
How do they administer epinephrine?
This medicine is injected under the skin or into the muscle of your outer thigh only. Do not inject this medicine into a vein, into the muscle of your buttocks, or into your fingers, toes, hands, or feet. To do so, may increase the chance of having serious side effects.
Why is adrenaline not given subcutaneously?
The subcutaneous route for adrenaline is not recommended for treatment of an anaphylactic reaction as it is less effective.
Is an epi pen IM or SUBQ?
The product label of EpiPen, the only autoinjection epinephrine product approved in the US for anaphylaxis, recommends IM intramuscular injection into the anterolateral aspect of the thigh, but it also states that epinephrine, when given intramuscularly or subcutaneously, has a rapid onset of action, which supports ...
What is subcutaneous epinephrine used for?
Intramuscular And Subcutaneous Use For Anaphylaxis Through its action on beta-adrenergic receptors, epinephrine causes bronchial smooth muscle relaxation and helps alleviate bronchospasm, wheezing and dyspnea that may occur during anaphylaxis.
Where should you never inject epinephrine?
This medicine is injected under the skin or into the muscle of your outer thigh only. Do not inject this medicine into a vein, into the muscle of your buttocks, or into your fingers, toes, hands, or feet.
How long does subcutaneous epinephrine last?
How long does a dose of epinephrine last? According to Dr. Brown, studies have shown there is “epinephrine in your system for at least 6 hours. It's at a higher level for about an hour, and it peaks around 5 minutes.
Why is epinephrine given intramuscularly?
When treating anaphylaxis, epinephrine is generally given via an intramuscular (IM) route. This is well established to be effective and life-saving. One advantage of IM administration is immediate use (without requiring intravenous access), including by patient auto-injection.
How do you administer epinephrine subcutaneously?
0:343:26The dose for adults. And children 66 pounds or more is 0.3 to 0.5 milligrams. Which is 0.3 to 0.5MoreThe dose for adults. And children 66 pounds or more is 0.3 to 0.5 milligrams. Which is 0.3 to 0.5 milliliters every 5 to 10 minutes as necessary.
Why is epipen given IM?
Sharma: Epinephrine is recommended to be given into the muscle, and not the subcutaneous tissue, because administration into the muscle will provide a more rapid increase in its concentrations in the blood and tissues. This fast uptake of epinephrine is critical in the treatment of anaphylaxis.
Is epinephrine IM or SC?
For two decades, epinephrine injections have been recommended to be delivered intramuscularly (IM) into the mid antero-ventral thigh [7]. The evidence for IM injection in the mid antero-ventral thigh being superior to subcutaneous injection originates from the studies by Simons et al.
Is epinephrine given IM?
Intramuscular epinephrine injection (preferred) — Intramuscular (IM) injection is the preferred route for initial administration of epinephrine for anaphylaxis in most settings and in patients of all ages (table 3) [37,38].
Why is epinephrine not given IV?
RESULTS: Epinephrine is safe for anaphylaxis when given at the correct dose by intramuscular injection. The majority of dosing errors and cardiovascular adverse reactions occur when epinephrine is given intravenously or incorrectly dosed.
What happens if you inject adrenaline into your body?
Adrenaline injections An adrenaline injection, such as EpiPen or Adrenaline Mylan, is used as a treatment for a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). It works by quickly reducing swelling in the throat, opening up the airways and preventing the blood pressure from falling too low.
Why is adrenaline injected and not given orally?
As adrenaline is destroyed by enzymes in the stomach, it needs to be injected. It cannot be given by mouth, and inhaled adrenaline is ineffective. Adrenaline injected into the outer mid-thigh muscle works rapidly to reduce throat swelling, open up the airways and maintain heart function and blood pressure.
Why is heparin not given subcutaneously?
Background: Heparin is an anticoagulant medication that is usually injected subcutaneously. Subcutaneous administration of heparin may result in complications such as bruising, haematoma, and pain at the injection site. One of the factors that may affect pain, haematoma, and bruising is injection speed.
Why is epinephrine not administered orally?
That adrenalin is ineffective when administered by mouth seems to be an accepted fact. That it is destroyed by the gastric and intestinal juice is the general belief. Systemic effects from oral administration are thus questionable.
