An atom
Atom
An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small; typical sizes are around 100 picometers (1×10⁻¹⁰ m, a ten-milliont…
Why do we add energy to a system?
What happens before binding an electron to an atom?
What does it mean when an electron is weakly bound?
When there is another electron between a valence electron and the nucleus, what happens?
How many protons does helium have?
Which is smaller, helium or hydrogen?
What happens when a state changes?
See 4 more
About this website

Do electrons release energy?
An electron in an excited state can release energy and 'fall' to a lower state. When it does, the electron releases a photon of electromagnetic energy.
How do you determine if energy is absorbed or emitted?
Emission is when electrons return to energy levels. Absorption is when electrons gain energy and jump to higher energy levels.
What does it mean when an electron absorbs energy?
an excited stateWhen an electron in an atom has absorbed energy it is said to be in an excited state. An excited atom is unstable and tends to rearrange itself to return to its lowest energy state. When this happens, the electrons lose some or all of the excess energy by emitting light.
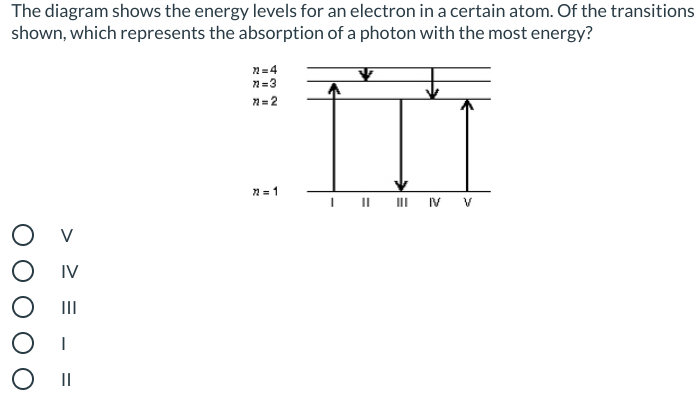
Is energy absorbed or released for the electron transition shown in the diagram?
Energy is absorbed for the electron transition shown in the diagram to the right since the electron is moving from an energy level close to the nucleus up to an energy level further away from the nucleus and energy will be needed to pull the electrons away from the nucleus which contains protons which will be ...
Is a photon absorbed or emitted?
An atom can absorb or emit one photon when an electron makes a transition from one stationary state, or energy level, to another. Conservation of energy determines the energy of the photon and thus the frequency of the emitted or absorbed light.
Is radiation emitted or absorbed?
All bodies (objects) emit and absorb types of electromagnetic radiation. They do this regardless of their temperature . The intensity of radiation increases as the body gets hotter and gives out more radiation in a given time. The type of radiation emitted also changes with temperature.
What happens to energy when it is absorbed?
When it is absorbed, it is converted into heat energy, and the object heats up. For example, black objects absorb a lot of light, so if you wear a black shirt on a sunny day, your shirt will absorb the sunlight and convert it into heat, making you feel hot!
Why do electrons not lose energy?
1) If an electron is in the electric field of a nucleus, the electron can occupy only certain energy levels. When it is sitting on one of these energy levels, it does not radiate, it does not loose energy.
How do electrons absorb energy from photons?
Photon absorption by an atomic electron occurs in the photoelectric effect process, in which the photon loses its entire energy to an atomic electron which is in turn liberated from the atom. This process requires the incident photon to have an energy greater than the binding energy of an orbital electron.
During which phase is energy absorbed?
The change is endothermic, meaning that the system absorbs energy on going from solid to liquid. The change is exothermic (the system releases energy) when the direction is from liquid to solid.
In which of the cases energy is absorbed?
When an anion (having unit negative charge) gains an electron, energy is absorbed.
How do you know if heat is evolved or absorbed?
The sign of q for an endothermic process is positive because the system is gaining heat. A chemical reaction or physical change is exothermic if heat is released by the system into the surroundings. Because the surroundings are gaining heat from the system, the temperature of the surroundings increases.
How do you know if light is being reflected or absorbed?
If a material or matter absorbs light of certain wavelengths or colours of the spectrum, an observer will not see these colours in the reflected light. On the other hand, if certain wavelengths of colours are reflected from the material, an observer will see them and see the material in those colours.
What determines the energy of emitted light?
According to Planck's equation, the energy of a photon is proportional to the frequency of the light, ν.
How do we measure heat released or absorbed in a reaction?
The heat of reaction can be calculated based on the standard heat of formation of all reactants involved. However, it is usually determined by measuring the heat production over time using a reaction calorimeter, such as a heat flow calorimeter.
The energy required to remove an electron from a neutral isolated ...
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ The energy required to remove an electron from a neutral isolated gaseous atom and convert it into a positively charged gaseous ion is called . (electron affinity, ionisation potential, electronegativity).
Pts question 11 your answer an is the smallest - Course Hero
3.44 / 3.44 pts Question 17 Your Answer: When sufficient energy is absorbed and an electron is pulled away from the atom, the atom is left with a net _____ charge. The atom becomes a _____.
Solved When sufficient energy is absorbed and an electron is | Chegg.com
When sufficient energy is absorbed and an electron is pulled away from the atom, the atom is left with a net _____ charge. The atom becomes a _____.
Analytical Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Board Exam Questions
Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Analytical Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry board year questions and solutions. below which have come in past board exams.You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry and prepare accordingly.
Question 35 [1] The simplest ratio of the atoms of carbon and hydrogen ...
Question 35 [1] The simplest ratio of the atoms of carbon and hydrogen is 1:1. Identify the possible molecular formula. 1. C6H6 2. C2H4 3. C6H2 4. C3H4 - 46997826
Why do we add energy to a system?
Energy must be added to the system to kick out electrons from their position in space above the nucleus (note that I am avoiding the term orbital). The lost electron changes the field dynamics of the system as there now remains a positron whose field energy is not bonded. This field energy extends into space to in effect make the system more energetic, providing energy that this ion can use to undergo a chemical reaction.
What happens before binding an electron to an atom?
So before binding an electron to an atom or binding atoms together there is potential energy to be released.
What does it mean when an electron is weakly bound?
A weakly bound electron means there is not much energy released and something else will compete for it. So a high energy species is not strong, it is weak and in chemistry it is the pathetic weak bonding that provides the greater energy source. The most reactive electron is one that is virtually free, unbound.
When there is another electron between a valence electron and the nucleus, what happens?
When there is another electron between a valence electron and the nucleus, the pull of the nucleus on the valence electron decreases.
How many protons does helium have?
Also, in helium, we have 2 protons and two neutrons pulling on 2 electrons, whereas in hydrogen, we have 1 proton pulling on 1 electron. This means the effective nuclear charge ( Z effective) of helium is higher than that of hydrogen.
Which is smaller, helium or hydrogen?
Thus, the pull by the nucleus is greater in helium than in hydrogen, making a helium atom smaller than a hydrogen atom.
What happens when a state changes?
State Change. Every state of being is energy condensed in a form. Whenever that state changes energy is either gained or released depending upon the type of change.
