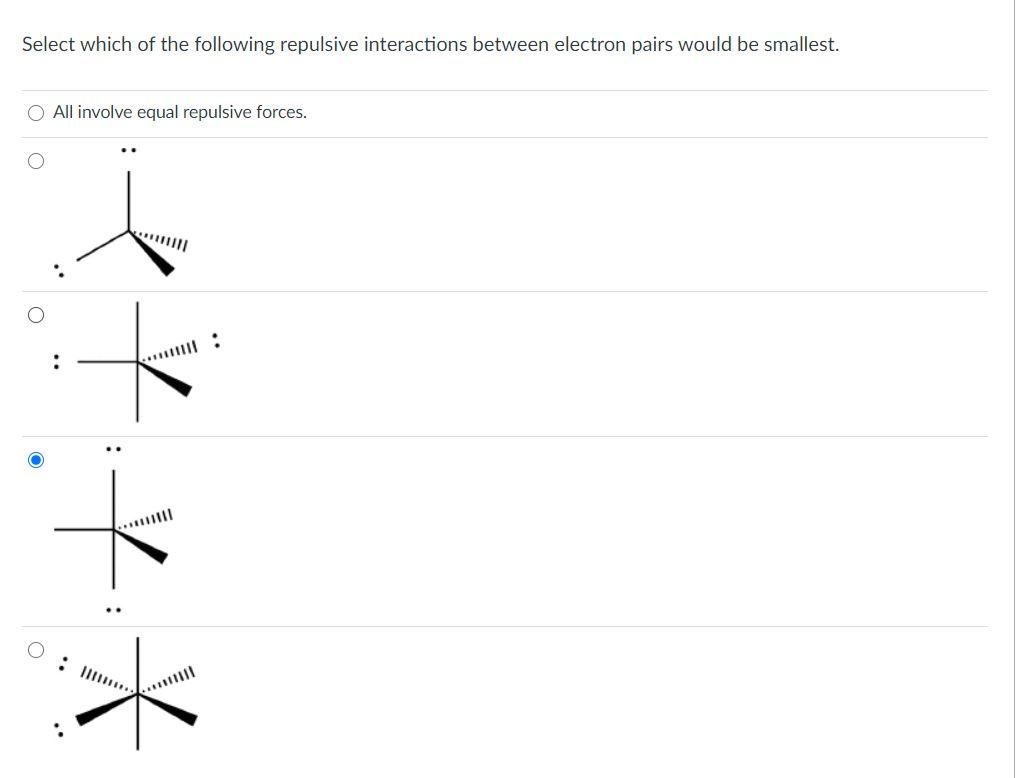
What is the name of the phenomenon where electrons repel one another?
This phenomenon is described as VSEPR, or Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion.
What is the electron domain?
Updated July 20, 2019. In chemistry, the electron domain refers to the number of lone pairs or bond locations around a particular atom in a molecule. Electron domains may also be called electron groups. Bond location is independent of whether the bond is a single, double, or triple bond.
How many domains are there in a double bond?
Use the angular arrangement of the chemical bonds between the atoms to determine the molecular geometry. Keep in mind, multiple bonds (i.e., double bonds, triple bonds) count as one electron domain. In other words, a double bond is one domain, not two.
What happens when you add a third balloon?
The balloons automatically repel one another. Add a third balloon, and the same thing happens so that the tied ends form an equilateral triangle. Add a fourth balloon, and the tied ends reorient themselves into a tetrahedral shape. The same phenomenon occurs with electrons.
Molecular Geometry vs Electron Domain Geometry
What is the difference between the molecular geometry versus the electron domain geometry of a structure and how are they determined differently?
Re: Molecular Geometry vs Electron Domain Geometry
Electron geometry is the arrangement of electron groups whereas molecular geometry just focuses on the arrangement of atoms based on the central atom and doesn’t include lone pairs.
Re: Molecular Geometry vs Electron Domain Geometry
Hi, To determine the electron domain geometry you take into account both the position of bonding electron pairs and lone electron pairs. Instead, for the molecular geometry, you only consider the bonding electron pairs. Hope this helps!