Usual Adult Dose For Asystole
Injectable Solution of 0.1 mg/mL (1:10,000):-IV: 0.5 to 1 mg (5 to 10 mL) IV once; during resuscitation effort, 0.5 mg (5 mL) should be given IV ev...
Usual Adult Dose For Asthma - Acute
Injectable Solution of 0.1 mg/mL (1:10,000):0.1 to 0.25 mg (1 to 2.5 mL) IV slowly onceUse: For the treatment of acute asthmatic attacks to relieve...
Usual Adult Dose For Allergic Reaction
Auto-Injector:30 kg or greater: 0.3 mg IM or subcutaneously into anterolateral aspect of thigh; repeat as neededComments:-The manufacturer product...
Usual Adult Dose For Pupillary Dilation
Injectable Solution of 1 mg/mL (1:1000):-Intraocular: Dilute 1 mL of the 1 mg/mL single-use vial (1:1000) in 100 to 1000 mL of an ophthalmic irriga...
Usual Adult Dose For Hypotension
Injectable Solution of 1 mg/mL (1:1000): 0.05 to 2 mcg/kg/min IV and titrate to achieve desired mean arterial pressure (MAP)-Dosage may be adjusted...
Usual Adult Dose For Bradyarrhythmia
The manufacturer gives no specific dosing instructions.The AHA recommends:2 to 10 mcg/min IV and titrate to patient response-Alternate dose: 0.1 to...
Usual Pediatric Dose For Cardiac Arrest
The manufacturer gives no specific dosing instructions.The AHA recommends:Neonates:-IV: 0.01 to 0.03 mg/kg (1:10,000 injectable solution) IV once-E...
Usual Pediatric Dose For Allergic Reaction
Auto-Injector:7.5 to 15 kg: 0.1 mg IM or subcutaneously into anterolateral aspect of thigh; repeat as needed15 to 30 kg: 0.15 mg IM or subcutaneous...
Usual Pediatric Dose For Asthma - Acute
Injectable Solution of 0.1 mg/mL (1:10,000):-Neonate: 0.01 mg/kg IV slowly once-Infant: 0.05 mg IV slowly once; may repeat at 20 to 30 minute inter...
How to use an Epipen Jr?
If you are about to use the autoinjector, pull up straight the blue safety release (EpiPen® or EpiPen Jr®) with one hand and hold the pen with the other hand. Do not flip the blue safety release off using the thumb or by pulling it sideways, or by bending and twisting it. This may activate the device by accident (a "click is heard, the orange needle is extended, and the window is blocked), making it unusable in case of an emergency. Push the needle end (orange end of the autoinjector) firmly against the outer thigh until it "clicks". This signals that the injection has started. The autoinjector needs to stay in place for a minimum of 3 seconds following activation.
Where to store injection kits?
Store the injection kits at room temperature, away from heat, moisture, and direct light. Do not store the medicine in the refrigerator or freezer, or into your vehicle's glove box.
Does Auvi Q come with an autoinjector?
This medicine comes with an autoinjector trainer and a separate trainer instructions for use. Be sure to practice first with your autoinjector trainer before an allergy emergency happens to make sure you are ready to use the real Auvi-Q®, Adrenaclick®, EpiPen®, or EpiPen Jr® autoinjector in an actual emergency. The autoinjector trainer has a grey color (for Auvi-Q®, EpiPen® or EpiPen Jr®) or beige color (for Adrenaclick®) and does not contain any medicine or needle.
Can you reuse a prefilled syringe?
Do not reuse the remaining portion of the medicine that is left in the autoinjector, prefilled syringe, or vial. Throw away the autoinjector, prefilled syringe, or vial after you have used it.
Can you remove the blue safety release on an Epipen?
Do not remove the blue safety release (EpiPen® or EpiPen Jr®), the gray end caps (Adrenaclick®), or the red safety guard (Auvi-Q®) on the autoinjector until you are ready to use it. Do not put your thumb, fingers, or hand over the black base (Auvi-Q®), orange (EpiPen® or EpiPen Jr®), or red (Adrenaclick®) tip of the autoinjector or over the needle of the Symjepi® prefilled syringe. This is to avoid an accidental injection.
