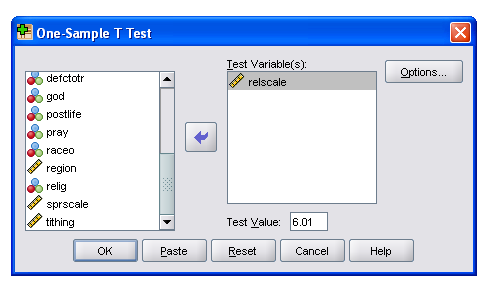
How do I report ESPP on my tax return?
So you must report $225 on line 7 on the Form 1040 as "ESPP Ordinary Income." You must also report the sale of your stock on Schedule D, Part II as a long-term sale. It's long term because there is over one year between the date acquired (6/30/2017) and the date of sale (1/20/2021).Jan 21, 2022
Do you have to report ESPP on my tax return?
With an immediate sale of your ESPP shares at purchase, the discount is reported on your W-2 and on your tax return as ordinary income.Mar 23, 2021
Is ESPP included in Box 1 of w2?
I'd say with high confidence that this $358 is included in Box 1. So, for example, if you have a salary of $30,000 per year, sold some stock acquired via an ESPP and that sale created compensation income of $358, then the Box 1 amount would be $30,358.Jun 1, 2019
Does ESPP count as income?
When you buy stock under an employee stock purchase plan (ESPP), the income isn't taxable at the time you buy it. You'll recognize the income and pay tax on it when you sell the stock. When you sell the stock, the income can be either ordinary or capital gain.
How do you avoid double tax on ESPP?
1, 2014, through an employee stock option or purchase plan. They can only report the unadjusted basis — what the employee actually paid. To avoid double taxation, the employee must use Form 8949. The information needed to make this adjustment will probably be in supplemental materials that come with your 1099-B.Feb 17, 2015
How do I report ESPP on Turbotax?
0:291:09How Do I Enter Employee Stock Purchase Plan (ESPP) Sales in ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWith your return open in turbotax search for 1099-b. And select the jump to link have your 1099-bMoreWith your return open in turbotax search for 1099-b. And select the jump to link have your 1099-b form 3922 for the shares you sold and w-2 or year-end pay stub available for reference.
How is ESPP taxed in Canada?
ESPP Income Tax The income tax on ESPP is two-fold. You have to pay regular tax on the discounted price you get and then you pay capital gains on the profit.Nov 22, 2021
How much is ESPP taxed?
Short term capital gains are taxed as ordinary income. Long term capital gains tax rates are 0%, 15%, or 20% depending on your ordinary income. What is this? If there are any commission or transaction costs, you can deduct this from the selling price of your ESPP share.
How is ESPP contribution calculated?
1. You contribute to the ESPP from 1% to 10% of your salary. The contribution is taken out from your paycheck. This is calculated on pre-tax salary but taken after tax (unlike 401k, no tax deduction on ESPP contributions).Nov 22, 2006
Are ESPP contributions pre tax?
Unlike pre-tax contributions to a 401(k), contributions to an ESPP are made with after-tax dollars. This means a “true” reduction of $22,500 per year of cash flow from your paycheck.Feb 27, 2020
What is a form 3922?
IRS Form 3922 Transfer of Stock Acquired Through an Employee Stock Purchase Plan Under Section 423(c) is for informational purposes only and isn't entered into your return. Keep the form for your records because you'll need the information when you sell, assign, or transfer the stock.
How does employee stock purchase plan work?
An ESPP allows you to purchase company stock at a discounted price, often between 5-15% off the fair market value. For example, if the fair market value on the applicable date is $10 per share, and your plan offers a 15% discount, you can purchase those shares for $8.50 per share.
What is an ESPP?
Buying company stock at a discount. Many large companies offer Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPP) that let you buy your employer's stock at a discount. These plans are offered as an employment incentive, giving you an opportunity to share in the growth potential of your company's stock (and by implication, work hard to keep ...
Do you owe taxes when a company buys you shares?
When the company buys the shares for you, you do not owe any taxes. You are exercising your rights under the ESPP. You have bought some stock. So far so good.
Does my employer have to pay taxes on stock?
Your employer is not required to withhold Social Security (FICA) taxes when you exercise the option to purchase the stock. Also, your employer is not required to withhold income tax when you dispose of the stock. But you still owe some income tax on any gain resulting from the sale of the stock.
Preliminary explanation
These rules impose reporting requirements on a disposition of ESPP shares that occurs after you have held the shares long enough to avoid a disqualifying disposition.
What you need
Income from a qualifying disposition of ESPP stock may or may not appear on Form W-2, so that is one item you need. If you sold the shares (instead of making a different kind of disposition, such as a gift), you should also have Form 1099-B, which reports your proceeds from the sale.
Step 1: Calculate compensation income
Your compensation income from ESPP shares in a qualifying disposition is the lesser of two amounts.
Step 2: Check your W-2
The compensation income from a qualifying disposition may be reflected on Form W-2 received from the company maintaining the plan. That doesn’t always happen, so you should check your W-2. It may be difficult to isolate this amount because it is not listed separately.
Step 3: Report your compensation income
If the compensation income from your qualifying disposition was included in the wages reported on Form W-2, simply report the number from your W-2 on your tax return the way you normally do. If it was not included on your W-2, add the ESPP compensation to the wages on your Form W-2 and report the total as wages on your tax return.
Step 4: Calculate your basis
Next you need to calculate your basis for the shares. This is the amount you paid for the shares, increased by the amount of compensation income reported. If your qualifying disposition was a gift, you should provide this basis information to the recipient of the gift. If the disposition was a sale, proceed to Step 5.
Step 5: Report the sale of the shares
Report the sale of the shares on Schedule D, using the sales proceeds reported on Form 1099-B and the basis calculated in Step 4. You had to hold the shares more than a year (and perhaps longer) to have a qualifying disposition, so your gain or loss is long-term.
What is included in W-2?
Remember that it’s not just for reporting your salary to you and the IRS. Your W-2 includes income from any other compensation sources you may have, such as stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units, employee stock purchase plans, and cash bonuses. If you have income and withholding from what the IRS considers supplemental wage income ...
What is an incentive stock option?
With incentive stock options (ISOs), the value of the exercise income appears on Form W-2 only if you made what is technically called a disqualifying disposition. That means you sold or gifted the stock before you met the required holding periods of one year from exercise and two years from grant.
How long do you have to be employed to exercise an option?
Also, you must stay employed by the company until at least three months before you exercise the option. If you meet the holding-period requirements, your ordinary income from the sale depends on the option price. The option price: Might be less than the fair market value (FMV) of the stock on the date you received it.
What happens if you don't meet the holding period requirement?
If you don’t meet the holding period requirement, it’s a disqualifying disposition. You can only recognize ordinary income. To figure the ordinary income amount: Determine the FMV of the stock on the date you received it (exercise date). Subtract the amount paid for the stock (option price).
How long do you have to hold stock to sell?
When you sell the stock, the income can be either ordinary or capital gain. The sale will qualify for capital gain treatment as long as the stock is held for both of these: 1 At least two years after the option is granted 2 At least one year after you buy the stock