Can you throw an expired Epipen in the trash?
Throw away expired, unwanted, or unused EpiPen® or EpiPen Jr® in an FDA-cleared sharps container. Do not throw it away in the trash bin.
Can you inject a syringe through clothing?
You may inject the medicine through your clothing, if you need to.
How much epinephrine is in a 10 ml vial?
Injection solution: 10 mL clear glass vial containing 1 mg/10 mL (0.1 mg/mL) epinephrine in a sterile, nonpyrogenic, clear and colorless solution. Each vial is co-packaged with an injector, which together make a single-dose ABBOJECT ® Syringe.
How long does epinephrine stay in the blood?
Following intravenous injection, epinephrine is rapidly cleared from the plasma with an effective half-life of < 5 min. A pharmacokinetic steady state following continuous intravenous infusion is achieved within 10–15 min. In patients with septic shock, epinephrine displays dose-proportional pharmacokinetics in the infusion dose range of 0.03 to 1.7 mcg/kg/min.
Why is my epinephrine blanching?
Blanching along the course of the infused vein, sometimes without obvious extravasation, may be attributed to vasa vasorum constriction with increased permeability of the vein wall, permitting some leakage. This also may progress on rare occasions to a superficial slough. Hence, if blanching occurs, consider changing the infusion site at intervals to allow the effects of local vasoconstriction to subside.
What is the effect of epinephrine on the pancreas?
Epinephrine increases glycogenolysis, reduces glucose up take by tissues, and inhibits insulin release in the pancreas, resulting in hyperglycemia and increased blood lactic acid.
What happens when epinephrine constricts the blood vessels?
Epinephrine constricts renal blood vessels, which may result in oliguria or renal impairment.
What is the molecular weight of epinephrine?
The molecular weight of epinephrine is 183.2.
How much dextrose to dilute epinephrine?
Dilute 10 mL (1 mg) of epinephrine from the syringe in 1,000 mL of 5 percent dextrose solution or 5 percent dextrose and sodium chloride solution to produce a 1 mcg per mL dilution. The diluted solutions can be stored for up to 4 hours at room temperature or 24 hours under refrigerated conditions.
Usual Adult Dose for Asystole
Injectable Solution of 0.1 mg/mL (1:10,000): -IV: 0.5 to 1 mg (5 to 10 mL) IV once; during resuscitation effort, 0.5 mg (5 mL) should be given IV every 5 minutes -Intracardiac: 0.3 to 0.5 mg (3 to 5 mL) via intracardiac injection into left ventricular chamber once -Endotracheal: 0.5 to 1 mg (5 mL to 10 mL) via endotracheal tube directly into bronchial tree once Comments: -Intracardiac injection should only be administered by personnel well trained in this technique and only if there has not been sufficient time to establish an IV route. Use: For prophylaxis and treatment of cardiac arrest and attacks of transitory atrioventricular heart block with syncopal seizures (Stokes-Adams Syndrome) The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends: -IV or intraosseous: 1 mg IV or intraosseous every 3 to 5 minutes during cardiac arrest -Endotracheal: 2 to 2.5 mg endotracheally every 3 to 5 minutes during cardiac arrest if IV or intraosseous route cannot be established Use: For administration during cardiac arrest.
Usual Adult Dose for Ventricular Fibrillation
Injectable Solution of 0.1 mg/mL (1:10,000): -IV: 0.5 to 1 mg (5 to 10 mL) IV once; during resuscitation effort, 0.5 mg (5 mL) should be given IV every 5 minutes -Intracardiac: 0.3 to 0.5 mg (3 to 5 mL) via intracardiac injection into left ventricular chamber once -Endotracheal: 0.5 to 1 mg (5 mL to 10 mL) via endotracheal tube directly into bronchial tree once Comments: -Intracardiac injection should only be administered by personnel well trained in this technique and only if there has not been sufficient time to establish an IV route. Use: For prophylaxis and treatment of cardiac arrest and attacks of transitory atrioventricular heart block with syncopal seizures (Stokes-Adams Syndrome) The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends: -IV or intraosseous: 1 mg IV or intraosseous every 3 to 5 minutes during cardiac arrest -Endotracheal: 2 to 2.5 mg endotracheally every 3 to 5 minutes during cardiac arrest if IV or intraosseous route cannot be established Use: For administration during cardiac arrest.
Usual Adult Dose for Ventricular Tachycardia
Injectable Solution of 0.1 mg/mL (1:10,000): -IV: 0.5 to 1 mg (5 to 10 mL) IV once; during resuscitation effort, 0.5 mg (5 mL) should be given IV every 5 minutes -Intracardiac: 0.3 to 0.5 mg (3 to 5 mL) via intracardiac injection into left ventricular chamber once -Endotracheal: 0.5 to 1 mg (5 mL to 10 mL) via endotracheal tube directly into bronchial tree once Comments: -Intracardiac injection should only be administered by personnel well trained in this technique and only if there has not been sufficient time to establish an IV route. Use: For prophylaxis and treatment of cardiac arrest and attacks of transitory atrioventricular heart block with syncopal seizures (Stokes-Adams Syndrome) The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends: -IV or intraosseous: 1 mg IV or intraosseous every 3 to 5 minutes during cardiac arrest -Endotracheal: 2 to 2.5 mg endotracheally every 3 to 5 minutes during cardiac arrest if IV or intraosseous route cannot be established Use: For administration during cardiac arrest.
Usual Adult Dose for Cardiac Arrest
Injectable Solution of 0.1 mg/mL (1:10,000): -IV: 0.5 to 1 mg (5 to 10 mL) IV once; during resuscitation effort, 0.5 mg (5 mL) should be given IV every 5 minutes -Intracardiac: 0.3 to 0.5 mg (3 to 5 mL) via intracardiac injection into left ventricular chamber once -Endotracheal: 0.5 to 1 mg (5 mL to 10 mL) via endotracheal tube directly into bronchial tree once Comments: -Intracardiac injection should only be administered by personnel well trained in this technique and only if there has not been sufficient time to establish an IV route. Use: For prophylaxis and treatment of cardiac arrest and attacks of transitory atrioventricular heart block with syncopal seizures (Stokes-Adams Syndrome) The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends: -IV or intraosseous: 1 mg IV or intraosseous every 3 to 5 minutes during cardiac arrest -Endotracheal: 2 to 2.5 mg endotracheally every 3 to 5 minutes during cardiac arrest if IV or intraosseous route cannot be established Use: For administration during cardiac arrest.
Usual Adult Dose for Asthma - Acute
Injectable Solution of 0.1 mg/mL (1:10,000): 0.1 to 0.25 mg (1 to 2.5 mL) IV slowly once Use: For the treatment of acute asthmatic attacks to relieve bronchospasm not controlled by inhalation or subcutaneous administration of other solutions of the drug
Usual Adult Dose for Allergic Reaction
Auto-Injector: 30 kg or greater: 0.3 mg IM or subcutaneously into anterolateral aspect of thigh; repeat as needed Comments: -The manufacturer product information for the specific auto-injector being used should be consulted for administration instructions. -More than 2 sequential doses should only be administered under direct medical supervision. -The auto-injectors are intended for immediate administration as emergency supportive therapy only and not as a replacement or substitute for immediate medical care. Injectable Solution of 1 mg/mL (1:1000): 30 kg or greater: 0.3 to 0.5 mg (0.3 to 0.5 mL) of undiluted drug IM or subcutaneously into anterolateral aspect of the thigh; repeat every 5 to 10 minutes as needed -Maximum dose per injection: 0.5 mg (0.5 mL) Comments: -For IM administration, use a long enough needle (at least 1/2 inch to 5/8 inch) to ensure injection into the muscle. -Repeated injections should not be administered at the same site as resulting vasoconstriction may cause tissue necrosis. -The patient should be monitored clinically for reaction severity and cardiac effects with repeat doses titrated to effect. Injectable Solution of 0.1 mg/mL (1:10,000): 0.1 to 0.25 mg (1 to 2.5 mL) IV slowly once Convenience Kit 1 mg/mL (1:1000): 0.2 to 1 mg IM or subcutaneous Uses: For the emergency treatment of allergic reactions (Type I) including anaphylaxis to stinging or biting insects, allergen immunotherapy, foods, drugs, diagnostic testing substances, and other allergens, as well as idiopathic anaphylaxis or exercise-induced anaphylaxis; and for immediate administration in patients who are determined to be at increased risk for anaphylaxis, including those with a history of anaphylactic reactions.
Usual Adult Dose for Anaphylaxis
Auto-Injector: 30 kg or greater: 0.3 mg IM or subcutaneously into anterolateral aspect of thigh; repeat as needed Comments: -The manufacturer product information for the specific auto-injector being used should be consulted for administration instructions. -More than 2 sequential doses should only be administered under direct medical supervision. -The auto-injectors are intended for immediate administration as emergency supportive therapy only and not as a replacement or substitute for immediate medical care. Injectable Solution of 1 mg/mL (1:1000): 30 kg or greater: 0.3 to 0.5 mg (0.3 to 0.5 mL) of undiluted drug IM or subcutaneously into anterolateral aspect of the thigh; repeat every 5 to 10 minutes as needed -Maximum dose per injection: 0.5 mg (0.5 mL) Comments: -For IM administration, use a long enough needle (at least 1/2 inch to 5/8 inch) to ensure injection into the muscle. -Repeated injections should not be administered at the same site as resulting vasoconstriction may cause tissue necrosis. -The patient should be monitored clinically for reaction severity and cardiac effects with repeat doses titrated to effect. Injectable Solution of 0.1 mg/mL (1:10,000): 0.1 to 0.25 mg (1 to 2.5 mL) IV slowly once Convenience Kit 1 mg/mL (1:1000): 0.2 to 1 mg IM or subcutaneous Uses: For the emergency treatment of allergic reactions (Type I) including anaphylaxis to stinging or biting insects, allergen immunotherapy, foods, drugs, diagnostic testing substances, and other allergens, as well as idiopathic anaphylaxis or exercise-induced anaphylaxis; and for immediate administration in patients who are determined to be at increased risk for anaphylaxis, including those with a history of anaphylactic reactions.
How to administer subcutaneous injections?
How to administer a subcutaneous injection. 1. Wash your hands. Wash your hands with soap and warm water to prevent potential infection. Be sure to thoroughly scrub between fingers, on the backs of hands, and under fingernails. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Trusted Source.
What is subcutaneous injection?
Overview. A subcutaneous injection is a method of administering medication. Subcutaneous means under the skin. In this type of injection, a short needle is used to inject a drug into the tissue layer between the skin and the muscle. Medication given this way is usually absorbed more slowly than if injected into a vein, ...
What is the thickness of a subcutaneous injection needle?
Vials can also be filled with a powder to which liquid needs to be added. Syringes: The needles are short, at 5/8 inches long. The thickness of the needle is usually 25 or 27 gauge.
How to treat bleeding from a syringe injection?
Apply pressure to the site. Use gauze to apply light pressure to the injection site . If there’s any bleeding, it should be very minor. You may notice a little bruising later. This is common and nothing to be concerned about.
How many ml of insulin is safe?
Medications administered by subcutaneous injection include drugs that can be given in small volumes (usually less than 1 mL but up to 2 mL is safe). Insulin and some hormones are commonly administered as subcutaneous injections.
What pain medication can be given by injection?
Some pain medications like morphine and hydromorphone (Dilaudid) can be given this way as well. Drugs that prevent nausea and vomiting like metoclopramide (Reglan) or dexamethasone (DexPak) can also be given via subcutaneous injection.
How to clean skin before injecting medication?
Alternate injection sites to prevent damage to an area with repeated injections. Then you should clean the skin with an alcohol swab.
How to administer subcutaneous epinephrine?
To deliver subcutaneous epinephrine for asthma (on the right), use a short 25 gauge needle, a syringe that can measure 0.1 ml increments, and 1:1000 epinephrine. The dose ranges from 0.1 to 0.5 mg (ml equals mg with this concentration). Epinephrine can be given every 20 minutes for the first three doses, and can be used in conjunction with other asthma therapies. Note that crash cart epinephrine (on the left) is a 10 ml vial of 1:10,000 concentration, where 1 ml equals 0.1 mg. In a severe emergency (such as anaphylaxis with shock), 1 ml aliquots of IV epinephrine in this concentration have been used.
What is the 20 minute interval protocol for subcutaneous epinephrine?
The 20-minute interval protocol for subcutaneous epinephrine was at that time a standard approach and universally accepted as an intervention of choice for asthma. Of the 108 episodes of acute asthma, patients were grouped by age of over or under 40. Ages ranged from 15 to an amazing 96 years. If the patient had a history of angina or recent myocardial infarction, they were excluded. Patients with hypertension or other nonactive forms of cardiac disease were eligible for epinephrine for their asthma, however. Criteria for the early termination of the protocol included ventricular tachycardia, three or more PVCs with hypotension, or the precipitation of angina. The authors monitored heart rate, EKG rhythm, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and peak expiratory flow.
How much epinephrine is discharged?
More often, curious children will accidentally discharge the device. Although only 0.3 mg (adult version) or 0.15 mg (EpiPen Junior) of epinephrine is discharged per dose, this small amount of epinephrine in a digit will almost invariably cause acute ischemia.
What are the adverse outcomes of epinephrine?
Explicit criteria for adverse outcomes included development of a new arrhythmia (other than sinus tachycardia) within 60 minutes of intravenous epinephrine; cardiac ischemia as manifested by new ischemic EKG changes; development of a new focal neurological finding believed to be possibly caused by cerebral ischemia; new or worsening hypotension; or new or worsening hypertension related to the epinephrine infusion.
Is terbutaline better than epinephrine?
Comment: A number of articles have demonstrated the benefit of subcutaneous terbutaline for the treatment of acute asthma, but it has never been proven to be any better or safer than e pinephrine. Both drugs will give significant tremor and anxiety, but subcutaneous terbutaline has fallen out of favor. Its main use today is for the treatment of premature labor. I note that the dose of epinephrine in this study was on the high side (0.5 mg), and I refer to my previous comment that 0.3 mg would be a reasonable starting dose for most adults. As noted in all other studies, the treatment of acute bronchospasm with the potent alpha and beta agonist epinephrine decreased blood pressure and pulse rate because of improved pulmonary parameters.
Does subcutaneous epinephrine help with asthma?
The patient arriving by ambulance in extremis is another story. I personally use subcutaneous epinephrine as my first-line treatment in most seriously ill asthmatics. It's easy to administer, it works, and the blood pressure and heart rate invariably decline despite the puzzled look of the house staff and young nurses. In fact, I often have to give the drug myself because a nurse will not give it to someone who has a pulse rate of 160 or a blood pressure of 180 systolic. The hypertension and tachycardia are due to hypoxia, anxiety, and the work of breathing, and these only get better with the relief of bronchospasm. I realize this is a difficult concept to understand unless you have personal experience with it, but I am certain that this technique has saved many an asthmatic from intubation and periods of prolonged hypoxia.
Can you inject epinephrine in thin people?
In thin individuals, an intramuscular injection may occur, but this is not disadvantageous. Although the authors cautioned against the use of epinephrine in older asthmatics with coronary artery disease, their findings supported the use of subcutaneous epinephrine for all patients with acute asthma, regardless of age.
How is epinephrine administered?
Epinephrine is prepared as part of an injectable solution. Also, different types of injections can administer this medication, as needed:
What is epinephrine used for?
Epinephrine is useful mainly for the treatment of cardiac arrest and anaphylactic reactions. Last update: 19 November, 2020. Epinephrine, better known as adrenaline, is a hormone and neurotransmitter used in emergencies when the patient is suffering from cardiac arrest. This drug has historically been used to treat bronchospasms and hypoglycemia.
Why is epinephrine added to local anesthetics?
The reason for this combination is that the vasoconstrictive effects of adrenaline make it possible to delay absorption and thus prolong the effect of the anesthetic drug.
Why is epinephrine used for heart problems?
The purpose of administering epinephrine is to cause vasoconstriction and increase cardiac output. In other words, it contracts the heart and increases your heart rate ...
What is adrenaline used for?
This drug has historically been used to treat bronchospasms and hypoglycemia. However, today there are other more specific drugs in existence to treat these conditions. Adrenaline is a substance that increases heart rate, constricts blood vessels, dilates the airways, and participates in the fight or flight reaction of the nervous system in an ...
What is adrenaline epinephrine?
Epinephrine, or adrenaline, is a drug that administered through different channels depending on the patient’s condition and situation. Additionally, it’s a valuable treatment for cardiac arrest and anaphylactic reactions.
What is IV in medical terms?
Intravenous (IV) Intracardiac: only in cases of extreme severity, and if the intravenous route is not practicable. The last two types of administration must be carried out in the hospital, under cardiac monitoring.
Why do plastic surgeons administer epinephrine?
Plastic surgeons commonly administer subcutaneous epinephrine to reduce operative blood loss. In the pediatric population, delivering enough epinephrine-containing local anesthetic to adequately cause vasoconstriction around large vascular lesions can be difficult. The younger the child, the less volume of local anesthetic that can be used based on the patient's weight. We present an evidence-based evaluation of the maximum amount and optimal concentration of subcutaneously delivered epinephrine.
Is epinephrine safe to take?
Although e pinephrine has the potential to cause tachy cardia, hypertension, and arrhythmia, its subcutaneous administration in healthy patients is very safe. As much as 10 mg of epinephrine 1:1,000,000 may be given to an adult as part of tumescent solution (0.12 mg/kg). Serum epinephrine levels may be elevated four times normal but are equivalent to those associated with exercise and are well below toxic concentrations. 1,2 Hemodynamic parameters are normal, and signs of catecholamine overdose have not been noted. 1,2 Although systemic effects of more concentrated solutions of epinephrine are unknown, 200 ml of 1:200,000 epinephrine every 10 minutes in an adult (3 ml/kg every 10 minutes) was the recommended limit in the past for patients receiving halothane anesthesia, which lowered the arrhythmogenic threshold to epinephrine. 3
Why do we need subcutaneous injections?
Subcutaneous injections are used to: get a rapid and systemic effect of the drug; give small amounts and certain kinds of medicine that cannot be administered orally due to poor absorption in gastrointestinal tract; when the drug is toxic and irritating to the gastrointestinal mucosa.
What is subcutaneous injection maximum volume?
The dosage that can be given subcutaneous injection is usually less than 1 ml, but up to 2 ml is safe.
What areas of the body should you inject insulin into?
Each of the main four areas (abdomen, buttocks, outer thighs and upper arms) should give a give a good area of flesh to inject into. Using different areas of the body to inject into is insulin injection site rotation.
How to use a syringe for muscle injection?
Place the syringe between your thumb and first finger. Let the barrel of the syringe rest on your second finger. Pinch up on the fatty (subcutaneous) tissue to prevent injection into muscle: With your other hand, grasp the skin.
How to get a syringe injection?
Have the person getting the injection stand with his hand on his hip. Stand next to and a little behind the person. Find the area halfway between the elbow and shoulder. Gently grasp the skin at the back of the arm between your thumb and first 2 fingers. You should be able to grasp 1 to 2 inches of skin.
What pain medication can be given by injection?
Some pain medications like morphine and hydromorphone (Dilaudid) can be given this way as well. Drugs that prevent nausea and vomiting like metoclopramide (Reglan) or dexamethasone (DexPak) can also be given via subcutaneous injection.
How to give an injection with alcohol wipe?
Open the alcohol wipe: Wipe the area where you plan to give the injection. Let the area dry. Do not touch this area until you give the injection.
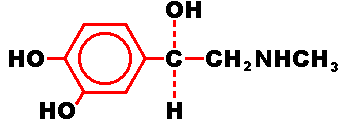
Indications and Usage For Epinephrine Injection
Epinephrine Injection Dosage and Administration
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Warnings and Precautions
Adverse Reactions
Drug Interactions
Use in Specific Populations
- Pregnancy
Risk Summary Prolonged experience with epinephrine use in pregnant women over several decades, based on published literature, does not identify a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. However, there are risks to the mot… - Lactation
Risk Summary There is no information regarding the presence of epinephrine in human milk or the effects of epinephrine on the breastfed infant or on milk production. However, due to its poor oral bioavailability and short half-life, epinephrine exposure is expected to be very low in the breastfe…
Overdosage
Epinephrine Injection Description
Epinephrine Injection - Clinical Pharmacology